User:Michel W/Self-learning: Difference between revisions
(→Tag) |
|||
| Line 156: | Line 156: | ||
} | } | ||
===<pre>tag=== | ===<pre> tag=== | ||
Text in a <pre> element is displayed in a fixed-width font, and the text preserves both spaces and line breaks. | Text in a <pre> element is displayed in a fixed-width font, and the text preserves both spaces and line breaks. | ||
Revision as of 17:28, 27 January 2024
⭑HTML⭑
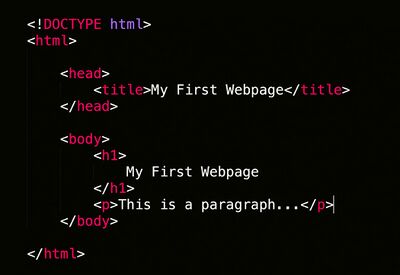
⊹A Simple HTML Document:
⊹Well chosen content of H1 element is crucial to SEO.
Entities
- Help avoid rendering issues
- Safeguard against more limited character encoding
- Provide characters not available on a keyboard
| Instead of | < | > | & |
| Use: | < ; | > ; | & ; |
Use nbsp; HTML document ALWAYS appear together on 1 line
After the 1st word and after the 2nd word (with no spaces in between words and entity references)
⊹Option + Command + I --- Google Chrome
Class
- The class attribute can be used on any HTML element.
- The HTML class attribute specifies one or more class names for an element.
- Different HTML elements can point to the same class name.
- JavaScript can access elements with a specific class name with the getElementsByClassName() method
⭑CSS⭑
⊹Syntax simple CSS selectors
- Element
- class (define with .)
- id (define with #)
⊹Combining Selectors:
- Element with class selectors (selector.class)
- Child (direct) selector (selector > selector)
- Descendant selector (selector selector)
-Didn't cover:
- Adjacent sibling selector (selector + selector)
- General sibling selector (selector ~ selector)
⊹Pseudo-Class Selector
- : link
- : visited
- : hover
- : active
- : nth-child
<link ref="stylesheet" href="style.css">
⊹Conflict Resolution
- Origin precedence: Last declaration wins
- Inheritance: DOM Tree
- Specificity: Most specific selector combination wins
(Score) 1. Style="..." 2. ID 3. Class, pseudo-class, attribute 4. # of Elements
⊹Styling Text
.style {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
color: #0000ff;
font-style: italic;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 24px;
text-transform: uppercase;
text-align: center;
}
Set Font Size With Em:
To allow users to resize the text (in the browser menu), many developers use em instead of pixels.
1em is equal to the current font size. The default text size in browsers is 16px. So, the default size of 1em is 16px.
The size can be calculated from pixels to em using this formula: pixels/16=em
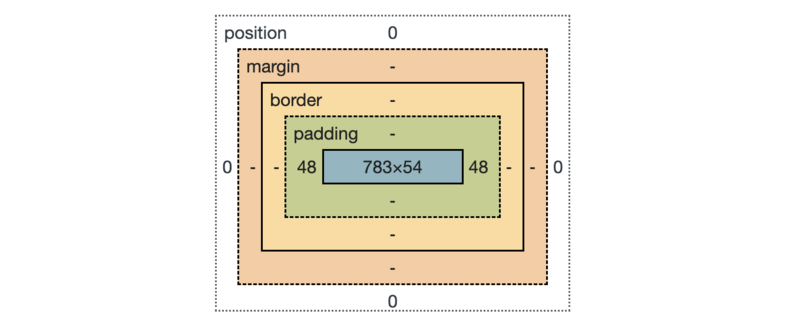
⊹The Box Model
⊹The box-sizing property allows us to include the padding and border in an element's total width and height.
If you set box-sizing: border-box; on an element, padding and border are included in the width and height
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
The * selector selects all elements.
The * selector can also select all elements inside another element.
⊹Margin Collapse:
Vertical(Top and bottom) margins that touch collapse and the larger one wins.
Horizontal margins combine together.
- Margins don't define the width of the box. Just define how far other elements should be pushed away from it.
⊹The float property is used for positioning and formatting content e.g. let an image float left to the text in a container.
float: left|right|none|inherit;
<style>
img {
float: right;
}
</style>
- Float don't have vertical margin collapse
⊹The clear property controls the flow next to floated elements.
Specifies what should happen with the element that is next to a floating element.
clear: none|left|right|both|initial|inherit;
img {
float: left;
}
p.clear {
clear: left;
}
<pre> tag
Text in a <pre> element is displayed in a fixed-width font, and the text preserves both spaces and line breaks.
⊹<pre> elements with the default values:
pre {
display: block;
font-family: monospace;
white-space: pre;
margin: 1em 0;
}
⭑JAVA SCRIPT⭑
<script src="js/script.js"></script> <script> </script>