RESEARCH 01
RESEARCH 01
Sequence 01 on my website
SELF DIRECTED RESEARCH
05.12.2018
INTRODUCTION
1 THE PROJECT, THE RESEARCH
1.1 Artistic Research (Identity, Fluidity, Fixity)
1.2 Sociological / Psychoanalytical Concerns (Zygmunt BAUMAN + Paul VERHAEGHE (identity))
2 THE INSTRUMENT
2.1 Building the tool / Instrument / Camera / Aims
2.1 Minolta SRT01- 35 mm Experiments / Results / Evolution
2.2 Focal Camera – Medium format
3 THE PROCESS
3.1 Description / Analog (why?)
3.2 History: How does it relates and differ from Slit-Photography (Marteen VANVOLSEM)
3.3 Time, Space, Movement (vs Fixity in mainstream photography)
3.3 Particular Gesture: control, selective process, randomness, figuration, abstraction, colors.
3.5 Limitations & Improvements
4 THE IMAGES
4.2 Building a specific vocabulary: group presentation, reception & interpretation
4.3 Subjects and objects of the images
5 THE BODY
5.1 From Gesture to Techniques of the body (Marcel MAUSS) Corporeal language / Education / Control / Power
5.2 The body in the photographic process: Giving body to the gaze (Daniel DESMEDT) PSY
5.3 Toward auto-performative practice: Turning the camera toward the operator (Roland BARTHES)
5.5 (Auto)Portrait, Face, Identity (Marion ZILLO)
6 CONCEPTS
6.1 Definitons & Relations: Fixity, Fluidity, Continuity, Permanence, Duration, Identity
Draft text – work in progress
03.12.2018
The self-directed research brings together various thought and disciplines. The concept of identity, fixity and fluidity are explored through photographic practices. Reconsider the practice of image making / image recording / identity recording.
1.
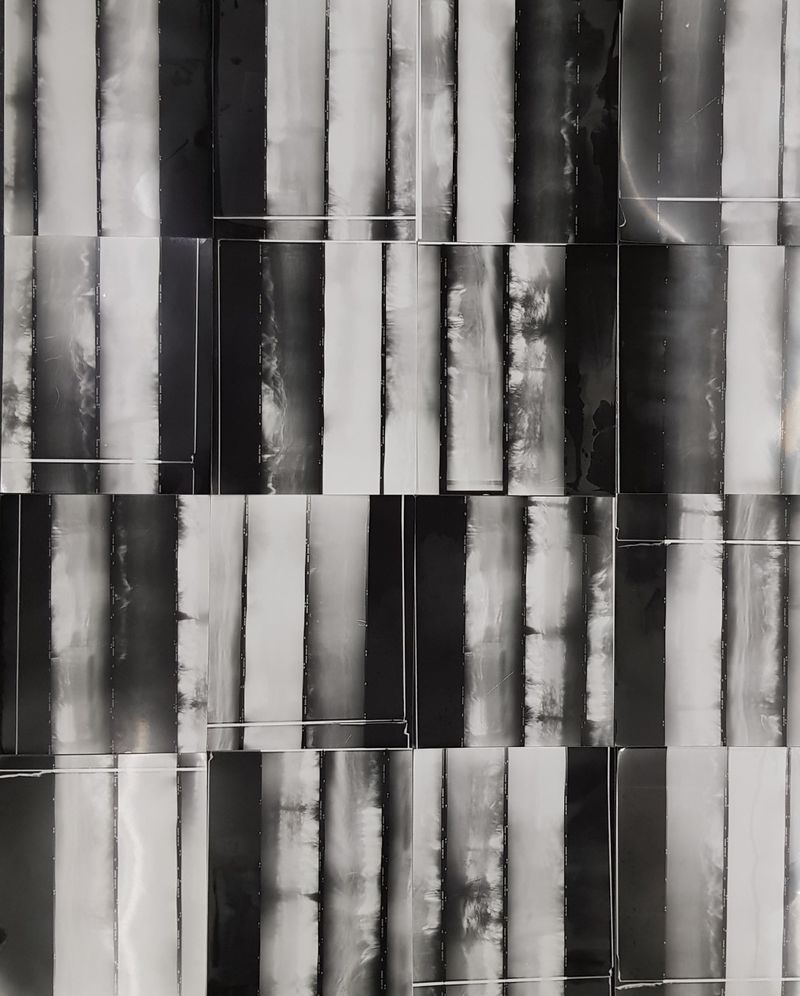
I explore image making by using the whole surface of the photographic film. To use the whole film as one photograph I am rewinding the film in front of the lens with the shutter open. In my first trials I used and old minolta srt101 because it allows me to control the rewinding and the shutter manually. As expected, there is a lot of blur. More precisely motion blur, because the rewinding gesture transform the still photography camera into a moving-image camera. I am therefore taking photographs with a moving image camera. The resulting image is a representation of the displacement of things in time and space. It is also a direct representation of the movement of my body and the gesture attached to it.
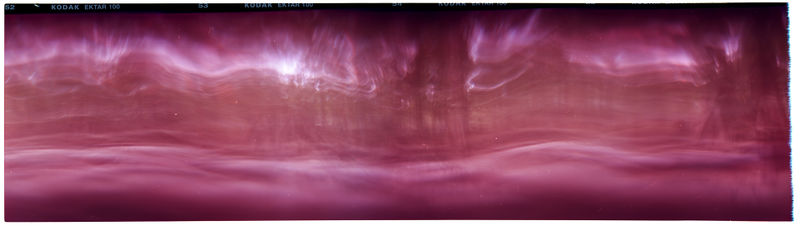
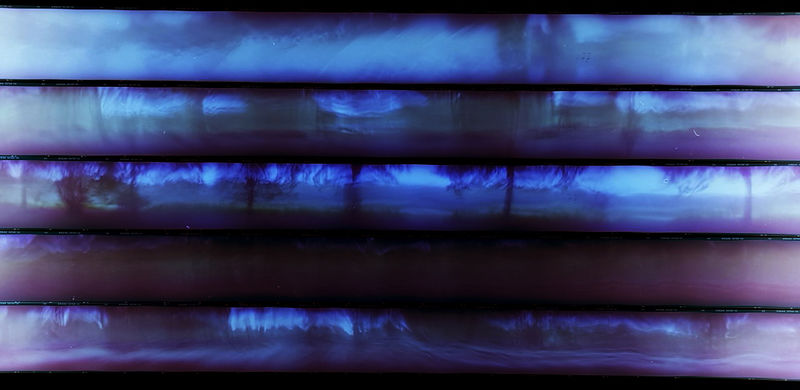
The first trials were made with black and white films but I quickly move to use color films. In a process where abstraction and motion blur can dominate, color films seem to bring a balance by allowing more details to be visible or even recognizable. One could say that the images are a combination of both abstract and figurative elements melted together by motion blur. In fact, during a group presentation where I remained silent, someone described a series of those images as a dream like melted landscape. An atmosphere both contemplative and disturbing: a moment before a storm during monsoon, a forest fire with surreal waves of smokes, a personal view of someone panicking. For some participants, the images were full of sounds, the sound of a storm, of breath and of noise. The image presented was a reversed photograph of medium format films I putted together on a lightbox table. Films are 56*720mm. The neon lighting of the box resulted in a strong blue hue and uneven lighting of the original photograph that had a strong impact on the way images were read and interpreted. Nonetheless, the vocabulary deployed to describe the images fits my underlining concept of Liquidity: Monsoon, Humididty, Storm, Rain, Gas, Fire, Waves, Breath, Noise, Dissolved movement.
2.
I built a medium format camera with a DIY lens made of three glass elements glued together. The camera doesn't have a shutter and I only add a small crank to the original design provided by Mathijs van Oosterhoudt. The crank allows me to pull the film with more control, allowing both continuity and variation in speed. In common practices of photography, the shutter controls the time of exposure and plays an important role in the selective process of the subject. The shutter regulates the light and is a means of selection and expression. Shutter speed plays an important role in the mainstream assertion of the power of photography to stop time. But happens when the camera doesn't have a shutter? The control of exposure is transferred to the movement of the film. The speed of the film passing behind the aperture determines the exposure. Without a shutter or a lens cap, the light is always going in the camera through the lens. Most of the experiments were taken within a five to ten-second exposure time. The exposure time is determined by the speed and the length of the film. At the start the aperture was roughly f4. After noticing a tendency to overexposure, I reduced the aperture to a thin strip made of transparent red plastic. I didn't use any metering for the exposure, I guessed it, playing with the speed of the rewinding, the now-reduced aperture (+-f10) and film sensibility 100-160iso.
3
Body Techniques and the photographic gesture. For anthropologist M.Mauss, [name text] each society, group and individual possess specific techniques of the body (Mauss 193* [Harvard method]). Mauss considers the body as the first and most natural object and technical means of man. Every technique has a specific form. We all learn to walk, eat and talk, but every technique is linked to a specific education, tradition and transmission. How did I learn to take pictures, hold and use a camera? Did I receive a photographic education? How do we transmit those techniques? What is the place of the body in our vision of the world? [this is a good point but outline in one sentence what is at stake here]
For Desmedt, [in... cite text] photography gives body to the gaze. Because I am not using a viewfinder I have the feeling that my process is more driven by intention and imagination. I can only imagine, with great difficulties, what the result will be. The movement of my body, both as a displacement in space and time and as a technical gesture to take the picture, is constitutive of the image. In a way, my photography is based on physiology and observation (Desmedt). “The activity of observation is, in fact, inextricably linked to our way of thinking, imagination, memory of past experiences and our ability to combine these elements” (E.Brignante [ text, page number and date here]).
For the moment I see my practice as mainly structured around two simultaneous gestures: the movement of my body in space in relation with still and moving objects and the particular technique of pulling the film in front of the lens. Both actions form what I consider to be my photographic gesture. There is a hierarchy and a reciprocity between the both. I consider the pulling of the film gesture to be the most influential. The movement of my body is influenced by the way I have to make the image, but the image is also influenced by the movement of my body.
3.1
In most case, I am holding the camera near my chest with the left hand and pull the film with the right hand. The pull the film in front of the lens I use a small crank on the top-right of the camera. The film is loaded on the left side and moves laterally. The crank is operated manually, allowing a greater variation of speeds and exposures. The pace of the film is a way to control the exposure and the subject’s representation. An object in front of the lens appear sharper when the film movement match the object’s velocity. At this point the matching of speeds is more of an intuitive guess than a mathematical calculation. Once, in a train circulating at high speed, I managed to record some trees on the film that were barely visible with my eyes. At that precise moment, the speed of the film was probably close to the speed of the train. To a certain extend this means that in this process where the photographic surface is always moving, the subject should always be in movement to allow his figurative representation. The subject’s movement in front of the lens is also determined by the position of the photographer’s body in space and time. The subject or the camera must move if one want to avoid abstraction or motion blur. This process seems to promote and encourage movement, as oppose to the fixity ruling on mainstream photography
3.2
Body, Performance, Meaning in motion Moving in the space = Multiple point of view VS renaissance uni-perspective
“The making of strip images, as mentioned before, is actually a performance. It is a performance in which the movements of the camera, the film and the artist are collaborating with the environment in the making of the photographic image” (M.Vanvolsem page number).
To develop>>
4.
The continuity of the image Photographic image, fluidity and continuity in moving-image Getting a closer representation of the fluid character of the human experience. An identity that the photographic process cannot grasp. cannot fix, always becoming, always escaping. Moving Shifting Transient
To develop>>
How the memory is working: Maurice Hallbach / Cadres sociaux de la memoire Le mecanisme de la memoire et son dereglement: deregulate the memory mechanism (any mechanism) to use it for something else, reinvention of the usage.
5
Fixity in photography and the impact on defining reality, identity as a fix and certain concept. Breaking the idea of a static use of photography and reality.
Photography and Zygmunt BAUMAN liquid modernity. Can we read the metaphor of Bauman through the photographic process (ie Random extrapolation), Liquidity in society is caused by the deregulation and the separation of power and politic. What will be the deregulation in the photographic practice? Deregulate the photographic mechanism. What is the power, what is the politic.
We can approach Bauman’s thesis by a literal transcription: making liquid photography to record and represent a liquid society. Using a liquid photographic emulsion process, can we print an image on a liquid emulsion, a stagnant emulsion at the bottom of a tank, on a canvas (J.Baldessari). Can we project the image on the wet surface and incline it, making it look like melt-down. What is different with print-tinner-non-fixed ink? Can we print on photographic jelly.
STAGNANT (of a body of water or the atmosphere of a confined space) having no current or flow and often having an unpleasant smell as a consequence. "a stagnant ditch" synonyms: still, motionless, immobile, inert, lifeless, dead, standing, slack, static, stationary; More showing no activity; dull and sluggish. "a stagnant economy" synonyms: inactive, sluggish, slow, slow-moving, lethargic, static, flat, depressed, quiet, dull, declining, moribund, dying, dead, dormant, stagnating "a stagnant economy"
A photography that isn’t fix chemically. Can we conserve and present it under a UV/RED light filtering glass?
Fixity & Certainty of the past Fluidity & Uncertainty of the future
Power Control Negotiation Intention Politic
How do we explore the transformation from fixity to movement?
The precise instant when still image become motion-picture? (Marker, C. (1962). La Jetée) How do we represent, interpret or record the fluid character of time and space?
The place of the body in our vision of the world: the photographer’s body. The photographic gesture, the photographic performance.
REFERENCES: Zygmunt BAUMAN Marteen VANVOLSEM John TAGG Paul VERHAEGHE Daniel DESMEDT Roland BARTHES Elisa BIGNANTE The use of photo-elicitation in field research.