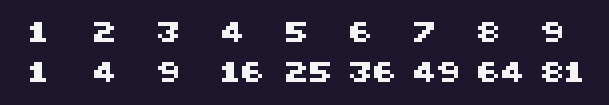Lua for TIC80
Revision as of 22:44, 31 January 2021 by Michael Murtaugh (talk | contribs)
Like most (imperative) programming languages lua is based on variables, if-then and loop structures, and functions.
Assignment
See: https://www.lua.org/pil/4.1.html
Remember, the equals sign *isn't* stating an equality like you might remember from your past algebra classes. Assignments are active statements that (1) evaluate / calculate the RHS (right hand side), then (2) store the computed value to a named reference (either a simple variable, or reference inside a table).
a = "hello" .. "world"
t.n = t.n + 1
tables
squares={1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81}
function TIC()
cls(0)
for i=1,#squares do
print(i,i*16,0)
print(squares[i],i*16,10)
end
end
Lua tables can also be like python dictionaries (and javascript objects)...
PLANE={
START_FUEL=2000,
MAX_FUEL=4000,
FUEL_INC=1000,
FUEL_BAR_W=50
}
Tables can be *nested* (one inside the other)...
LVL={
{
name="1-1",bg=2,
palor={},
pkstart=8,pklen=3,
mus=BGM.A,
},
{
name="1-2",bg=0,
palor={[8]=0x102428},
pkstart=11,pklen=2,
mus=BGM.B,
}
}
Examples from: 8-bit panda
if
See: https://www.lua.org/pil/4.3.1.html
if btn(0) then
t=t+1
elseif btn(1) then
t=t-1
end

for
See: https://www.lua.org/pil/4.3.4.html
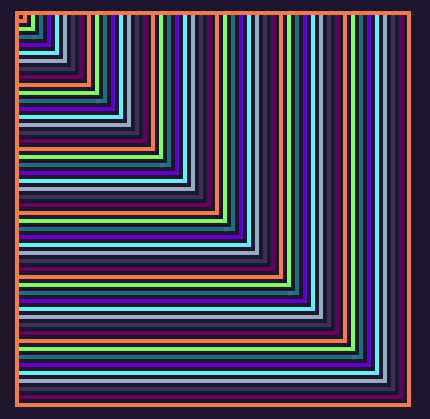
function TIC()
cls(0)
for i=1,100,2 do
rect(0,0,i,i,i%16)
end
end