User:Wyn/Special Issue 25/VCV Rack!!: Difference between revisions
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
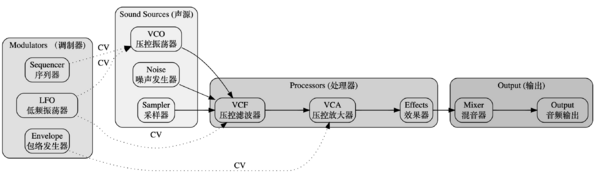
After learning VCV Rack in the course, our group members wanted to make a sound jamming, distinguishing from the previous radio show. VCV Rack is an open-source software, imitating the working process of synthesis modules. The basic modules contain VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator), VCF (Voltage Controlled Filter), VCA (Voltage Controlled Amplifier), LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator), ADSR (Attack, Decay, Sustain, Release). The special synthesis modules include Physical Modelling Synthesis, Granular synthesizer modules, FM-OP (Frequency Modulation Operators) and so on. | After learning VCV Rack in the course, our group members wanted to make a sound jamming, distinguishing from the previous radio show. VCV Rack is an open-source software, imitating the working process of synthesis modules. The basic modules contain VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator), VCF (Voltage Controlled Filter), VCA (Voltage Controlled Amplifier), LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator), ADSR (Attack, Decay, Sustain, Release). The special synthesis modules include Physical Modelling Synthesis, Granular synthesizer modules, FM-OP (Frequency Modulation Operators) and so on. | ||
[[File:Working_process.png| | [[File:Working_process.png|600px|How the synthesis makes sound]] | ||
Revision as of 18:29, 3 November 2024
Introduction
After learning VCV Rack in the course, our group members wanted to make a sound jamming, distinguishing from the previous radio show. VCV Rack is an open-source software, imitating the working process of synthesis modules. The basic modules contain VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator), VCF (Voltage Controlled Filter), VCA (Voltage Controlled Amplifier), LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator), ADSR (Attack, Decay, Sustain, Release). The special synthesis modules include Physical Modelling Synthesis, Granular synthesizer modules, FM-OP (Frequency Modulation Operators) and so on.
We all agreed to combine typing sounds (made by VCV modules) with text reading, and each member was assigned their role in the thesis. This approach made the radio show improvisational.
Practice
My practice learning path involved referencing others' VCV modulation methods, as I wanted to try creating more realistic/spatial/hybrid sounds and experiment with electronic sound synthesis (strings, wind instruments, and percussion synthesis). Also, the sound is a decline process while while setting up more modules, and I needed to reduce the elements to set up the right sound.
Karplus-Strong String Synthesis Patch
Core Module Components
Sound Source and Processing: Noise Source Module ADSR EG (Envelope Generator) Delay Module VCA (Voltage Controlled Amplifier)
Control System:
Large Matrix Switch
Multiple ADSR Modules
Clock/Trigger Sources
Working Principle 1. Sound Generation Path: Noise Source -> ADSR -> Delay -> VCA -> Output
2. Modulation Path: Clock -> Matrix -> Multiple Triggers ADSR -> VCA Modulation Delay Feedback -> Input Sound Formation Process
Basic Sound Generation:
Noise source generates initial excitation signal
Delay module creates echo effect, simulating string vibration
Envelope controls sound dynamics
Modulation Control:
Matrix controller manages trigger timing
Multiple ADSRs generate complex modulation signals
Delay feedback forms sustained string tones
Function Generator Breathing Modulation Patch
Core Module Components
Signal Processing Chain:
VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator)
VCF (Voltage Controlled Filter)
VCA (Voltage Controlled Amplifier)
ADSR EG (Envelope Generator)
Modulation System:
Function Generator/Rampage LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator) Multiple Attenuators
Working Principle Main Signal Path: VCO -> VCF -> VCA -> Output
2. Modulation Path: Function Generator -> Multiple Destinations LFO -> Filter Cutoff ADSR -> Amplitude Control Sound Formation Process
Basic Timbre Generation:
VCO produces fundamental waveform
VCF shapes timbral characteristics
VCA controls volume dynamics
Breathing Modulation:
Function Generator creates slowly evolving modulation signals
LFO adds periodic variations
Multiple modulation destinations create complex dynamics
Key Parameter Settings Karplus-Strong Settings
Delay Parameters:
Time: 0.1-10ms (affects pitch)
Feedback: 60-90% (affects sustain)
Mix: 50-100% (wet/dry ratio)
Envelope Settings:
Attack: 5-10ms
Decay: 100-500ms
Sustain: 50-70%
Release: 200-1000ms
Function Generator Settings
Primary Parameters:
Rise Time: 500-2000ms
Fall Time: 1000-3000ms
Curve Shape: Exponential
Modulation Depths:
Filter Cutoff: 30-50%
Amplitude: 20-40%
Rate Modulation: 10-30%
Live
Technical Experiments:
Successful Elements:
Karplus-Strong synthesis implementation Function generator modulation Keyboard control integration
Challenges Faced:
Filter ping-pong collision attempts Cable routing complexity Volume control issues
Sound Characteristics:
Achieved Effects:
Electronic timbre Rhythmic elements Spatial depth
Technical Limitations:
Unpredictable amplification Connection stability issues
Radio Application:
Interactive Elements:
Background typing sounds Audience comment integration Real-time text response
Performance Aspects:
Role-play enhancement Chat board interaction Live sound modulation
Reflection
Inspired by the role play, it could be an expressive way of quoting others' speech. The project demonstrated the potential of modular synthesis in interactive radio; The importance of balancing technical precision with creative expression; The value of host/audience engagement through sound design.