Prototyping 2014-01-13 (Lens Based Media)
<slidy theme="aa" />
The uses of 3D
- 3D graphics & Animation
- CGI for Film (joining 3D graphics with real life footage and compositing)
- Design (3D printing, Architectural pre-viz)
- Gaming
- Motion Graphics
The 6 steps of 3D Graphics
1. Pre-Production
- Sketching
- Defining color schemes
- Storyboarding
2. 3D Modelling
Basic Modelling is made out of 2 types of objects. A 3D scene can be made out of a mix of these elements.
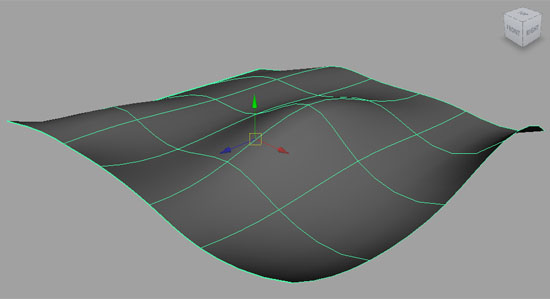
NURBS surface
A surface that is defined by 2 or more vector curves, and which the software connects. High level of mathematical precision and provides smooth surfaces
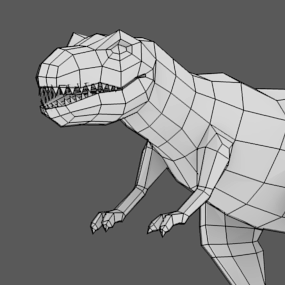
Polygon models
Start as a simple geometric shape, like a cube, sphere, or cylinder, which is then made more complex. This can be done by modifying or adding:
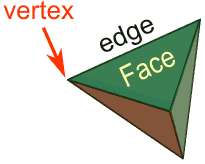
- Faces
- Edges
- Vertices
3. Shading & Texturing
Defining the look of an object.
- Define a Material = giving the object different properties (called shaders), for instance: color, transparency, glossiness etc etc
- Adding textures = projecting a two dimensional image onto the model
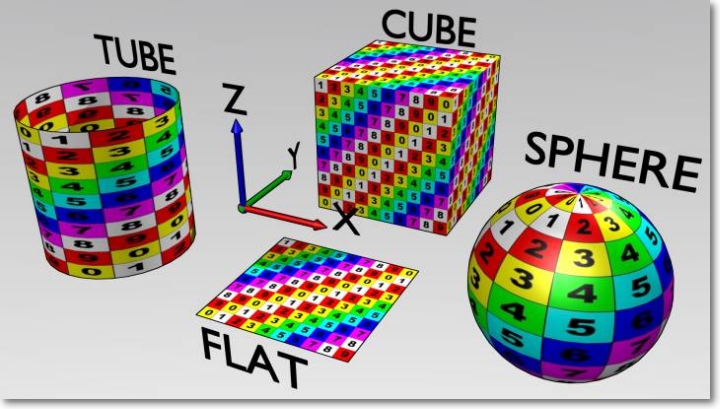
Texture mapping:
4. Lighting
The key to realism!
- Related to materials
- Shadows
5. Animation
- Motion Rigging
- Pose-to-Pose (key-frame animation)
- Physics (particles/collision/fluids)
Rendering & Post-Production
- Finalizing Lighting: Shadows and reflections must be computed for each object.
- Special Effects: This is typically when effects like depth-of-field blurring, fog, smoke, and explosions would be integrated into the scene.
- Render Layers (for freedom in compositing)
- Render Farms (using multiple machines to render a frame simultaniously) Although that might be history
3D Software
- Maya
- 3d Studio Max
- Blender (python!)
- Cinema 4D
- etc etc
- Google Sketchup / AutoCAD (Computer Aided Design)
- 2.5d (After Effects etc etc)
- 3D in the Browser! [1], []http://madebyevan.com/webgl-water/]