Glossary of productive play: Difference between revisions
Carmen Gray (talk | contribs) |
Mirischoeb (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
'''See also'''[[Glossary of productive play#Counterhegemony | Counterhegemony]] and [[Glossary of productive play#Mainstream | Mainstream]] | '''See also'''[[Glossary of productive play#Counterhegemony | Counterhegemony]] and [[Glossary of productive play#Mainstream | Mainstream]] | ||
== Entertainment == | |||
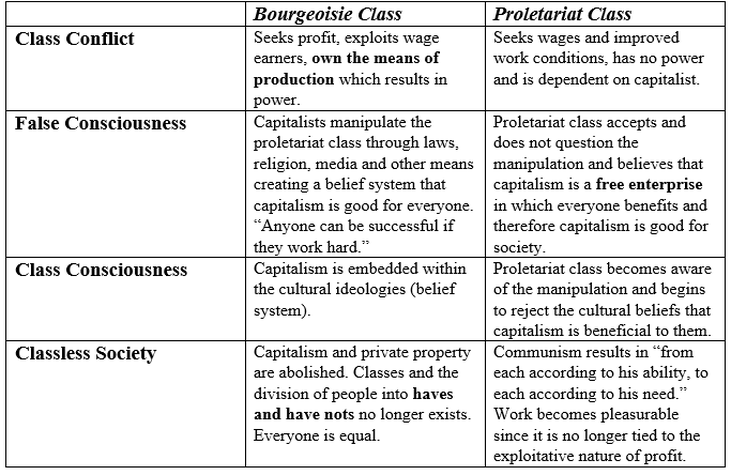
==False Consciousness== | ==False Consciousness== | ||
Revision as of 15:05, 2 February 2022
Click farm
A form of click fraud where a large group of low-paid workers are hired to click on paid advertising links for the click farmer. The workers click the links, surf the target website for a period of time, and possibly sign up for newsletters prior to clicking another link. It is extremely difficult for an automated filter to detect this simulated traffic as fake because the visitor behavior appears exactly the same as that of an actual legitimate visitor.
Context
Click farms are used by all sorts of businesses, often to inflate their following or engagement, and they can be hired to do multiple actions such as:
Services offered by click farms can include:
- Social media followers and likes
- Posting comments on websites or social media
- Generating website traffic
- Creating backlinks
- Carrying out repetitive click based tasks
- Channelling traffic to fraudulent sites to increase rankings, domain authority or to collect payouts on display ads
- Sharing , often fake, news articles (troll factories)*
With the majority of the world’s click farms based in countries with minimal employment and labour laws, their main legal issues are around employee rights, working conditions and wages.
In a sentence
As online engagement became currency, click farms exploit workers in order to mass produce fraudulent user interactions.
Who said it
Lee Munson
Mentioned in
See also Term
Counterculture

Definition (a) "A counterculture is a culture whose values and norms of behavior differ substantially from those of mainstream society, sometimes diametrically opposed to mainstream cultural mores. A countercultural movement expresses the ethos and aspirations of a specific population during a well-defined era." [wiki] (b) countercultures often are of dissenting character in relation to the established superstructure/ruling ideologies. They become part of the popular culture or fully integrated to culture after revolutionary actions or activist actions, consistent and confident defiance of established "rules". Counter culture can also purposefully present themselves as disturbances of defiance of any current stream (may they cross as certain times) as way to protest, as emancipation or contestation.
In context (1) (a) one famous counterculture is the hippy movement from the 60s-70s which was demonstrated by very defying aesthetically "divergent" hair features, sexual liberation, eye-catching fashion and uprisal against the dominant political/social structures. (b) nowadays the queer community holds some of the keys to one of the main counterculture stream, where gender defaults are refuted, social norms re-evaluated and contested, communal cohesion starts with individual expression and affirmation, diversity first and foremost. Feminism has shared platforms between counter- and mainstream culture, where different aspects have been shared, when the queer community has always mainly evolved on the side-lines, it is now coming more and more in the main cultural streams. (c) mainstream culture uses countercultures as fashionable ideologies on and off, but counterculture also makes use of mainstream society to vehiculate ideologies (pop culture, artists like Lady Gaga, channels counter-communities within mainstream medias). “Born this way” has been the rallying cry of the mainstream gay rights movement [[1]]
In context (2) See Fred Turner's From Counterculture to Cyberculture: Stewart Brand, the Whole Earth Network, and the Rise of Digital Utopianism (2008), which charts how the [(left)Libertarian] values of the US 1960s counterculture (hippy communes, experiments with LSD &c) are taken up by the big tec companies ; so a lot of the 'freedom' rhetoric on the internet in the 2000s is related to the US 60s counterculture movement. The model for the network is provided by The. Whole Earth Catalog (1968) which advanced freedom via "access to tools"
In a sentence Counterculture stands in opposition to the mainstream society until it gets incorporated within the mainstream society, mostly arises from social/political divergences/conflicts/defiance.
See also Counterhegemony and Mainstream
Entertainment
False Consciousness
Definition "False consciousness is a term used by some to describe ways in which material, ideological, and institutional processes are said to mislead members of the proletariat and other class actors within capitalist societies, concealing the exploitation intrinsic to the social relations between classes." (wiki)
Who said it Mentioned in [ Gamification as twenty-first-century ideology, Mathias Fuchs ] (a)"When the evangelists of gamification tell us that work must be play, that our personalities will be playful, that the whole economy is a game, and that each and every activity from cradle to grave can be turned into a game, we encounter false consciousness that is socially necessary." (b) "This state of alienation has also been referred to as ‘false consciousness’. In the closing chapter of Alfred Sohn-Rethel’s Intellectual and Manual Labour (1978: 196), the author invokes the concept of ‘necessary false consciousness’. This is a type of false consciousness that is not just faulty consciousness; necessary false consciousness is rather a type of false consciousness that is logically correct. However cruel, meaningless or destructive it might seem, it is necessary for the system in which we are working to keep working until we die so that we will shop until we drop."
From leftypedia [ Consciousness, Class consciousness] "A materialist understanding of class is known by Marxists as 'class consciousness'. This understanding is the knowledge of one's own position in the economic hierarchy, and the acceptance of the interests which therefore benefit the individual. The term is most often used to describe the working class, or elements of it, becoming aware of their own exploitation and working to oppose it in unity with their fellow workers, but it can also be used to describe the self-awareness of the bourgeoisie of their superior position in society and their efforts to maintain the present hierarchy. It is often contrasted with its inverse, 'false consciousness', which describes the lack of this knowledge causing the worker to labour contrary to his own interests as a member of the oppressed class (for instance through vocal support of the ruling classes and existing power structures)."
In context [ Gamification as twenty-first-century ideology, Mathias Fuchs] "Gamification propaganda in the style of ‘work is play’, ‘work can be play’ or ‘work harder, play harder’ are suggesting that work can be contained within the ‘sphere of play’ (Huizinga [1938] 1949). Such statements and consequently the whole concept of gamification are ideological as they express false consciousness of the nature of work and play (see, e.g., the magazine covers in Figure 3, designed by Anthony Burrill 2008). "
In a sentence False consciousness is the state in which one feels like they are given full agency of their own choices/actions when in fact they are subject to a certain ideology that has come to seem so self-speaking they wouldn't question it
See also Gamification, Capitalism, Alienation and Play
Fan culture/fandom
A fandom is a subculture composed of fans characterized by a feeling of empathy and camaraderie with others who share a common interest. Fans typically are interested in even minor details of the objects of their fandom and spend a significant portion of their time and energy involved with their interest, often as a part of a social network with particular practices, differentiating fandom-affiliated people from those with only a casual interest. [Wiki]
The history of the word “fandom” starts with a very old word — “fanatic.” “Fanatic” arose out of a Latin word, “fānāticus,” which, in turn, came from the word “fanum,” meaning “temple” or “shrine". In the late 19th-century, the word "fan" started to be used to describe an enthousiast of a certain sports team.
Mentioned in
- "On productivity and game fandom" by Hanna Wirman
- “Textual Poachers: Television Fan & Participatory Culture” by Henry Jenkins
In context Members of a fandom associate with one another and build a community around their fan interest (e.g.: celebrities, hobbies, genres, fashion, ...). A fan culture often includes fan activities such as conventions, writing fan fictions, participating in fan online forums and discussions, purchasing merchandise and collector items, etc. Some of the largest fandoms are the Harry Potter fandom, Anime fandom and the BTS army (BTS is a K-Pop group).
In a sentence A fandom is a subgroup of fans that share a common interest.
Gamification
Definition the application of typical elements of game playing (e.g. point scoring, competition with others, rules of play) to other areas of activity, typically as an online marketing technique to encourage engagement with a product or service. Who said it Mentioned in [ Fuchs, Gamification as twenty-first century ideology ], [ Jennifer Dewinter, Katy A Kocurek, Randall Nichols, Gamification as twenty-firstcentury ideology]
In context
[ Gamification as the process of turning extra-ludic activities into play. I argue that gamification might be seen as a form of ideology and therefore a mechanism of the dominant class to set agenda and to legitimize actions taken by this very class or group. [Gamification is based on similar principles of measurement and observation with a focus on both the reorganization of work and leisure
In a sentence to put it simply, a way to make any other thing look like a game, therefore it seems like a fun/desirable activity instead of an imposition/exploitation/slavery. Strategy used to motivate the user/employee/citizen in order to get more/better results/data.
Period 2003 - now
See also
IKEA effect
The IKEA effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers place a disproportionately high value on products they partially created. The name refers to Swedish manufacturer and furniture retailer IKEA, which sells many items of furniture that require assembly. [Wiki]

Who said it Michael I. Norton, Daniel Mochon, Dan Ariely
Mentioned in "The 'IKEA Effect': When Labor Leads to Love" by Michael I. Norton, Daniel Mochon and Dan Ariely [2]
In context IKEA customers can build their own furniture. People can choose colours to customize their own shoes online. Children can design their own cuddly toy. Customers can order their own creations at chocolate manufacturers.
In a sentence The IKEA effect describes how people tend to value an object more if they make (or assemble) it themselves.
Ideology
In a sentence Barthes: "ideology is disguised in plain sight"
Definition 1) a system of ideas and ideals, especially one which forms the basis of economic or political theory and policy. "the ideology of democracy"
2) a system of ideas which seem self evident and 'natural' to those that hold them.
3) the science of ideas; the study of their origin and nature.
Context [ How does gamification express ideology? Note: "Hegemony and Ideology are two concepts that come in social sciences between which a key difference can be identified. In a general sense, hegemony is the dominance of one group or state over another. On the other hand, ideology is a system of ideas forming the basis of an economic or political theory."
Who said it Mentioned in Marx, Gramsci, Barthes , Hall, Hebdidge, Williams
Mentioned in
See also
Hook Model / Hook - Habit - Hobby
At its simplest form, the hook model describes how businesses can fundamentally change behaviour within their users, and create day-to-day habits around their products. The heart of the principle is that businesses should always seek to connect a user’s problem to your solution with enough frequency to make it a habit. A four-phase process companies use to form habits; through consecutive hook cycles, successful products reach their ultimate goal of unprompted user engagement, bringing users back repeatedly, without depending on costly advertising or aggressive messaging.