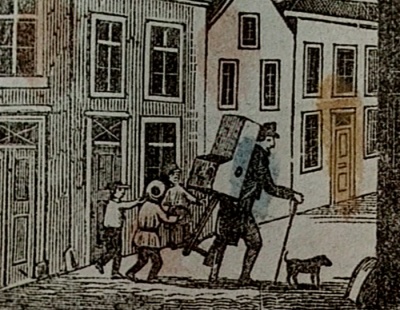User:Quinten swagerman/Research/Nekes: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''A selection of optical toys as shown in Werner Nekes' 1985 documentary 'Was geschah wirklich | '''A selection of optical toys as shown in Werner Nekes' 1985 documentary 'Was geschah wirklich zwischen den Bildern?', in order of appearance''' | ||
[[image:nekes_00.17.jpg|thumb]] | [[image:nekes_00.17.jpg|thumb]] | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
00:07:49 | 00:07:49 | ||
'Anamorphosis - cone and cilinder mirrors - have been painted since the 17th century' | |||
''Anamorphosis - cone and cilinder mirrors - have been painted since the 17th century'' | |||
== Shadow play == | == Shadow play == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
00:09:39 | 00:09:39 | ||
'The oldest form of the artistic use of light is the shadowplay | |||
''The oldest form of the artistic use of light is the shadowplay...'' | |||
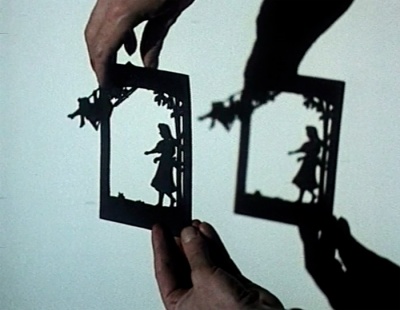
[[Image:nekes_10.23.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_10.23.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:10:23 | 00:10:23 | ||
'These scissorcuts derived from the Chinese shadowplay | |||
''These scissorcuts derived from the Chinese shadowplay'' | |||
[[Image:nekes_11.25.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_11.25.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:11:25 | 00:11:25 | ||
'Hand shadows are still a popular game' | |||
''Hand shadows are still a popular game'' | |||
[[Image:nekes_11.38.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_11.38.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:11:38 | 00:11:38 | ||
'In 1678, van Hoogstraten ran his own shadow theatre' | |||
''In 1678, van Hoogstraten ran his own shadow theatre'' | |||
[[Image:nekes_12.22.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_12.22.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:12:22 | 00:12:22 | ||
'Miniature mechanical shadow theatre scenes were also very popular' | |||
''Miniature mechanical shadow theatre scenes were also very popular'' | |||
== Ombro cinema == | == Ombro cinema == | ||
| Line 47: | Line 53: | ||
[[Image:nekes_14.13.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_14.13.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:13:39 'The ombro cinema, a shadow theatre of 1915, animates the shadows by conceiling and reveiling the different phases of movement behind black bars' | 00:13:39 | ||
''The ombro cinema, a shadow theatre of 1915, animates the shadows by conceiling and reveiling the different phases of movement behind black bars'' | |||
== Mechanical projection discs == | == Mechanical projection discs == | ||
| Line 55: | Line 63: | ||
[[Image:nekes_20.10.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_20.10.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:19:59 'This scientific disc simulates the complicated movements of the planetary movements in the solar system' | 00:19:59 | ||
''This scientific disc simulates the complicated movements of the planetary movements in the solar system'' | |||
== Peepshows == | == Peepshows == | ||
| Line 68: | Line 78: | ||
00:29:05 | 00:29:05 | ||
'The peepshow was being developed from perspective boxes and miracle cabinets. In the 17th century, showman began to travel in Europe, presenting their spectacles.' | |||
''The peepshow was being developed from perspective boxes and miracle cabinets. In the 17th century, showman began to travel in Europe, presenting their spectacles.'' | |||
== Scrolling panorama == | == Scrolling panorama == | ||
[[Image:nekes_35. | [[Image:nekes_35.58.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:35:43 | 00:35:43 | ||
'Panorama of a trip from Hamburg to Luttener. The double-length panorama by Zoër (?) was seven centimeters high and high meters long' | |||
''Panorama of a trip from Hamburg to Luttener. The double-length panorama by Zoër (?) was seven centimeters high and high meters long'' | |||
== Theatre of perspective == | == Theatre of perspective == | ||
[[Image:nekes_38.17.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_38.17.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_38.22.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_38.22.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:38:17 | 00:38:17 | ||
'Around 1700, Martin Engelbrecht from Alsburg constructs his theatre of perspective. He explores the sense of depth within the spacial dimensions of an image' | |||
''Around 1700, Martin Engelbrecht from Alsburg constructs his theatre of perspective. He explores the sense of depth within the spacial dimensions of an image'' | |||
== Stereoscopy == | == Stereoscopy == | ||
| Line 90: | Line 104: | ||
00:43:41 | 00:43:41 | ||
'In 1838, Winston invented the mirror stereoscope' | |||
''In 1838, Winston invented the mirror stereoscope...'' | |||
[[Image:nekes_43.49.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_43.49.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:43:49 | 00:43:49 | ||
'In 1849, Brewster the lens stereoscope' | |||
''In 1849, Brewster the lens stereoscope'' | |||
[[Image:nekes_46.50.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_46.50.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:46:50 | 00:46:50 | ||
'3D glasses for anaglyphs and for polarized images' | ''3D glasses for anaglyphs and for polarized images'' | ||
== The afterimage effect == | == The afterimage effect == | ||
[[Image:nekes_48.15.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_48.15.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_48.24.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_48.24.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:48:15 | 00:48:15 | ||
'A demonstration of the afterimage effect - the family has been looking at the red devil for a long while, then they look at the ceiling where they can see the devil's afterimage in its complementary color: green | |||
''A demonstration of the afterimage effect - the family has been looking at the red devil for a long while, then they look at the ceiling where they can see the devil''s afterimage in its complementary color: green.'' | |||
== The thaumatrope == | == The thaumatrope == | ||
[[Image:nekes_51.46.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_51.46.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_51.47.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_51.47.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
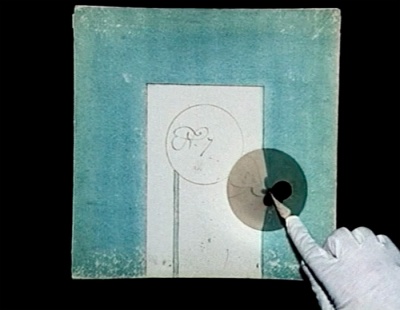
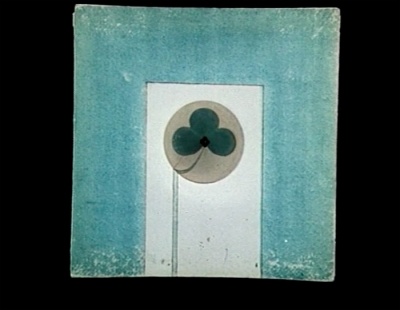
00:51:45 | 00:51:45 | ||
The thaumatrope, or miracle disc, was invented in England by doctor John | |||
''The thaumatrope, or miracle disc, was invented in England by doctor [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Ayrton_Paris John Ayrton Paris], in 1826'' | |||
[[Image:nekes_52.45.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_52.45.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:52:45 | 00:52:45 | ||
Two sets of half-letters, which, added together, say "Hab Mich Lieb" | |||
''Two sets of half-letters, which, added together, say "Hab Mich Lieb" '' | |||
== Lens-prism animation == | == Lens-prism animation == | ||
[[Image:nekes_56.24.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_56.24.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_56.25.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_56.25.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
| Line 131: | Line 153: | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.00.08.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.00.08.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.02.12.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.02.12.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
The designoscope - two mirrors meet at an angle of 60 degrees, as in the kaleidoscope, and produce an infinite variaty of patterns | 01:00:08 | ||
''The designoscope - two mirrors meet at an angle of 60 degrees, as in the kaleidoscope, and produce an infinite variaty of patterns'' | |||
== The phenakistoscope == | == The phenakistoscope == | ||
| Line 140: | Line 165: | ||
01:02:41 | 01:02:41 | ||
Inspired by Faradays wheel, Joseph Plateau in Brussels and Simon Stampfer | |||
Inspired by [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Faraday_Wheel Faradays wheel], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joseph_Plateau Joseph Plateau] in Brussels and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simon_von_Stampfer Simon von Stampfer] in Vienna, invent the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phenakistoscope phenakistoscope] independently of one another in 1832. Stampfer called it the stroboscope. In England it was known as the phantascope. This disc demonstrates continuous movement for the first time. | |||
A selection of discs: | A selection of discs: | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.02.49.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.02.49.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.02.57.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.02.57.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
| Line 149: | Line 177: | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.03.08.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.03.08.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.03.31.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.03.31.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
01:03:08 | 01:03:08 | ||
In 1833, Horner invented the | |||
''In 1833, [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_George_Horner Horner] invented the Daedalum, later called the zoetrope, or wheel of life. Here, the phases of movement are also seen as an infinite loop through the slits'' | |||
A selection of strips: | A selection of strips: | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.03.21.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.03.21.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.03.25.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.03.25.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.03.46.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.03.46.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
| Line 163: | Line 195: | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.03.55.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.03.55.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.05.03.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.05.03.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.05.14.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.05.14.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
01:03:55 | 01:03:55 | ||
''In 1877, [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Émile_Reynaud Émile Reynaud] built his praxinoscope, where you see the images in the mirrors. The function of the dark space in between the slits is taken over by the angle of the mirror at which it is set up.'' | |||
In 1880, he managed to project his moving images. | ''Two years later he succeeded in showing the moving image within a scene, which is in fact a mirror reflection.'' | ||
''In 1880, he managed to project his moving images.'' | |||
A selection of strips: | A selection of strips: | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.05.18.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.05.18.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.05.46.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.05.46.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.05.52.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.05.52.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
| Line 181: | Line 219: | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.07.04.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.07.04.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.07.13.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.07.13.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
01:07:04 | 01:07:04 | ||
The myriorama, the show of the ten thousands. A panaroma in stripes which brings a new image in vertical montage. | |||
''The myriorama, the show of the ten thousands. A panaroma in stripes which brings a new image in vertical montage.'' | |||
== Movement-producing grids == | == Movement-producing grids == | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.12.13.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.12.13.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.12.56.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.12.56.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
| Line 194: | Line 235: | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.13.34.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.13.34.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.13.51.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.13.51.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:13:34 | 00:13:34 | ||
The painter Lautenberg is reputed to have created the first flip book, or thumb cinema, in 1760. Leaving through the book creates the illusion of movement | |||
''The painter Lautenberg (?) is reputed to have created the first flip book, or thumb cinema, in 1760. Leaving through the book creates the illusion of movement.'' | |||
== The Kinora == | == The Kinora == | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.14.07.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.14.07.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.14.09.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.14.09.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
[[Image:nekes_1.14.29.jpg|border|400px]] | [[Image:nekes_1.14.29.jpg|border|400px]] | ||
00:14:07 | 00:14:07 | ||
In 1898, the brothers Lumiere built the Kinora, three years after their first film shows | |||
In 1898, [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Auguste_and_Louis_Lumière the brothers Lumiere] built the Kinora, three years after their first film shows. | |||
Latest revision as of 17:04, 22 February 2012
A selection of optical toys as shown in Werner Nekes' 1985 documentary 'Was geschah wirklich zwischen den Bildern?', in order of appearance
Mirrors
00:07:49
Anamorphosis - cone and cilinder mirrors - have been painted since the 17th century
Shadow play
00:09:39
The oldest form of the artistic use of light is the shadowplay...
00:10:23
These scissorcuts derived from the Chinese shadowplay
00:11:25
Hand shadows are still a popular game
00:11:38
In 1678, van Hoogstraten ran his own shadow theatre
00:12:22
Miniature mechanical shadow theatre scenes were also very popular
Ombro cinema
00:13:39
The ombro cinema, a shadow theatre of 1915, animates the shadows by conceiling and reveiling the different phases of movement behind black bars
Mechanical projection discs
00:19:59
This scientific disc simulates the complicated movements of the planetary movements in the solar system
Peepshows
00:29:05
The peepshow was being developed from perspective boxes and miracle cabinets. In the 17th century, showman began to travel in Europe, presenting their spectacles.
Scrolling panorama
00:35:43
Panorama of a trip from Hamburg to Luttener. The double-length panorama by Zoër (?) was seven centimeters high and high meters long
Theatre of perspective
00:38:17
Around 1700, Martin Engelbrecht from Alsburg constructs his theatre of perspective. He explores the sense of depth within the spacial dimensions of an image
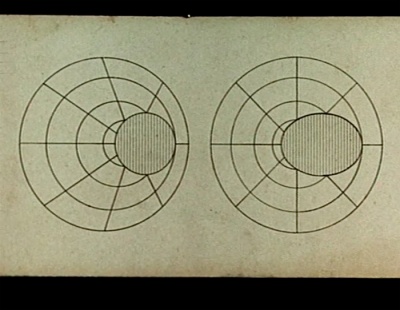
Stereoscopy
00:43:41
In 1838, Winston invented the mirror stereoscope...
00:43:49
In 1849, Brewster the lens stereoscope
00:46:50 3D glasses for anaglyphs and for polarized images
The afterimage effect
00:48:15
A demonstration of the afterimage effect - the family has been looking at the red devil for a long while, then they look at the ceiling where they can see the devils afterimage in its complementary color: green.
The thaumatrope
00:51:45
The thaumatrope, or miracle disc, was invented in England by doctor John Ayrton Paris, in 1826
00:52:45
Two sets of half-letters, which, added together, say "Hab Mich Lieb"
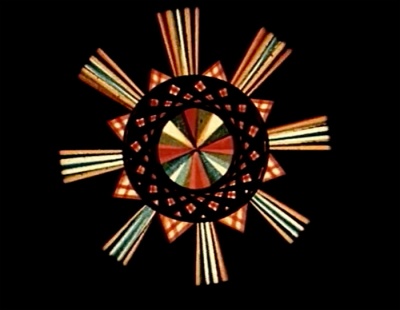
Lens-prism animation
The designoscope
01:00:08
The designoscope - two mirrors meet at an angle of 60 degrees, as in the kaleidoscope, and produce an infinite variaty of patterns
The phenakistoscope
01:02:41
Inspired by Faradays wheel, Joseph Plateau in Brussels and Simon von Stampfer in Vienna, invent the phenakistoscope independently of one another in 1832. Stampfer called it the stroboscope. In England it was known as the phantascope. This disc demonstrates continuous movement for the first time.
A selection of discs:
The zoetrope
01:03:08
In 1833, Horner invented the Daedalum, later called the zoetrope, or wheel of life. Here, the phases of movement are also seen as an infinite loop through the slits
A selection of strips:
The praxinoscope
01:03:55
In 1877, Émile Reynaud built his praxinoscope, where you see the images in the mirrors. The function of the dark space in between the slits is taken over by the angle of the mirror at which it is set up.
Two years later he succeeded in showing the moving image within a scene, which is in fact a mirror reflection.
In 1880, he managed to project his moving images.
A selection of strips:
Myriorama
01:07:04
The myriorama, the show of the ten thousands. A panaroma in stripes which brings a new image in vertical montage.
Movement-producing grids
The flip book
00:13:34
The painter Lautenberg (?) is reputed to have created the first flip book, or thumb cinema, in 1760. Leaving through the book creates the illusion of movement.
The Kinora
00:14:07
In 1898, the brothers Lumiere built the Kinora, three years after their first film shows.