Universal Resource Locator: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
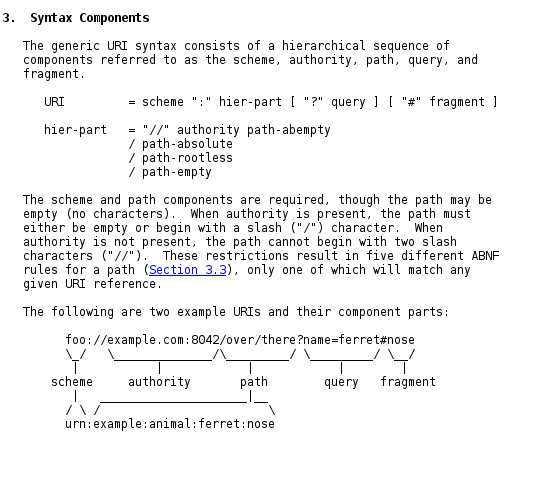
[[File:RFC3986_SyntaxDiagram.png]] | [[File:RFC3986_SyntaxDiagram.png]] | ||
https://cascadingmedia.com/assets/images/insites/2015/02/url-anatomy/url-anatomy-55598c24.png | |||
Revision as of 10:55, 17 April 2018
Core part of the specification of the web. URLs name locations of resources online. The "names" used by the HTTP protocol to request and transmit documents/resources on the web.
Closely related to:
URI: Universal Resource Identifier,
URN: Universal Resource Name
From the RFC Specification,
A URI can be further classified as a locator, a name, or both. The term "Uniform Resource Locator" (URL) refers to the subset of URIs that, in addition to identifying a resource, provide a means of locating the resource by describing its primary access mechanism (e.g., its network "location"). The term "Uniform Resource Name" (URN) has been used historically to refer to both URIs under the "urn" scheme [RFC2141], which are required to remain globally unique and persistent even when the resource ceases to exist or becomes unavailable, and to any other URI with the properties of a name.