HTML/CSS Memo: Difference between revisions
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
in CSS '''classes''' are always written with a '''.''' before <br> | in CSS '''classes''' are always written with a '''.''' before <br> | ||
and ID's are always written with a '''#''' before | and ID's are always written with a '''#''' before | ||
<br><br> | |||
'''Note''' you can also always use the HTML tag itself as a target, like this: | |||
<source lang="CSS"> | |||
div { | |||
background-color: green; | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
but sometimes you want to address only specific <code><div></code>, this is when you use Classes and ID's | |||
==CSS Properties== | ==CSS Properties== | ||
Revision as of 12:31, 8 November 2024
Intro
This is for the beginners
In the first session we want to look at this page: Protocols for Collective Performance: Radio Broadcast 2
HTML Tags
| Human Language | HTML Tag |
|---|---|
| Html document | <htm></html>
|
| Metadata (title, link to css and script etc) | <head></head>
|
| Content of the page | <body></body>
|
| Section | <section></section>
|
| Container (it can contain text, images, sound) | <div></div>
|
| Headline | <h1></h1>
|
| Paragraph | <p></p>
|
| Linebreak | <br> or </br>
|
| Word wrapper | <span></span>
|
| Link | <a href="[url here]">[link title here]</a>
|
| Image | <img src="[file path here]" alt="[alternative text]">
|
| Audio | <audio src="[file path here]" controls></audio>
|
| Video | <video src="[file path here]" controls loop></video>
|
| Unordered List | <ul></ul>
|
| Ordered List | <ol></ol>
|
| List Item | <li></li>
|
| Button | <button></button>
|
| Table | <table></table>
|
| Table Row | <tr></tr>
|
| Table Cell | <td></td>
|
| Column Header | <th></th>
|
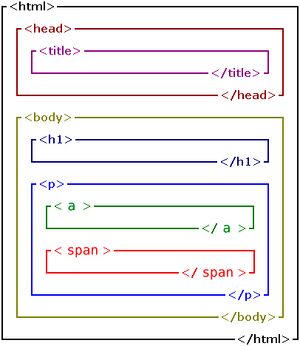
HTML Structure
HTML has a nested structure:
HTML Head
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title of this page</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Classes + ID's
HTML Tags can Have Classes or ID's
<div class="box">
...
</div>
<div ID="firstBox">
...
</div>
this can make it easier to target them in CSS:
.box {
background-color: green;
}
#firstBox {
background-color: blue;
}
in CSS classes are always written with a . before
and ID's are always written with a # before
Note you can also always use the HTML tag itself as a target, like this:
div {
background-color: green;
}
but sometimes you want to address only specific
CSS Properties
○ requires numerical input (like: 10px, 50%)
● requires textual input (like: pink, bold)
| Human Language | CSS Property |
|---|---|
| Outer Margin | margin: ; ○
margin-top: ;
margin-left: ;
margin-right: ;
margin-bottom: ;
|
| Inner Margin | padding: ; ○
padding-top: ;
padding-left: ;
padding-right: ;
padding-bottom: ;
|
| Width | width: ; ○
|
| Height | height: ; ○
|
| Text Color | color: ; ○ ●
|
| Background Color | background-color: ; ○ ●
|
| Font Size | font-size: ; ○ ●
|
| Embed Font | @font-face {
font-family: '[name your font]' ; ●
src: url('[font file path]'); ●
}
|
| The Font you want to use on a specific element | font-family:' '; ●
|
| Font Weight | font-weight: ; ○ ●
|
| Font Style (Italic, normal) | font-style: ; ●
|
| Text Underline, Overline, Linethrough | text-decoration: ; ●
|
| Text Shadow | text-shadow: ; ○
|
| Text Justification | text-align: ; ●
|
| Border | border: [border thickness] [border style] [border color]; ● ○
|
| Round Edges | border-radius: ; ○
|
| Outline (not taking up element space) | outline: [border thickness] [border style] [border color]; ● ○
|
| Filter | filter: [filter name]([value %]); ● ○
|
| How layers blend | mix-blend-mode: ; ●
|
| Opacity | opacity: ; ○
|
| Transform (rotate, skew, scale, translate) | transform: [transform property]([value + unit]); ● ○
|
Pseudo Classes in CSS
- Hover describes whats happening when your cursor is moving over an element on the page
element:hover { [CSS properties here] }
- A Link that has been clicked
element:active { [CSS properties here] }
- Target an element only if it has [selector] inside
element:has([selector]) { [CSS properties here] }
- Target an element only if it does not have [selector] inside
element:not([selector]) { [CSS properties here] }
Wiki Ring
Other Pages on this Wiki about HTML and CSS:
HTML
HTML + CSS
User:Kiara/Code