User:ThomasW/First Proposal Outline v2: Difference between revisions
| (67 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
To find older versions, look here [https://pzwiki.wdka.nl/mediadesign/User:ThomasW/First_Proposal_Outline Old] | |||
http://www.textfiles.com/underconstruction/Nova1466underconstruction.gif | |||
== | '''//////// WARNING DYSLEXIA AHEAD \\\\\\\\\//////// WARNING DYSLEXIA AHEAD \\\\\\\\\''' | ||
--------------------- | |||
== Current Project Page == | |||
[https://pzwiki.wdka.nl/mediadesign/User:ThomasW/MyHard-DriveDied_V2 Project Page] | |||
== New Proposal (to late for deadline) == | |||
[[https://pzwiki.wdka.nl/mediadesign/User:ThomasW/First_Proposal_Outline_v3 NEW, BUT TO LATE]] | |||
=="Constantly on the Edge of Oblivion 14.11.15 "== | |||
For my graduation project at Piet Zwart Institute, I want to question the Utopic view that any given new electronic storage medium is the final solution to our storage needs, by the fact that nothing stays permanent, and has never been. Since the beginning of history there have always been great promises for the future of information storage. | |||
I want to explore this question by making a collections of works that tells peoples individual experience with storage mediums after they fail. How did this change their relationship to the mediums? My work will explore different storage mediums from Hard-Drives, USB thumb drive, and online “cloud” storage. | |||
My first part of the project “My Hard-Drive Died” explores peoples relationship to their hard-drives by transmitting stories through a modified hard-drive. The stories are collected from Twitter. | |||
'''“We have the capacity to store everything for possible recall, but these same extended memory technologies are capable of generating oblivion in other ways—not least of which is through the technology.” (Gabrys, 2007, p120-123 )“''' | '''“We have the capacity to store everything for possible recall, but these same extended memory technologies are capable of generating oblivion in other ways—not least of which is through the technology.” (Gabrys, 2007, p120-123 )“''' | ||
===Introduction=== | |||
Today we are often promised instant relocation and storage for free. How does this effect our connection to what we make? And how does this supposedly “easy life” change what we make and think about how we store it? | |||
My interest in the topic of finding and spreading information and knowledge started early by visiting the school library at the age of nine for technology and history books. | |||
Later in life I made a computer game magazine when I was 13 years old. I had folders of images, texts and project files from the project, but even being incredibly careful where I saved them, moving them around from computers to floppy disks to other computers, it all got lost somewhere. | |||
[[File:BASFunlimited.jpg|300px|]] | |||
Now its not just computer games, but history itself that is in danger: we put information onto platforms that claim they will archive for ever, “they tell its safe and saved, you don’t need to think about it” but history tells us that platforms and formats never stays forever. From papyrus or the next “cloud” services, they all will disappear. | |||
“Your data maybe safe for tomorrow, but what about a 50 or 100 years from now? And is it really that important? | |||
'''“Digital is the paradigm for content and quantity of information; analogue is the paradigm for usability and interfacing.” (Ludovico,2013,p151) | |||
Printed books can last hundreds of years if they are not exposed to fire, water, war and the stupidity of man, but a digital text can disappear and be left unaccessible in the future on the reasons like, unsupported file formats, dead storage formats, defunct “cloud” services or End User Licenses Agreements that deny you to the right to save or delete your own information. | |||
Online platform or “the cloud” are now often put forward as a final solution for your storage problems, but not even they can guaranty that they still be in business in one months time or what about 100 years from now? | |||
By using the “cloud” as a metaphor, it makes it even harder for most people to understand what “the cloud” really is. In reality, “the cloud” is traditional computer storage on devices, but just on other peoples machines, somewhere in the world in big and highly physical buildings made of steel and concrete. | |||
By looking back at history, no formats have truthfully been everlasting without a constant supervision and copying of its content over to new formats. By being more aware how things work and being the one that decides what stays and what gets deleted you can control what what to keep or what to deleted. | |||
'''“[P]aper was introduced during the ninth or tenth centuries, and the first paper found there is of the oriental type (called bombykinon or bambakeron). The fact that is was cheap than and other material gradually gave it ascendancy, but its rapid deterioration was a matter of great concern to the monks” (Fernando, 2008, p95)''' | |||
===Relation to previous practice=== | |||
''''“It must be understood that as long as art stand aside from the problems of life it will only interest a very few people.” (Munari,1966, p25)''' | |||
During my Bachelor. I made a project called “The Library of Babel” based on the short story by the same name by the Argentinian author Jorge Luis Borges. This project was made on the topic of “bit-rot” in text documents. This project got me really interesting in the long term storage of information and how we as society deal with it. A thread that goes through my previous projects are always these topics that I find interesting, but never get the attention I think they deservers. | |||
http://payload252.cargocollective.com/1/9/310277/7352872/IMG_5644.jpg “The Library of Babel” | |||
In my previous term at Piet Zwart I made the project Imagery Storage Formats, this project explored | |||
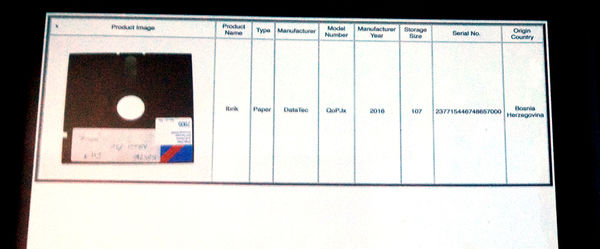
With my random generating encyclopaedia of imagery storage formats I wanted to make fun of the computer industry and putting a question out to people, If the new formats are so good and as stable as they say they are, can you really believe them? | |||
Since the invention of electronic storage devices, there have been many promises of the durability of the medium from their inventors. The computer industry have spent 50 years of over-promising and under-delivery. If the computer industry can make loft claims, why can I not make up my own collection of storage formats? | |||
With my random generating encyclopaedia of imagery storage formats. I wanted to make fun of the computer industry and put a question out to people; Are the new formats really so good that you can believe that you data is safe? | |||
[[File:Encyclopedia of storage formats.jpg|600px ]] | |||
''' | ===Relation to a larger context=== | ||
''''“In 1961, the British science fiction author Arthur C. Clarke suggested that “any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.” (Feigelfeld, 2015, Online)“''' | |||
http://www.etsisi.upm.es/sites/default/files/museo/memex.gif Vannevar Bush’s Memex machine. | |||
=== | Technology is becoming more and more distant from the peoples understanding of it. The first to start using a technology know more about how it works than those who become acquainted later. Most computer and computer storage technology’s are mysterious. Its hidden away in black boxes, warning labels and security screws and hyper-bull marketing words. The technology industry has always been “fetishising the notion of optimization” From paper medium to the cloud, people have always been looking for quick solutions for their problems, storing their memory is one of them. | ||
''' | '''Rather than getting caught up in speed, then, we must analyze, as we try to grasp a present that is always degenerating, the ways in which ephemerality is made to endure. What is surprising is not that digital media fades but rather that it stays at all and that we stay transfixed by our screens as its ephemerality endures. (Hui Kyong Chun, 2008, p171 ) | ||
===Thesis intention=== | |||
The thesis will focus on the topic of society and how we deal with this increasing amount of information and how and why we are making that amount of information. “Can less mean more?” | |||
'''“I am afraid that future theorists and historians of computer media will be left with not much more than the equivalents of the newspaper reports and film programs from cinema first decade. They will find that analytical texts from our area recognize the significance of computers take over of culture, yet, by and large, contains speculations about the future rather then a record and theory of the present. (Manovich,2001, p6-7)“''' | |||
===Practical steps=== | |||
'''“The design artefact you leave behind will be your ultimate legacy" (Beirut ,2006, p6) | |||
My work will explore different current and past storage mediums like Hard-Drives, USB thumb drives, CDs, floppy disks and online “the cloud” storage. | |||
The Hard-Drive part of the project exist now as a prototype in the form of “My Hard Drive Died” where I transmit 750 stories gathers from twitter true one old drive that is reworked as a speaker. The voice is done with a synthesizers voice as it make it more as a voice that comes from the hard-drive itself. | |||
Loss of control of the personal archive means a loss of societal control of the cultural record. (Abreu, 2008, Online) | Loss of control of the personal archive means a loss of societal control of the cultural record. (Abreu, 2008, Online) | ||
Small selection of tweets | |||
' | *@anaima92: Yesterday, my laptop's hard drive died. I went to the Apple Store today, learned that it is "vintage" and they can't replace … | ||
*@jeffromusic: Yup my hard drive died. RIP jeffro | |||
*@TalyaJohnson: My hard drive has gone away from this world. It died too young, not even two years old. Yet I feel its loss... http://t.c… | |||
I | |||
*@flybyjerry: Was gonna stream but I think my hard drive on my MacBook Pro finally died after 6 years... I'm seriously so depressed right… | |||
*@NilsorVault: Noooooo! My desktop computer just died, the hard drive is unreadable. Rip my companion of 9 years :( | |||
===Bibliography=== | ===Bibliography=== | ||
Latest revision as of 00:17, 27 November 2015
To find older versions, look here Old
//////// WARNING DYSLEXIA AHEAD \\\\\\\\\//////// WARNING DYSLEXIA AHEAD \\\\\\\\\
Current Project Page
New Proposal (to late for deadline)
"Constantly on the Edge of Oblivion 14.11.15 "
For my graduation project at Piet Zwart Institute, I want to question the Utopic view that any given new electronic storage medium is the final solution to our storage needs, by the fact that nothing stays permanent, and has never been. Since the beginning of history there have always been great promises for the future of information storage.
I want to explore this question by making a collections of works that tells peoples individual experience with storage mediums after they fail. How did this change their relationship to the mediums? My work will explore different storage mediums from Hard-Drives, USB thumb drive, and online “cloud” storage. My first part of the project “My Hard-Drive Died” explores peoples relationship to their hard-drives by transmitting stories through a modified hard-drive. The stories are collected from Twitter.
“We have the capacity to store everything for possible recall, but these same extended memory technologies are capable of generating oblivion in other ways—not least of which is through the technology.” (Gabrys, 2007, p120-123 )“
Introduction
Today we are often promised instant relocation and storage for free. How does this effect our connection to what we make? And how does this supposedly “easy life” change what we make and think about how we store it? My interest in the topic of finding and spreading information and knowledge started early by visiting the school library at the age of nine for technology and history books. Later in life I made a computer game magazine when I was 13 years old. I had folders of images, texts and project files from the project, but even being incredibly careful where I saved them, moving them around from computers to floppy disks to other computers, it all got lost somewhere.
Now its not just computer games, but history itself that is in danger: we put information onto platforms that claim they will archive for ever, “they tell its safe and saved, you don’t need to think about it” but history tells us that platforms and formats never stays forever. From papyrus or the next “cloud” services, they all will disappear. “Your data maybe safe for tomorrow, but what about a 50 or 100 years from now? And is it really that important?
“Digital is the paradigm for content and quantity of information; analogue is the paradigm for usability and interfacing.” (Ludovico,2013,p151)
Printed books can last hundreds of years if they are not exposed to fire, water, war and the stupidity of man, but a digital text can disappear and be left unaccessible in the future on the reasons like, unsupported file formats, dead storage formats, defunct “cloud” services or End User Licenses Agreements that deny you to the right to save or delete your own information. Online platform or “the cloud” are now often put forward as a final solution for your storage problems, but not even they can guaranty that they still be in business in one months time or what about 100 years from now? By using the “cloud” as a metaphor, it makes it even harder for most people to understand what “the cloud” really is. In reality, “the cloud” is traditional computer storage on devices, but just on other peoples machines, somewhere in the world in big and highly physical buildings made of steel and concrete. By looking back at history, no formats have truthfully been everlasting without a constant supervision and copying of its content over to new formats. By being more aware how things work and being the one that decides what stays and what gets deleted you can control what what to keep or what to deleted.
“[P]aper was introduced during the ninth or tenth centuries, and the first paper found there is of the oriental type (called bombykinon or bambakeron). The fact that is was cheap than and other material gradually gave it ascendancy, but its rapid deterioration was a matter of great concern to the monks” (Fernando, 2008, p95)
Relation to previous practice
'“It must be understood that as long as art stand aside from the problems of life it will only interest a very few people.” (Munari,1966, p25)
During my Bachelor. I made a project called “The Library of Babel” based on the short story by the same name by the Argentinian author Jorge Luis Borges. This project was made on the topic of “bit-rot” in text documents. This project got me really interesting in the long term storage of information and how we as society deal with it. A thread that goes through my previous projects are always these topics that I find interesting, but never get the attention I think they deservers.
 “The Library of Babel”
“The Library of Babel”
In my previous term at Piet Zwart I made the project Imagery Storage Formats, this project explored With my random generating encyclopaedia of imagery storage formats I wanted to make fun of the computer industry and putting a question out to people, If the new formats are so good and as stable as they say they are, can you really believe them? Since the invention of electronic storage devices, there have been many promises of the durability of the medium from their inventors. The computer industry have spent 50 years of over-promising and under-delivery. If the computer industry can make loft claims, why can I not make up my own collection of storage formats?
With my random generating encyclopaedia of imagery storage formats. I wanted to make fun of the computer industry and put a question out to people; Are the new formats really so good that you can believe that you data is safe?
Relation to a larger context
'“In 1961, the British science fiction author Arthur C. Clarke suggested that “any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.” (Feigelfeld, 2015, Online)“
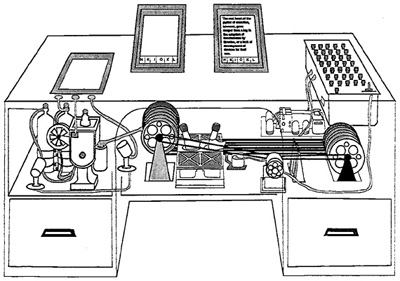 Vannevar Bush’s Memex machine.
Vannevar Bush’s Memex machine.
Technology is becoming more and more distant from the peoples understanding of it. The first to start using a technology know more about how it works than those who become acquainted later. Most computer and computer storage technology’s are mysterious. Its hidden away in black boxes, warning labels and security screws and hyper-bull marketing words. The technology industry has always been “fetishising the notion of optimization” From paper medium to the cloud, people have always been looking for quick solutions for their problems, storing their memory is one of them. Rather than getting caught up in speed, then, we must analyze, as we try to grasp a present that is always degenerating, the ways in which ephemerality is made to endure. What is surprising is not that digital media fades but rather that it stays at all and that we stay transfixed by our screens as its ephemerality endures. (Hui Kyong Chun, 2008, p171 )
Thesis intention
The thesis will focus on the topic of society and how we deal with this increasing amount of information and how and why we are making that amount of information. “Can less mean more?” “I am afraid that future theorists and historians of computer media will be left with not much more than the equivalents of the newspaper reports and film programs from cinema first decade. They will find that analytical texts from our area recognize the significance of computers take over of culture, yet, by and large, contains speculations about the future rather then a record and theory of the present. (Manovich,2001, p6-7)“
Practical steps
“The design artefact you leave behind will be your ultimate legacy" (Beirut ,2006, p6)
My work will explore different current and past storage mediums like Hard-Drives, USB thumb drives, CDs, floppy disks and online “the cloud” storage. The Hard-Drive part of the project exist now as a prototype in the form of “My Hard Drive Died” where I transmit 750 stories gathers from twitter true one old drive that is reworked as a speaker. The voice is done with a synthesizers voice as it make it more as a voice that comes from the hard-drive itself. Loss of control of the personal archive means a loss of societal control of the cultural record. (Abreu, 2008, Online)
Small selection of tweets
- @anaima92: Yesterday, my laptop's hard drive died. I went to the Apple Store today, learned that it is "vintage" and they can't replace …
- @jeffromusic: Yup my hard drive died. RIP jeffro
- @TalyaJohnson: My hard drive has gone away from this world. It died too young, not even two years old. Yet I feel its loss... http://t.c…
- @flybyjerry: Was gonna stream but I think my hard drive on my MacBook Pro finally died after 6 years... I'm seriously so depressed right…
- @NilsorVault: Noooooo! My desktop computer just died, the hard drive is unreadable. Rip my companion of 9 years :(
Bibliography
- Gabrys, Jennifer (2007) DIGITAL RUBBISH a natural history of electronics, Paperback , United States of America ,The University of Michigan Press
- Ludovico, Alessandro (2013) Post Digital Print, Onomatopee
- Munari, Bruno, Design as Art (1966) England, Penguin
- Feigelfeld, Paul (2015) Media Archaeology Out of Nature: An Interview with Jussi Parikka, e-flux.com [Online] Available: http://www.e-flux.com/journal/media-archaeology-out-of-nature-an-interview-with-jussi-parikka/ (Accessed:28.05.2015)
- Beirut, Michael, Drenttel, William, William, Steven (2006) Look Closer Five, Critical Writings on Graphic Design, New York, Allworth Press
- Manovich, Lev, (2001) The Language of New Media, United States of America, The MIT Press
- Baez, Fernando (2008) A Universal History of the Destruction of Books: From Ancient Sumer to Modern-day Iraq, Atlas & Co.
- The Enduring Ephemeral, or the Future Is a Memory Author(s): By Wendy Hui Kyong Chun Source: Critical Inquiry, Vol. 35, No. 1 (Autumn 2008), pp. 148-171 Published by: The University of Chicago Press Stable URL: http://www.jstor.org/stable/10.1086/595632 . Accessed: 22/09/2015 09:06
- Abreu, Amelia (2015) The Collection and the Cloud, The New Winquiry [Online] Available: http://thenewinquiry.com/essays/the-collection-and-the-cloud/ .(Accessed:10.10.2015)