User:Simon/Affirmative Generator
Affirmative Generator
Based on the power of having P.M.A (Positive Mental Attitude), the Affirmative Generator (AF) makes affirmations to print and display in the work space. Its use is not limited to this space, but this is taken as a departure point for testing. The AF borrows from a selection of words within a limited syntax and creates new meanings in the process.
Ambiguity
Inspiration comes from ideas of syntactic ambiguity and "lexical ambiguity", which are areas of linguistic study interested in sentences that may be read in several different ways due to the ambiguity of their components meaning (lexical) and also the way they are constructed in a sentence (syntax). A fluent speaker of a language parses the components of an utterance, often adding contextually implied meanings that may be common in their vernacular.
Buffalo buffalo Buffalo buffalo buffalo buffalo Buffalo buffalo
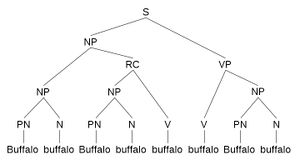
An example of lexical ambiguity is the "Buffalo buffalo Buffalo buffalo buffalo buffalo Buffalo buffalo" sentence, first appearing in 1967 in Beyond Language: Adventures in Word and Thought by Dmitri Borgmann.
This particular sentence uses the word "buffalo" as 3 discrete components:
1. A proper noun (meaning the city of Buffalo in upstate New York).
2. A verb (meaning to bully - an uncommon spoken use, but familiar to North American English speakers)
3. A common noun (meaning a kind of bison indigenous to certain parts of North America)
So the sentence can be read as:
Buffalo buffalo (Buffalo that are from the town of Buffalo)
Buffalo buffalo (that other buffalo from Buffalo) buffalo (bully)
[themselves] buffalo (bully)
Buffalo buffalo (buffalo from Buffalo)
This type of sentence (as well as many other examples) introduce the idea of syntactic ambiguity - by which a sentence may be interpreted in more than one way due to its ambiguity.