Prototyping 2014-01-13 (Lens Based Media): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
* Defining color schemes | * Defining color schemes | ||
* Storyboarding | * Storyboarding | ||
===2. 3D Modelling=== | ===2. 3D Modelling=== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 11: | ||
A surface that is defined by 2 or more vector curves, and which the software connects. High level of mathematical precision and provides smooth surfaces | A surface that is defined by 2 or more vector curves, and which the software connects. High level of mathematical precision and provides smooth surfaces | ||
[[File:Nurbs.jpeg| | [[File:Nurbs.jpeg|left]] | ||
<br /> | |||
====Polygon models==== | ====Polygon models==== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
* Vertices | * Vertices | ||
[[File:Edges-vertices.gif| | [[File:Edges-vertices.gif|left]] | ||
<br /> | |||
===3. Shading & Texturing=== | ===3. Shading & Texturing=== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
* Adding textures = projecting a two dimensional image onto the model | * Adding textures = projecting a two dimensional image onto the model | ||
Or a combination of the two | Or a combination of the two | ||
[[File:BSOD-Materials-Textures-mapping4.jpg| | [[File:BSOD-Materials-Textures-mapping4.jpg|left]] | ||
<br /> | |||
===4. Lighting=== | ===4. Lighting=== | ||
Revision as of 22:51, 12 January 2014
The 6 steps of 3D Graphics
1. Pre-Production
- Sketching
- Defining color schemes
- Storyboarding
2. 3D Modelling
Basic Modelling is made out of 2 types of objects:
NURBS surface
A surface that is defined by 2 or more vector curves, and which the software connects. High level of mathematical precision and provides smooth surfaces
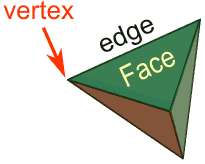
Polygon models
Start as a simple geometric shape, like a cube, sphere, or cylinder, which is then made more complex. This can be done by modifying or adding:
- Faces
- Edges
- Vertices
3. Shading & Texturing
Defining the look of an object.
- Define a Material = giving the object different properties (called shaders), for instance: color, transparency, glossiness etc etc
- Adding textures = projecting a two dimensional image onto the model
Or a combination of the two
4. Lighting
The key to realism!
- Related to materials
- Shadows
5. Animation
- Motion Rigging
- Pose-to-Pose
- Physics
Rendering & Post-Production
- Finalizing Lighting: Shadows and reflections must be computed for each object.
- Special Effects: This is typically when effects like depth-of-field blurring, fog, smoke, and explosions would be integrated into the scene.