HTML/CSS Memo: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(→Intro) |
||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Intro== | |||
This is for the beginners <br> | |||
In the first session we want to look at this page: [[Protocols for Collective Performance: Radio Broadcast 2]] | |||
[[File:Chalkboard-code.jpg|frameless|center|chalkboard-code]] | |||
==HTML Tags== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ HTML | |+ HTML | ||
| Line 4: | Line 10: | ||
! Human Language !! HTML Tag | ! Human Language !! HTML Tag | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Html document || <source lang="html"><htm></html></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Metadata (title, link to css and script etc) || <source lang="html"><head></head></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Content of the page || < | | Content of the page || <source lang="html"><body></body></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Section || < | | Section || <source lang="html"><section></section></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Container (it can contain text, images, sound)|| < | | Container (it can contain text, images, sound)|| <source lang="html"><div></div></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Headline || < | | Headline || <source lang="html"><h1></h1></source> (h2, h3, h4, h5, h6) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Paragraph || < | | Paragraph || <source lang="html"><p></p></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Linebreak || < | | Linebreak || <source lang="html"><br> or </br></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Word wrapper || < | | Word wrapper || <source lang="html"><span></span></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Link || < | | Link || <source lang="html"><a href="[url here]">[link title here]</a></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Image || < | | Image || <source lang="html"><img src="[file path here]" alt="[alternative text]"></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Audio || < | | Audio || <source lang="html"><audio src="[file path here]" controls></audio></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Video || < | | Video || <source lang="html"><video src="[file path here]" controls loop></video></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Unordered List || < | | Unordered List || <source lang="html"><ul></ul></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Ordered List || < | | Ordered List || <source lang="html"><ol></ol></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| List Item || < | | List Item || <source lang="html"><li></li></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Button || < | | Button || <source lang="html"><button></button></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Table || < | | Table || <source lang="html"><table></table></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Table Row || < | | Table Row || <source lang="html"><tr></tr></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Table Cell || < | | Table Cell || <source lang="html"><td></td></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Column Header || < | | Column Header || <source lang="html"><th></th></source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
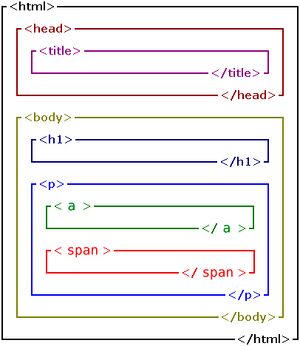
=== HTML Structure=== | |||
HTML has a nested structure: | |||
[[File:Structure-HTML-edit.jpg|frameless|center|HTML has a nested structure]] | |||
===HTML Head=== | |||
<source lang="html4strict"> | |||
<!DOCTYPE html> | |||
<html> | |||
<head> | |||
<meta charset="utf-8"> | |||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> | |||
<title>Title of this page</title> | |||
</head> | |||
<body> | |||
</body> | |||
</html> | |||
</source> | |||
===Classes + ID's=== | |||
HTML Tags can Have Classes or ID's | |||
a '''class''' can reappear on multiple elements in the HTML code. <br> | |||
an '''ID''' is more specific and only names one element. | |||
<source lang="html4strict"> | |||
<div class="box"> | |||
... | |||
</div> | |||
<div id="firstBox"> | |||
... | |||
</div> | |||
</source> | |||
this can make it easier to target them in CSS: | |||
<source lang="CSS"> | |||
.box { | |||
background-color: green; | |||
} | |||
#firstBox { | |||
background-color: blue; | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
in CSS '''classes''' are always written with a '''.''' before <br> | |||
and ID's are always written with a '''#''' before | |||
<br><br> | |||
'''Note''' you can also always use the HTML tag itself as a target, like this: | |||
<source lang="CSS"> | |||
div { | |||
background-color: green; | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
but sometimes you want to address only specific <nowiki><div></nowiki>, this is when you use Classes and ID's | |||
==CSS Properties== | |||
○ requires numerical input (like: 10px, 50%) <br> | |||
● requires textual input (like: pink, bold) | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 54: | Line 114: | ||
! Human Language !! CSS Property | ! Human Language !! CSS Property | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Outer Margin || margin: ; ○ | | Outer Margin || <source lang=CSS>margin: ; ○ | ||
margin-top: ; | |||
margin-left: ; | |||
margin-right: ; | |||
margin-bottom: ;</source> | |||
|- | |||
| Inner Margin || <source lang=CSS>padding: ; ○ | |||
padding-top: ; | |||
padding-left: ; | |||
padding-right: ; | |||
padding-bottom: ;</source> | |||
|- | |||
| Width || <source lang=CSS>width: ; ○</source> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Height || <source lang=CSS>height: ; ○</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Text Color || <source lang=CSS>color: ; ○ ●</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Background Color || <source lang=CSS>background-color: ; ○ ●</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Font Size || <source lang=CSS>font-size: ; ○ ●</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Embed Font || <source lang=CSS>@font-face { | ||
font-family: '[name your font]' ; ● | |||
src: url('[font file path]'); ● | |||
}</source> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Font | | The Font you want to use on a specific element || <source lang=CSS>font-family:' '; ●</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Font Weight || <source lang=CSS>font-weight: ; ○ ●</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Font Style (Italic, normal) || <source lang=CSS>font-style: ; ●</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Text Underline, Overline, Linethrough || <source lang=CSS>text-decoration: ; ●</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Text Shadow || <source lang=CSS>text-shadow: ; ○</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Text | | Text Justification || <source lang=CSS>text-align: ; ●</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Border || <source lang=CSS>border: [border thickness] [border style] [border color]; ● ○</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Round Edges || <source lang=CSS>border-radius: ; ○</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Outline (not taking up element space) || <source lang=CSS>outline: [border thickness] [border style] [border color]; ● ○</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Filter || <source lang=CSS>filter: [filter name]([value %]); ● ○</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | How layers blend || <source lang=CSS>mix-blend-mode: ; ●</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Opacity || <source lang=CSS>opacity: ; ○</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Transform (rotate, skew, scale, translate) || <source lang=CSS>transform: [transform property]([value + unit]); ● ○</source> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
===Pseudo Classes in CSS=== | |||
; Hover describes whats happening when your cursor is moving over an element on the page | |||
: <source lang=CSS>element:hover { [CSS properties here] }</source> | |||
; A Link that has been clicked | |||
: <source lang=CSS>element:active { [CSS properties here] }</source> | |||
; Target an element only if it has [selector] inside | |||
: <source lang=CSS>element:has([selector]) { [CSS properties here] }</source> | |||
; Target an element only if it does not have [selector] inside | |||
: <source lang=CSS>element:not([selector]) { [CSS properties here] }</source> | |||
===CSS Position=== | |||
To layout elements on your webpage you can give them a '''position''' <br> | |||
[https://hub.xpub.nl/cerealbox/~kim/cssposition/ web example] | |||
<br> | |||
'''static''' is the default value: Elements render in order, as they appear in the document flow <br> | |||
'''absolute''' positions the element relative to its first positioned (not static) ancestor element <br> | |||
'''fixed''' the element is positioned relative to the browser window <br> | |||
'''relative''' The element is positioned relative to its normal position | |||
==Wiki Ring== | |||
Other Pages on this Wiki about HTML and CSS: <br> | |||
[[HTML]] <br> | |||
[[HTML + CSS]] <br> | |||
[[User:Kiara/Code]] <br> | |||
==Websites== | |||
[https://hub.xpub.nl/cerealbox/~martina/index/ Martina's website <3] | |||
[https://hub.xpub.nl/cerealbox/~chrissy/html_css%20gym/ Chrissy's website 🧃] | |||
[https://hub.xpub.nl/cerealbox/~feline/HTML_Workshop/ Felines Website] | |||
[https://hub.xpub.nl/cerealbox/~aksellr/Personal_Reader_Exp_1/personal_reader_exp1.html/ tessa's website] | |||
[https://hub.xpub.nl/cerealbox/~eleni/html%20workshop/ Eleni's Website] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:53, 8 November 2024
Intro
This is for the beginners
In the first session we want to look at this page: Protocols for Collective Performance: Radio Broadcast 2
HTML Tags
| Human Language | HTML Tag |
|---|---|
| Html document | <htm></html>
|
| Metadata (title, link to css and script etc) | <head></head>
|
| Content of the page | <body></body>
|
| Section | <section></section>
|
| Container (it can contain text, images, sound) | <div></div>
|
| Headline | <h1></h1>
|
| Paragraph | <p></p>
|
| Linebreak | <br> or </br>
|
| Word wrapper | <span></span>
|
| Link | <a href="[url here]">[link title here]</a>
|
| Image | <img src="[file path here]" alt="[alternative text]">
|
| Audio | <audio src="[file path here]" controls></audio>
|
| Video | <video src="[file path here]" controls loop></video>
|
| Unordered List | <ul></ul>
|
| Ordered List | <ol></ol>
|
| List Item | <li></li>
|
| Button | <button></button>
|
| Table | <table></table>
|
| Table Row | <tr></tr>
|
| Table Cell | <td></td>
|
| Column Header | <th></th>
|
HTML Structure
HTML has a nested structure:
HTML Head
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title of this page</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Classes + ID's
HTML Tags can Have Classes or ID's
a class can reappear on multiple elements in the HTML code.
an ID is more specific and only names one element.
<div class="box">
...
</div>
<div id="firstBox">
...
</div>
this can make it easier to target them in CSS:
.box {
background-color: green;
}
#firstBox {
background-color: blue;
}
in CSS classes are always written with a . before
and ID's are always written with a # before
Note you can also always use the HTML tag itself as a target, like this:
div {
background-color: green;
}
but sometimes you want to address only specific <div>, this is when you use Classes and ID's
CSS Properties
○ requires numerical input (like: 10px, 50%)
● requires textual input (like: pink, bold)
| Human Language | CSS Property |
|---|---|
| Outer Margin | margin: ; ○
margin-top: ;
margin-left: ;
margin-right: ;
margin-bottom: ;
|
| Inner Margin | padding: ; ○
padding-top: ;
padding-left: ;
padding-right: ;
padding-bottom: ;
|
| Width | width: ; ○
|
| Height | height: ; ○
|
| Text Color | color: ; ○ ●
|
| Background Color | background-color: ; ○ ●
|
| Font Size | font-size: ; ○ ●
|
| Embed Font | @font-face {
font-family: '[name your font]' ; ●
src: url('[font file path]'); ●
}
|
| The Font you want to use on a specific element | font-family:' '; ●
|
| Font Weight | font-weight: ; ○ ●
|
| Font Style (Italic, normal) | font-style: ; ●
|
| Text Underline, Overline, Linethrough | text-decoration: ; ●
|
| Text Shadow | text-shadow: ; ○
|
| Text Justification | text-align: ; ●
|
| Border | border: [border thickness] [border style] [border color]; ● ○
|
| Round Edges | border-radius: ; ○
|
| Outline (not taking up element space) | outline: [border thickness] [border style] [border color]; ● ○
|
| Filter | filter: [filter name]([value %]); ● ○
|
| How layers blend | mix-blend-mode: ; ●
|
| Opacity | opacity: ; ○
|
| Transform (rotate, skew, scale, translate) | transform: [transform property]([value + unit]); ● ○
|
Pseudo Classes in CSS
- Hover describes whats happening when your cursor is moving over an element on the page
element:hover { [CSS properties here] }
- A Link that has been clicked
element:active { [CSS properties here] }
- Target an element only if it has [selector] inside
element:has([selector]) { [CSS properties here] }
- Target an element only if it does not have [selector] inside
element:not([selector]) { [CSS properties here] }
CSS Position
To layout elements on your webpage you can give them a position
web example
static is the default value: Elements render in order, as they appear in the document flow
absolute positions the element relative to its first positioned (not static) ancestor element
fixed the element is positioned relative to the browser window
relative The element is positioned relative to its normal position
Wiki Ring
Other Pages on this Wiki about HTML and CSS:
HTML
HTML + CSS
User:Kiara/Code