User:Tash/grad project proposal4
Graduation Project Proposal Draft 4 – November 11th 2018
What do you want to make?
As a publisher I have always been fascinated by the culture of the internet – what habits and relationships are we creating? And how can we design online platforms with an attitude? I want to apply these questions to the context of my home country Indonesia, where social media in particular has become inseparable from youth culture. Millenials like me use it as a space to access information, perform their identities, and engage in alternative political discourse. At the same time, rising religious and political conservatism is putting pressure on freedom of speech in the country.
With this project I want to explore the way social media could be used as a critical tool to resist these trends of state and self-censorship. What can I reveal about the subtle mechanisms that play out on these platforms? How do the self-censorship habits we have offline, manifest themselves online – and how do they affect women specifically? Can I experiment with these tendencies, or build tools to break them? Ultimately my aim is to intervene in these social processes and propose new tactics to challenge them.
Examples of existing projects which inspire me:
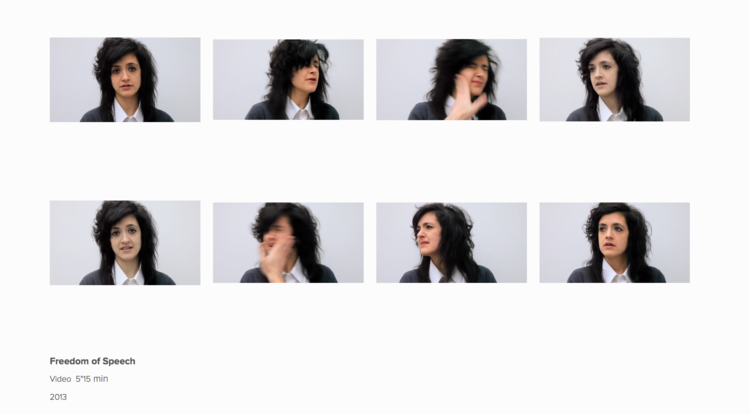
- Blind Carbon Copy by Stephanie Vilayphiou, a series of hacks which reveal mechanisms of copyright (a different but still related barrier to knowledge)
- an Anthem to Open Borders a performance on the phenomenon of social behavior on YouTube music videos which trigger emotional reactions that span from nostalgia to fierce political divisions
- Ethira a social, mobile app which allows users to post anonymous and ephemeral messages on a public forum
- Various works by Sarah Maple, which explore the convergence of her dual-Muslim heritage with feminism, and often deals with online abuse and trolling
Why do you want to make it? And relation to larger context
My motivations for this project are both personal and political. After 8 years living and working here in the Netherlands, I plan to return to Indonesia next year to set up my publishing practice there. But in the last few years, I’ve noticed a worrying trend in Indonesian public culture: while the number of media platforms seem to be growing, the scope of expression and discussion seem to be shrinking. New, stringent laws on issues like pornography, blasphemy and defamation, combined with rising religious intolerance in society, has slowly eaten away at freedom of speech in Indonesia. In fact, according to a recent index on democracy and media freedom, “Indonesia was the worst-performing country in 2017, falling by 20 places in the global rankings from 48th to 68th position.” (The Economist Intelligence Unit, 2017) Worryingly, these issues are not being talked about enough in mainstream media. As a publisher (and a non-muslim, biracial Indonesian woman myself), my instinct is to resist these mechanisms of suppression.
Not unlike many countries around the world today, Indonesia is at an interesting crossroads in its political and cultural evolution. In 1998, the authoritarian regime led by President Suharto finally collapsed, allowing the country to transition into democracy. However, in the power vacuum that followed, media freedom has become increasingly difficult to sustain. One of the most influential forces creating a backlash in Indonesian society today, is the rise of religious extremism. I see divides in society becoming politicized, and the moderate branch of Islam Indonesia was once known for, (and the one I remember growing up) is being traded in for a much more conservative, restrictive version. As a recent article by the Asian Correspondent warns, "Islamist conservatives are in many ways the local equivalent of America’s alt-right – and they are just as adept at online disruption and manipulation. Research by State Islamic University Jakarta links the rise of religious intolerance among young Muslims to their increased access to the internet and social media." (Lindsey, 2018) For a young democracy, and one which is heading towards another presidential election in 2019, these trends are worth questioning.
One of the most acute symptoms of this polarised political climate is the spread of (self)-censorship. Throughout the last ten years, the state has intensified its censorship activities, drawing up legislations which inhibit freedom of speech and religion (Heryanto, 2018). According to a 2017 report by Freedom House, under the current administration of President Joko Widodo, “religious and other minorities face ongoing harassment and intimidation, often with the tacit approval of local governments and security forces”. These processes play out both offline and online, with social media platforms like Facebook, Youtube, Twitter and Instagram becoming some of the most heated battlegrounds. Through social pressure, and fear of persecution, these mechanisms are become internalized by the people. Netizens are self-policing, and special interest groups take advantage, like the elusive Muslim Cyber Army, which appeared in its current form sometime in 2016 and has since worked to spread hate speech and fake news in the country (Juniarto, 2018). In this way, several subjects have become taboo, including the public expression of minor religions or traditions, female agency and sexuality, or even historical facts which threaten Indonesia's muslim identity.
This is where I would like to intervene. Thanks to its velocity, its polyvocal and participatory nature, social media offers valuable spaces for young Indonesians – especially young women – to experiment and engage with political issues. However, free and open discussion on these platforms need to be actively maintained – and defended. What if we could we troll the trollers, weaponize the silent majority, empower the ‘almost-speakers’? In a country which is becoming more sensitive to dissent, we need more tools and safe spaces to discuss, disagree and deconstruct what it means to be a modern Indonesian citizen.
This topic is also relevant beyond Indonesia, as politics becomes more polarised across the globe, and social media continues to be used and abused to great impact in public and political culture. In similar Islamic contexts, it has been indispensable; empowering revolutions across the Middle East during the Arab Spring. Social media has also been a powerful tool in the context of feminism, carrying the voices of women via hashtags like #MeToo and #BringBackOurGirls. Of course, just like in Indonesia, both of these examples have also produced backlashes. Today, governments have been known to take an aggressive hand in shutting down digital channels people use to organize against them (Hempel, 2016). In the case of women, incidents like Gamergate show that social media has a problem with online abuse, and "studies have consistently shown that attacks against women online are distinctly different from men’s. While both genders receive physical threats, those against women are sexually-related, meant to assert dominance, silence and intimidate." (Gutierrez, 2017). Under these pressures, I think it's important that we find a way to redress the balance.
How do you plan to make it?
I would start by conducting a close-reading of the current digital media landscape in Indonesia. Then, I will research how other groups / artists / publishers have negotiated online censorship in other countries, specifically in similar South-East Asia contexts.
During this time I want to continue last trimester’s experiments of prototyping software that encourages new ways of reading and sharing information. For example, could I write a programme which helps me analyse the indicators of self-censorship in comments sections? Something like Politwoops – using Selenium and html5lib – that scrapes Instagram comments periodically and captures those that have been subsequently deleted? What about an anonymous bot or proxy that reposts those conversations for you?
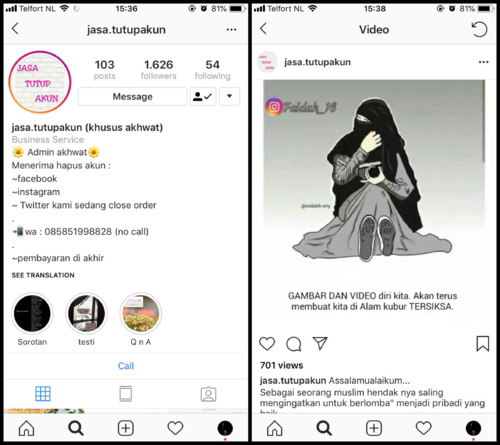
I've also recently come across social media profiles specifically aimed at Indonesian women ('akhwat' is the term used, which translates to Muslim sisterhood) which offer 'Account-closing' services. They target young women who have recently started wearing the hijab, and tell them they must erase all evidence of their previous 'sinful' lives – including their social media accounts and any old images of themselves pre-hijab. For me, this represents a kind of revisionism – a censorship on the identity and history of Indonesian women. Could I collect more of these kinds of online acts of suppression and hack their tactics?
Finally, I plan to learn more about web and mobile application frameworks like Django and Flask, so that I could prototype platforms or tools which allow for the open expression of its members.
What is your timetable?
September - October: Make an analysis of the current use of social media in Indonesia. Interview relevant figures in Indonesia. Research existing media tactics and platforms which play in the same context.
November: Prototype / make sketches of possible outcomes. Who is the end user? What is my role – editor, facilitator, gatekeeper? Develop my position while touching base with peers in Indonesia.
December - March: Develop prototypes, define scope of the project. How will I present it in the final exhibition? Sketch this out and start organising the materials I’ll need. Complete thesis.
April - June: Finish practical project, prepare final presentation.
Who can help you and how?
Clara Balaguer, for her experience running an alternative publishing platform in the Philippines. Amy Wu, for her knowledge on censorship in China and the political use of new digital media (memes, social media etc.) Artist Reinaart Vanhoe, for his connection to Indonesian collectives like Ruangrupa, Kunci Cultural Studies and Jatiwangi Art Factory. Other Indonesian platforms currently working in the intersection of media, technology and culture, such as Forum Lenteng, Lifepatch, Taman Baca Kesiman, Magdalene Indonesia and Perempuan Berpolitik (Women in Politics Indonesia).
Relation to previous practice
Similar questions explored during the Poortgebouw project:
What are the politics of representation and of erasure? The idea of the artist as an archivist (and vice versa). How to tell stories and create communities in precarious contexts?
Similar questions explored during the OuNuPo project: Technology is not a neutral practice. What cultures do we reproduce when we write programmes? Who is included / excluded in the process of knowledge production?
Similar questions explored during the XPPL / Interfacing the Law project: How do you engage with unstable information? Can we design reading / searching interfaces that are able to represent uncertainty, locate outsides, explore agonisms? How can we intervene during the process of ‘downloading’ and ‘uploading’ information? Where are the grey areas when it comes to accessing and distributing knowledge?
References
Heryanto, A. (2018). Identitas dan Kenikmatan: Politik Budaya Layar Indonesia. Jakarta: Kepustakaan Populer Gramedia.
Lindsey, Tim (2018). Is Indonesia retreating from democracy? [online]. Available at: https://asiancorrespondent.com/2018/07/is-indonesia-retreating-from-democracy/ [Accessed: 11 Nov 2018]
Gutierrez, Natashya (2017). The role of social media in women empowerment [online]. Available at: https://www.rappler.com/rappler-blogs/170047-social-media-feminism-women-empowerment/ [Accessed: 11 Nov 2018]
Hempel, Jessi (2016). Social Media Made The Arab Spring, But Couldn't Save It [online]. Available at: https://www.wired.com/2016/01/social-media-made-the-arab-spring-but-couldnt-save-it/ [Accessed: 11 Nov 2018]
Juniarto, Damar (2018). The Muslim Cyber Army: what is it and what does it want? [online]. Available at: http://indonesiaatmelbourne.unimelb.edu.au/the-muslim-cyber-army-what-is-it-and-what-does-it-want/ [Accessed: 11 Nov 2018]
Freedom House (2018) Freedom of the Press 2017: Press Freedom’s Dark Horizon [online]. Available at: https://freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-press/2017/indonesia/ [Accessed: 11 Nov 2018]