Optical character recognition with Tesseract
software
materials
2 hi-res (300dpi) PDFs
- a usual PDF: in English, with a common font
- a unusual PDF: in a non-latin script, or with an unusual font or with abundant images
install
Tesseract (with languages you will be using)
- Mac
brew install tesseract --all-languages - Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo aptitude install tesseract-ocr- See what language packages are available with:
sudo aptitude search tesseract-ocr- - install language packages:
sudo aptitude install tesseract-ocr-ara tesseract-ocr-port tesseract-ocr-spahere I am installing Arabic, Portuguese, Spanish
- See what language packages are available with:
poppler-utils whic include tools such as pdftotext and pdftohtml
- Mac
brew install poppler-utils - Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo aptitude install poppler-utils
imagemagick
- Mac
brew install imagemagick - Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo aptitude install imagemagick
pdftk
- Mac
brew install pdftk - Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo aptitude install pdftk
- with text layer
- without text layer
To find out the difference you can try to select the PDF's text in a PDF viewer. Only if the text layer is present will you be able to select it.
If it contains a text layer you can use pdftotext command-line application (from poppler-utils) to convert the PDF to text
Tesseract
Tesseract was originally developed at Hewlett-Packard Laboratories Bristol and at Hewlett-Packard Co, Greeley Colorado between 1985 and 1994, with some more changes made in 1996 to port to Windows, and some C++izing in 1998. In 2005 Tesseract was open sourced by HP. Since 2006 it is developed by Google.[1]
Tesseract is a Free software OCR package
one page prototype
Getting 1 page from PDF file with PDFTK burst
pdftk yourfile.pdf burst
Chose page you want to convert
Convert PDF to bit-map using imagemagick, with some options to optimize OCR
convert -density 300 page.pdf -depth 8 -strip -background white -alpha off ouput.tiff
-density 300resolution 300DPI. Lower resolutions will create errors :)-depth 8number of bits for color. 8bit depth == grey-scale-strip -background white -alpha offremoves alpha channel (opacity), and makes the background whiteoutput.tiffin previous versions Tesseract only accepted images as tiffs, but currently more bitmap formats are accepted
See Tessearct page on improving quality of images for OCR [2]
OCR
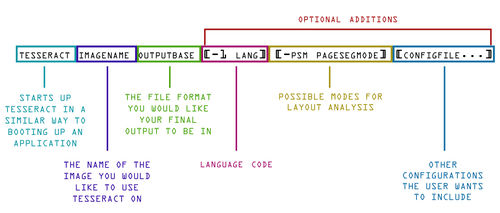
tesseract output.tiff -l eng output
Will generate the file output.txt
- -l is the option for language (English is the default)
Improving image quality
There are several image transformation that will improved the OCR results
The Tesseract wiki page on ImproveQuality[3] includes extensive notes on it.
Suggestion: implement of this options into Imagemagick convert command.
Advanced
language
Lists all tesseract languages available in your system.
tesseract --list-langs
If OCRing a document with more than one language Tesseract can use also more than one
tesseract output.tiff -l eng+spa output
multipages
Tiff files can be multi-page images. Hence if we use the prevoious IM command to convert a PDF to a TIFF, if the PDF is multi page, so will be it TIFF. Which Tesseract should handle.
$ tesseract TypewriterArt.tiff TypewriterArt
Tesseract Open Source OCR Engine v3.03 with Leptonica
Page 1 of 8
Page 2 of 8
Page 3 of 8
Another option is providing Tesseract with a text file containing the path/filename to each image in sequence:
list.txt:
p001.tiff
p002.tiff
p003.png
tesseract list.txt output
segmentation
Page Segmentation Mode (-psm) directs the layout analysis that Tesseract performs on the page.
By default, Tesseract automates the page segmentation, but does not perform orientation and script detection.
From Tesseract man page:
-psm N
Set Tesseract to only run a subset of layout analysis and assume a certain form of image. The options for N are:
0 = Orientation and script detection (OSD) only.
1 = Automatic page segmentation with OSD.
2 = Automatic page segmentation, but no OSD, or OCR.
3 = Fully automatic page segmentation, but no OSD. (Default)
4 = Assume a single column of text of variable sizes.
5 = Assume a single uniform block of vertically aligned text.
6 = Assume a single uniform block of text.
7 = Treat the image as a single text line.
8 = Treat the image as a single word.
9 = Treat the image as a single word in a circle.
10 = Treat the image as a single character.
searchable PDF
tesseract input.tiff output -l eng pdf
hocr
Tesseract 3.0x supports a hocr option, which creates horc file.
HOCR is an HTML+XML (XHTML) file consisting of recognized words and their coordinates.
The HOCR file contains all pages as ocr_page elements. with attribute that contains the following fields :
- ppageno: The physical page number
- image: The relative path (from the HOCR file) to the page image
- bbox: The dimensions of the image
class='ocr_page
The OCRed text is atomized into text elements of different magnitude, such as:
- paragraph "ocr_par"
- line "ocr_line"
- word "ocrx_word"
HOCR tools
using hocrjs
We will use User Script instruction with Tampermonkey.
Installing:
- open Firefox
- go to FF addons and search for Tampermonkey
- install it
- Browse to unpkg.com/hocrjs/dist/hocr.user.js
- click "Install". It will install the script in your browser Tampermonkey
- click the Tampermonkey and go to the "Dashboard". hocr-viewer should be enabled
Create an horc file with tesseract
Note: in this process will be more convenient to use a png or jpg input file, as the browser will not display a tiff.
Run tesseract to produce a hocr (language and segmentation options can also be used )
tesseract inputfilename.png inputfilename hocr
You have got a inputfilename.hocr
View the hocr int the Firefox
- change its extension from .hocr to .html
- open the .html file in firefox
hocr-viewer will automatically load

Editing and correcting
hocrjs does not support editing :(
A solution would be to use FF inspector to change the content of the HOCR, but the HTML inspector changes are not saved, even if we are working with a local html file :((
So the only option is to do the editing in a plain text editor :(((
converting the HOCR
To PDF:
It makes sense to use the position information and and plain-text content to create a text-based PDF.
hocr-pdf an application from hocr-tools is a possibility, but I only managed to create corrupted and empty PDFs
The following thread suggests using pdfbeads or HocrConverter.
HocrConverter showed the best results, but failed when including (-I) the page image in the PDF
python HocrConverter/HocrConverter.py -I -i pg_0012.hocr -o pg_0012.pdf pg_0012.png
python HocrConverter/HocrConverter.py -h
HocrConverter
Convert Files from hOCR to pdf
Usage:
HocrConverter.py [-tIcbmnrV] [-q | -v | -vv] [-i <inputHocrFile>] [-f <inputTtfFile>] (-o <outputPdfFile>) [<inputImageFile>]...
HocrConverter.py (-h | --help)
Options:
-h --help Show this screen.
-t Make ocr-text visible
-i <inputHocrFile> hOCR input file
-o <outputPdfFile> pdf output
-f <inputTtfFile> use custom TTF font
-I include images
-c use full line text
-b draw bounding boxes around ocr-text
-n don't read images supplied in hocr-file
-m do multiple pages in hocr and output pdf
-r take hOCR-image sizes as reference for size of page
-V vertical Inversion ( for ocropus: false, for tesseract: true )
-q | -v | -vv quiet ( only warnings and errors ) | verbose | very verbose = debug
Creating new fonts: Training
New fonts can be added to Tesseract through a training process.
Fonts are
The process of training for v.3 is complicated, but here are links for a few resources that can guide you in the process
- Tessearct (extensive) documentation on Training [4]
- Tutorial: Adding New Fonts to Tesseract 3 OCR Engine[5]
- Tutorial: A Guide on OCR with tesseract 3.03 [6]
- Tutorial: How to prepare training files for tessearct-orc and improve character recognition [7]
- Tutorial: Training Tesseract OCR for a New Font and Input Set on Mac [8]
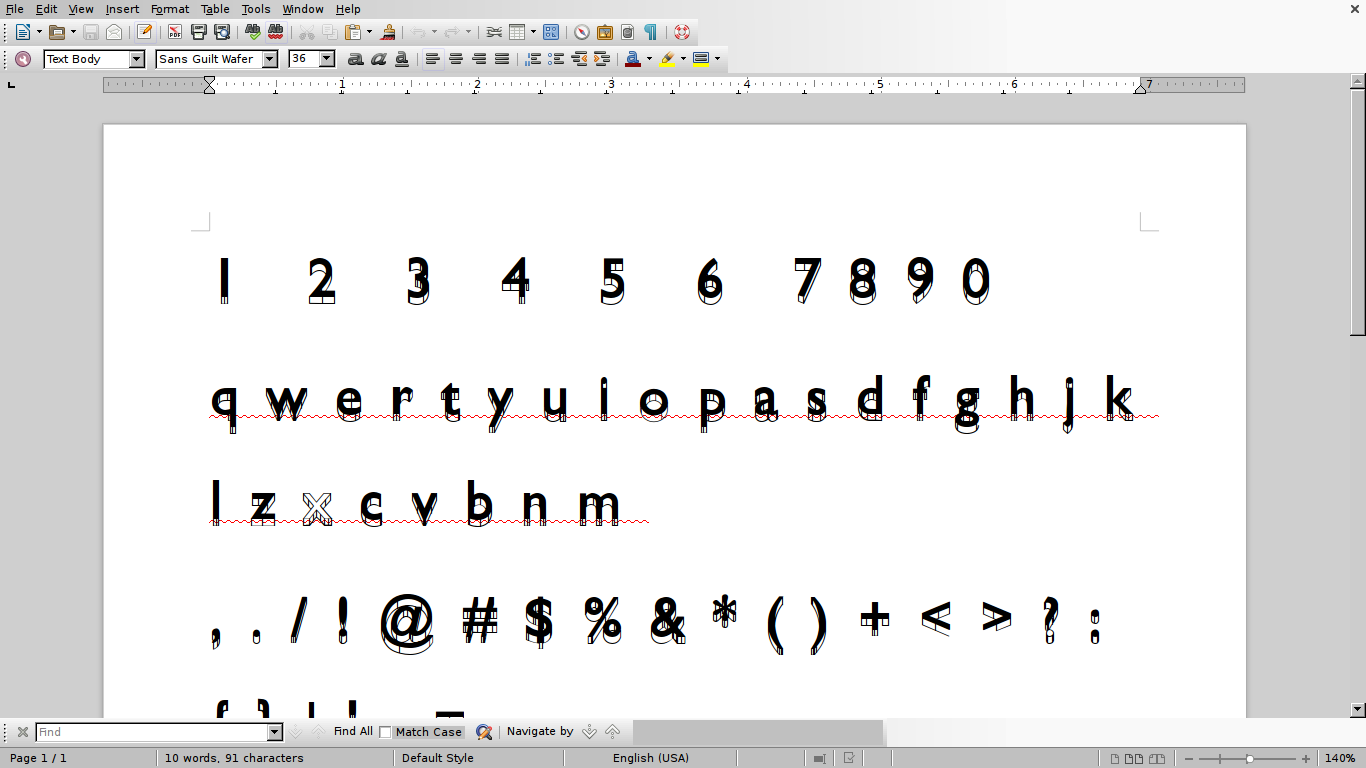
Tesseract needs to know about different shapes of the same character by having different fonts separated explicitly.
tessdata/ dir, where data files can be found, can be found on Debian at /usr/share/tesseract-ocr/tessdata
If the dir happens to be located elsewhere you can use the following commands to find it:
cd / sudo find -type d -name "tessdata"
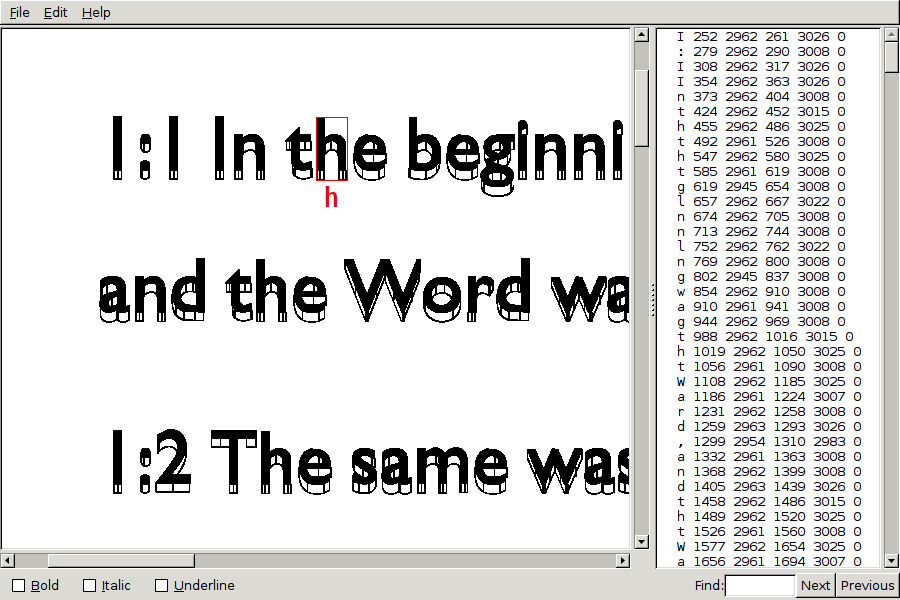
box ouput
The box file output consists of a plain-textfile containing x,y coordinates of each letter it found along with what letter it thinks it is
In cases where the input is a standard text, with a standard font, the result are not bad.
But when dealing with unusual fonts or hand-written scripts Tesseract has the possibility to train it.
Tesseract needs a 'box' file to go with each training image. The box file is a text file that lists the characters in the training image, in order, one per line, with the coordinates of the bounding box around the image. [9]
convert -density 300 wafer.pdf -depth 8 -strip -background white -alpha off wafer.tiff
tesseract wafer.tiff wafer makebox
Edit the box file with [moshpytt https://code.google.com/archive/p/moshpytt/]
./moshpytt.py
Boxmaker is a JavaScript online box editor
Artistic research
Reverse OCR by http://reverseocr.tumblr.com/
Kindle Scanner by Peter Purgathofer
We are human beings! by Silvio Lorusso
tesseract-ocr front-ends gImageReader: Debian install
sudo aptitude install gimagereader
HOCR
- hocr-tools - python library
- HOCR reader (javascript)
- Converting hOCR to PDF: HocrConverter (python script)
References
- ↑ https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tesseract/blob/master/README.md
- ↑ https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tesseract/wiki/ImproveQuality
- ↑ https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tesseract/wiki/ImproveQuality[ https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tesseract/wiki/ImproveQuality
- ↑ https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tesseract/wiki/TrainingTesseract
- ↑ http://michaeljaylissner.com/posts/2012/02/11/adding-new-fonts-to-tesseract-3-ocr-engine/
- ↑ https://www.joyofdata.de/blog/a-guide-on-ocr-with-tesseract-3-03/
- ↑ http://pretius.com/how-to-prepare-training-files-for-tesseract-ocr-and-improve-characters-recognition/
- ↑ https://medium.com/@sathishvj/training-tesseract-ocr-for-a-new-font-and-input-set-on-mac-7622478cd3a1
- ↑ https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tesseract/wiki/Training-Tesseract-%E2%80%93-Make-Box-Files