User:Zalán Szakács/grad prototyping: Difference between revisions
| Line 2,004: | Line 2,004: | ||
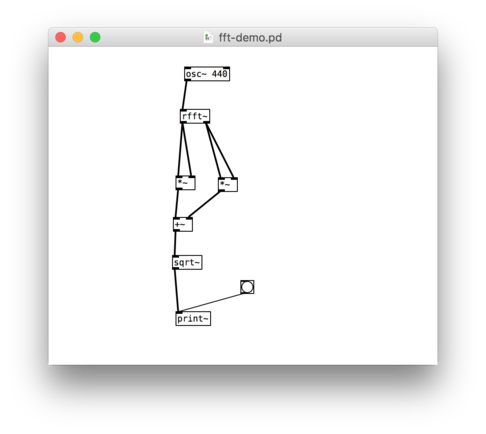
'''Fourier transformation'''<br> | '''Fourier transformation'''<br> | ||
It divides the entire frequency spectrum into parts of equal size and determines the amplitude and phase for each part. One could in turn reconstruct the original signal from these values. The derivation of the component parts is called analysis; the reconstruction is called resynthesis. You can realize this using the objects "rfft~" and "irfft~". | It divides the entire frequency spectrum into parts of equal size and determines the amplitude and phase for each part. One could in turn reconstruct the original signal from these values. The derivation of the component parts is called analysis; the reconstruction is called resynthesis. You can realize this using the objects "rfft~" and "irfft~". | ||
<gallery class="center" widths=562px heights=434px> | |||
File:Screen Shot 2019-01-20 at 22.27.36.png|Analyis | |||
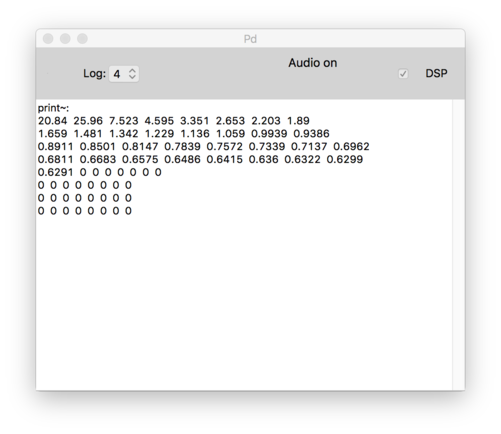
File:Screen Shot 2019-01-20 at 22.42.11.png|Output | |||
</gallery> | |||
Output = Shows the power of different frequency components that make up that sound. Each of the number represents an amplitude of a particular band of frequencies. | |||
Revision as of 22:43, 20 January 2019
P R O T O T Y P I N G
What is a Circuit?
What are Resistors?
conversion calculator resistor color code
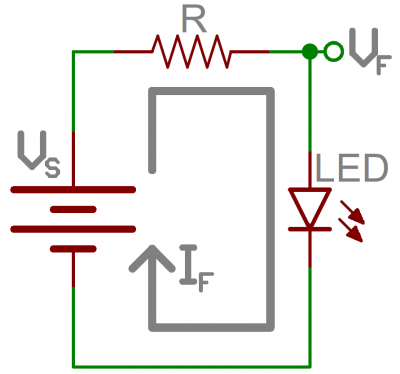
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
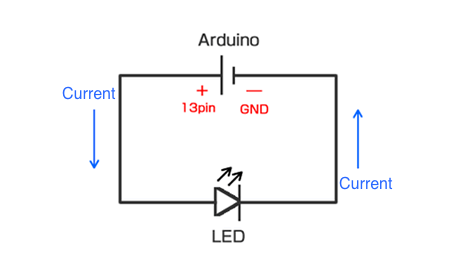
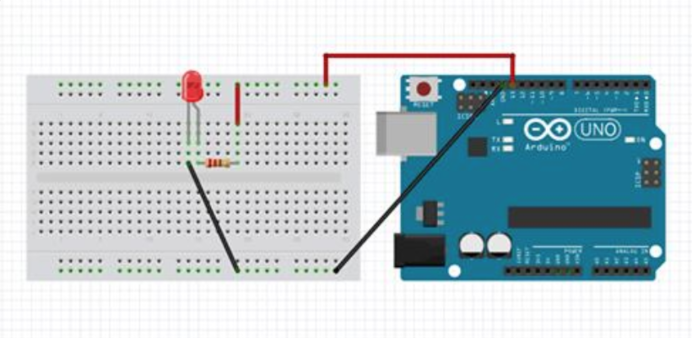
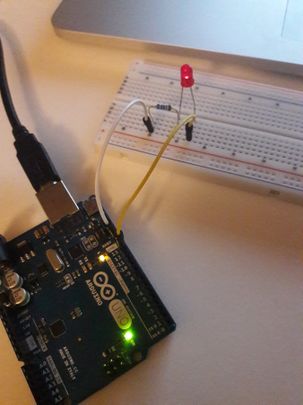
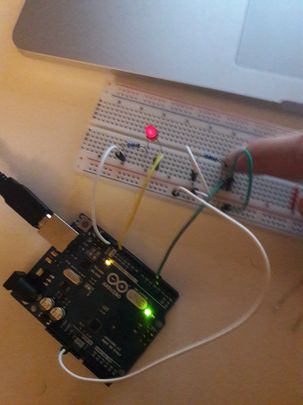
How to use Arduino?
1. Arduino Script
*
* Zalan's first Program
*/
int ledPin = 13;
void setup()
{
//initialize pins as outputs
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
delay(1000);
}
2. Arduino Script
int LED = 12;
int BUTTON = 4;
void setup()
{
pinMode(LED,OUTPUT);
pinMode(BUTTON,INPUT);
}
void loop()
{
if(digitalRead(BUTTON) == HIGH)
{
digitalWrite(LED,HIGH);
}else
{
digitalWrite(LED,LOW);
}
}
3. Arduino Script
int switchPin = 8;
int ledPin = 13;
boolean lastButton = LOW;
boolean currentButton = LOW;
boolean ledOn = false;
void setup()
{
pinMode(switchPin, INPUT);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
boolean debounce(boolean last)
{
boolean current = digitalRead(switchPin);
if (last != current)
{
delay(5);
current = digitalRead(switchPin);
}
return current;
}
void loop()
{
currentButton = debounce(lastButton);
if (lastButton == LOW && currentButton == HIGH)
{
ledOn -= !ledOn;
}
lastButton = currentButton;
digitalWrite(ledPin, ledOn);
}
4. Arduino Script
// NeoPixel Ring simple sketch (c) 2013 Shae Erisson
// released under the GPLv3 license to match the rest of the AdaFruit NeoPixel library
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#ifdef __AVR__
#include <avr/power.h>
#endif
// Which pin on the Arduino is connected to the NeoPixels?
// On a Trinket or Gemma we suggest changing this to 1
#define PIN 6
// How many NeoPixels are attached to the Arduino?
#define NUMPIXELS 16
// When we setup the NeoPixel library, we tell it how many pixels, and which pin to use to send signals.
// Note that for older NeoPixel strips you might need to change the third parameter--see the strandtest
// example for more information on possible values.
Adafruit_NeoPixel pixels = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
int delayval = 500; // delay for half a second
void setup() {
// This is for Trinket 5V 16MHz, you can remove these three lines if you are not using a Trinket
#if defined (__AVR_ATtiny85__)
if (F_CPU == 16000000) clock_prescale_set(clock_div_1);
#endif
// End of trinket special code
pixels.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library.
}
void loop() {
// For a set of NeoPixels the first NeoPixel is 0, second is 1, all the way up to the count of pixels minus one.
for(int i=0;i<NUMPIXELS;i++){
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(0,150,0)); // Moderately bright green color.
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
delay(delayval); // Delay for a period of time (in milliseconds).
}
}
5. Arduino Script
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#ifdef __AVR__
#include <avr/power.h>
#endif
#define PIN 10
#define NUM_LEDS 60
#define BRIGHTNESS 50
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS, PIN, NEO_GRBW + NEO_KHZ800);
byte neopix_gamma[] = {
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5,
5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 9, 10,
10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 13, 13, 13, 14, 14, 15, 15, 16, 16,
17, 17, 18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 20, 21, 21, 22, 22, 23, 24, 24, 25,
25, 26, 27, 27, 28, 29, 29, 30, 31, 32, 32, 33, 34, 35, 35, 36,
37, 38, 39, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 50,
51, 52, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 66, 67, 68,
69, 70, 72, 73, 74, 75, 77, 78, 79, 81, 82, 83, 85, 86, 87, 89,
90, 92, 93, 95, 96, 98, 99,101,102,104,105,107,109,110,112,114,
115,117,119,120,122,124,126,127,129,131,133,135,137,138,140,142,
144,146,148,150,152,154,156,158,160,162,164,167,169,171,173,175,
177,180,182,184,186,189,191,193,196,198,200,203,205,208,210,213,
215,218,220,223,225,228,231,233,236,239,241,244,247,249,252,255 };
void setup() {
// This is for Trinket 5V 16MHz, you can remove these three lines if you are not using a Trinket
#if defined (__AVR_ATtiny85__)
if (F_CPU == 16000000) clock_prescale_set(clock_div_1);
#endif
// End of trinket special code
strip.setBrightness(BRIGHTNESS);
strip.begin();
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
}
void loop() {
// Some example procedures showing how to display to the pixels:
colorWipe(strip.Color(255, 0, 0), 50); // Red
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 255, 0), 50); // Green
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 0, 255), 50); // Blue
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 0, 0, 255), 50); // White
whiteOverRainbow(20,75,5);
pulseWhite(5);
// fullWhite();
// delay(2000);
rainbowFade2White(3,3,1);
}
// Fill the dots one after the other with a color
void colorWipe(uint32_t c, uint8_t wait) {
for(uint16_t i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, c);
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
void pulseWhite(uint8_t wait) {
for(int j = 0; j < 256 ; j++){
for(uint16_t i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, strip.Color(0,0,0, neopix_gamma[j] ) );
}
delay(wait);
strip.show();
}
for(int j = 255; j >= 0 ; j--){
for(uint16_t i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, strip.Color(0,0,0, neopix_gamma[j] ) );
}
delay(wait);
strip.show();
}
}
void rainbowFade2White(uint8_t wait, int rainbowLoops, int whiteLoops) {
float fadeMax = 100.0;
int fadeVal = 0;
uint32_t wheelVal;
int redVal, greenVal, blueVal;
for(int k = 0 ; k < rainbowLoops ; k ++){
for(int j=0; j<256; j++) { // 5 cycles of all colors on wheel
for(int i=0; i< strip.numPixels(); i++) {
wheelVal = Wheel(((i * 256 / strip.numPixels()) + j) & 255);
redVal = red(wheelVal) * float(fadeVal/fadeMax);
greenVal = green(wheelVal) * float(fadeVal/fadeMax);
blueVal = blue(wheelVal) * float(fadeVal/fadeMax);
strip.setPixelColor( i, strip.Color( redVal, greenVal, blueVal ) );
}
//First loop, fade in!
if(k == 0 && fadeVal < fadeMax-1) {
fadeVal++;
}
//Last loop, fade out!
else if(k == rainbowLoops - 1 && j > 255 - fadeMax ){
fadeVal--;
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
delay(500);
for(int k = 0 ; k < whiteLoops ; k ++){
for(int j = 0; j < 256 ; j++){
for(uint16_t i=0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, strip.Color(0,0,0, neopix_gamma[j] ) );
}
strip.show();
}
delay(2000);
for(int j = 255; j >= 0 ; j--){
for(uint16_t i=0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, strip.Color(0,0,0, neopix_gamma[j] ) );
}
strip.show();
}
}
delay(500);
}
void whiteOverRainbow(uint8_t wait, uint8_t whiteSpeed, uint8_t whiteLength ) {
if(whiteLength >= strip.numPixels()) whiteLength = strip.numPixels() - 1;
int head = whiteLength - 1;
int tail = 0;
int loops = 3;
int loopNum = 0;
static unsigned long lastTime = 0;
while(true){
for(int j=0; j<256; j++) {
for(uint16_t i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) {
if((i >= tail && i <= head) || (tail > head && i >= tail) || (tail > head && i <= head) ){
strip.setPixelColor(i, strip.Color(0,0,0, 255 ) );
}
else{
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel(((i * 256 / strip.numPixels()) + j) & 255));
}
}
if(millis() - lastTime > whiteSpeed) {
head++;
tail++;
if(head == strip.numPixels()){
loopNum++;
}
lastTime = millis();
}
if(loopNum == loops) return;
head%=strip.numPixels();
tail%=strip.numPixels();
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
}
void fullWhite() {
for(uint16_t i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, strip.Color(0,0,0, 255 ) );
}
strip.show();
}
// Slightly different, this makes the rainbow equally distributed throughout
void rainbowCycle(uint8_t wait) {
uint16_t i, j;
for(j=0; j<256 * 5; j++) { // 5 cycles of all colors on wheel
for(i=0; i< strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel(((i * 256 / strip.numPixels()) + j) & 255));
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
void rainbow(uint8_t wait) {
uint16_t i, j;
for(j=0; j<256; j++) {
for(i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel((i+j) & 255));
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
// Input a value 0 to 255 to get a color value.
// The colours are a transition r - g - b - back to r.
uint32_t Wheel(byte WheelPos) {
WheelPos = 255 - WheelPos;
if(WheelPos < 85) {
return strip.Color(255 - WheelPos * 3, 0, WheelPos * 3,0);
}
if(WheelPos < 170) {
WheelPos -= 85;
return strip.Color(0, WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3,0);
}
WheelPos -= 170;
return strip.Color(WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3, 0,0);
}
uint8_t red(uint32_t c) {
return (c >> 16);
}
uint8_t green(uint32_t c) {
return (c >> 8);
}
uint8_t blue(uint32_t c) {
return (c);
}
Quick prototyping with Joca
Experiment question
How to make a stronger and more equal light beam of an LED light?'
Tools: Phone, aluminium foil, plexisheet 1 x 1 x 16 cm
Building new circuit together with Joca
19 | 10 | 18
Experimenting with light beam setup
23 | 10 | 18
components: 1 beamer, 1 smokemachine, 1 vault (dark room)
focus: How to divide the space with basic geometrical elements?
Adafruit NeoPixel Arduino experiment
05 | 11 | 18
Fade In and Fade Out: Red, Green and Blue
Facts:
- 1 m Adafruit NeoPixel
- 30 LEDs
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 8
#define NUM_LEDS 30
// Parameter 1 = number of pixels in strip
// Parameter 2 = pin number (most are valid)
// Parameter 3 = pixel type flags, add together as needed:
// NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs)
// NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers)
// NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products)
// NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2)
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
strip.begin();
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
}
void loop() {
RGBLoop();
}
void RGBLoop(){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++ ) {
// Fade IN
for(int k = 0; k < 256; k++) {
switch(j) {
case 0: setAll(k,0,0); break;
case 1: setAll(0,k,0); break;
case 2: setAll(0,0,k); break;
}
showStrip();
delay(3);
}
// Fade OUT
for(int k = 255; k >= 0; k--) {
switch(j) {
case 0: setAll(k,0,0); break;
case 1: setAll(0,k,0); break;
case 2: setAll(0,0,k); break;
}
showStrip();
delay(3);
}
}
}
void showStrip() {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
strip.show();
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
FastLED.show();
#endif
}
void setPixel(int Pixel, byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
strip.setPixelColor(Pixel, strip.Color(red, green, blue));
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
leds[Pixel].r = red;
leds[Pixel].g = green;
leds[Pixel].b = blue;
#endif
}
void setAll(byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
setPixel(i, red, green, blue);
}
showStrip();
}
Fade In and Fade Out: Custom colour
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 8
#define NUM_LEDS 30
// Parameter 1 = number of pixels in strip
// Parameter 2 = pin number (most are valid)
// Parameter 3 = pixel type flags, add together as needed:
// NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs)
// NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers)
// NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products)
// NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2)
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
strip.begin();
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
}
void loop() {
FadeInOut(0xff, 0x77, 0x00);
}
void FadeInOut(byte red, byte green, byte blue){
float r, g, b;
for(int k = 0; k < 256; k=k+1) {
r = (k/256.0)*red;
g = (k/256.0)*green;
b = (k/256.0)*blue;
setAll(r,g,b);
showStrip();
}
for(int k = 255; k >= 0; k=k-2) {
r = (k/256.0)*red;
g = (k/256.0)*green;
b = (k/256.0)*blue;
setAll(r,g,b);
showStrip();
}
}
void showStrip() {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
strip.show();
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
FastLED.show();
#endif
}
void setPixel(int Pixel, byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
strip.setPixelColor(Pixel, strip.Color(red, green, blue));
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
leds[Pixel].r = red;
leds[Pixel].g = green;
leds[Pixel].b = blue;
#endif
}
void setAll(byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
setPixel(i, red, green, blue);
}
showStrip();
}
Strobe
The function takes 6 parameters.
The first 3 are the same red, green and blue. In the example I used White.
The next parameter (StrobeCount) indicates how many flashes you’d like to see.
Parameters 5 (FlashDelay) and 6 (EndPause) are for delays between each individual flash and how long the function should wait once it completed all flashes.
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 8
#define NUM_LEDS 30
// Parameter 1 = number of pixels in strip
// Parameter 2 = pin number (most are valid)
// Parameter 3 = pixel type flags, add together as needed:
// NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs)
// NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers)
// NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products)
// NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2)
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
strip.begin();
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
}
void loop() {
// Slower:
// Strobe(0xff, 0x77, 0x00, 10, 100, 1000);
// Fast:
Strobe(0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 10, 30, 1000);
}
void Strobe(byte red, byte green, byte blue, int StrobeCount, int FlashDelay, int EndPause){
for(int j = 0; j < StrobeCount; j++) {
setAll(red,green,blue);
showStrip();
delay(FlashDelay);
setAll(0,0,0);
showStrip();
delay(FlashDelay);
}
delay(EndPause);
}
void showStrip() {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
strip.show();
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
FastLED.show();
#endif
}
void setPixel(int Pixel, byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
strip.setPixelColor(Pixel, strip.Color(red, green, blue));
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
leds[Pixel].r = red;
leds[Pixel].g = green;
leds[Pixel].b = blue;
#endif
}
void setAll(byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
setPixel(i, red, green, blue);
}
showStrip();
}
Cylon
The Cylon() function takes 6 parameters, where the first 3 are you preferred color. The 4th parameter (EyeSize) determines how many LEDs run around, or: the width of the “eye” (outer 2, faded, LEDs not counted).
The 5th parameter (SpeedDelay) influences how fast the eye moves, higher values means slow movement. The last parameter (ReturnDelay) sets how much time it should wait to bounce back.
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 8
#define NUM_LEDS 30
// Parameter 1 = number of pixels in strip
// Parameter 2 = pin number (most are valid)
// Parameter 3 = pixel type flags, add together as needed:
// NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs)
// NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers)
// NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products)
// NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2)
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
strip.begin();
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
}
void loop() {
CylonBounce(0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 4, 10, 50);
}
void CylonBounce(byte red, byte green, byte blue, int EyeSize, int SpeedDelay, int ReturnDelay){
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS-EyeSize-2; i++) {
setAll(0,0,0);
setPixel(i, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
for(int j = 1; j <= EyeSize; j++) {
setPixel(i+j, red, green, blue);
}
setPixel(i+EyeSize+1, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
showStrip();
delay(SpeedDelay);
}
delay(ReturnDelay);
for(int i = NUM_LEDS-EyeSize-2; i > 0; i--) {
setAll(0,0,0);
setPixel(i, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
for(int j = 1; j <= EyeSize; j++) {
setPixel(i+j, red, green, blue);
}
setPixel(i+EyeSize+1, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
showStrip();
delay(SpeedDelay);
}
delay(ReturnDelay);
}
void showStrip() {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
strip.show();
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
FastLED.show();
#endif
}
void setPixel(int Pixel, byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
strip.setPixelColor(Pixel, strip.Color(red, green, blue));
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
leds[Pixel].r = red;
leds[Pixel].g = green;
leds[Pixel].b = blue;
#endif
}
void setAll(byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
setPixel(i, red, green, blue);
}
showStrip();
}
KITT
Instead of bouncing back and forth it now follows this pattern:
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 8
#define NUM_LEDS 30
// Parameter 1 = number of pixels in strip
// Parameter 2 = pin number (most are valid)
// Parameter 3 = pixel type flags, add together as needed:
// NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs)
// NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers)
// NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products)
// NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2)
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
strip.begin();
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
}
void loop() {
NewKITT(0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 8, 10, 50);
}
void NewKITT(byte red, byte green, byte blue, int EyeSize, int SpeedDelay, int ReturnDelay){
RightToLeft(red, green, blue, EyeSize, SpeedDelay, ReturnDelay);
LeftToRight(red, green, blue, EyeSize, SpeedDelay, ReturnDelay);
OutsideToCenter(red, green, blue, EyeSize, SpeedDelay, ReturnDelay);
CenterToOutside(red, green, blue, EyeSize, SpeedDelay, ReturnDelay);
LeftToRight(red, green, blue, EyeSize, SpeedDelay, ReturnDelay);
RightToLeft(red, green, blue, EyeSize, SpeedDelay, ReturnDelay);
OutsideToCenter(red, green, blue, EyeSize, SpeedDelay, ReturnDelay);
CenterToOutside(red, green, blue, EyeSize, SpeedDelay, ReturnDelay);
}
void CenterToOutside(byte red, byte green, byte blue, int EyeSize, int SpeedDelay, int ReturnDelay) {
for(int i =((NUM_LEDS-EyeSize)/2); i>=0; i--) {
setAll(0,0,0);
setPixel(i, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
for(int j = 1; j <= EyeSize; j++) {
setPixel(i+j, red, green, blue);
}
setPixel(i+EyeSize+1, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
setPixel(NUM_LEDS-i, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
for(int j = 1; j <= EyeSize; j++) {
setPixel(NUM_LEDS-i-j, red, green, blue);
}
setPixel(NUM_LEDS-i-EyeSize-1, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
showStrip();
delay(SpeedDelay);
}
delay(ReturnDelay);
}
void OutsideToCenter(byte red, byte green, byte blue, int EyeSize, int SpeedDelay, int ReturnDelay) {
for(int i = 0; i<=((NUM_LEDS-EyeSize)/2); i++) {
setAll(0,0,0);
setPixel(i, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
for(int j = 1; j <= EyeSize; j++) {
setPixel(i+j, red, green, blue);
}
setPixel(i+EyeSize+1, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
setPixel(NUM_LEDS-i, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
for(int j = 1; j <= EyeSize; j++) {
setPixel(NUM_LEDS-i-j, red, green, blue);
}
setPixel(NUM_LEDS-i-EyeSize-1, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
showStrip();
delay(SpeedDelay);
}
delay(ReturnDelay);
}
void LeftToRight(byte red, byte green, byte blue, int EyeSize, int SpeedDelay, int ReturnDelay) {
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS-EyeSize-2; i++) {
setAll(0,0,0);
setPixel(i, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
for(int j = 1; j <= EyeSize; j++) {
setPixel(i+j, red, green, blue);
}
setPixel(i+EyeSize+1, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
showStrip();
delay(SpeedDelay);
}
delay(ReturnDelay);
}
void RightToLeft(byte red, byte green, byte blue, int EyeSize, int SpeedDelay, int ReturnDelay) {
for(int i = NUM_LEDS-EyeSize-2; i > 0; i--) {
setAll(0,0,0);
setPixel(i, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
for(int j = 1; j <= EyeSize; j++) {
setPixel(i+j, red, green, blue);
}
setPixel(i+EyeSize+1, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
showStrip();
delay(SpeedDelay);
}
delay(ReturnDelay);
}
void showStrip() {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
strip.show();
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
FastLED.show();
#endif
}
void setPixel(int Pixel, byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
strip.setPixelColor(Pixel, strip.Color(red, green, blue));
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
leds[Pixel].r = red;
leds[Pixel].g = green;
leds[Pixel].b = blue;
#endif
}
void setAll(byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
setPixel(i, red, green, blue);
}
showStrip();
}
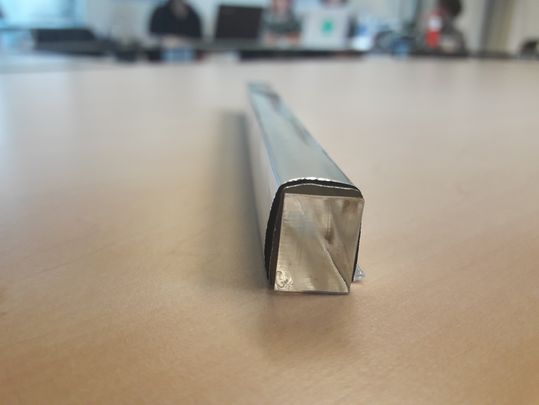
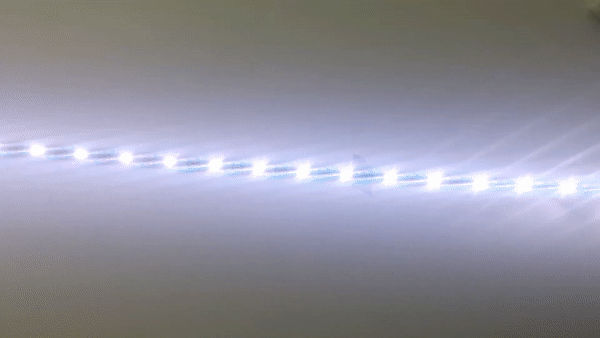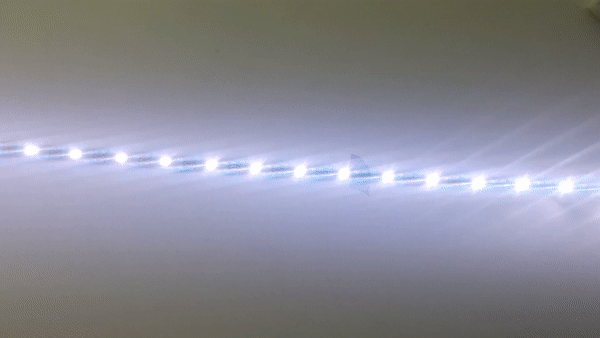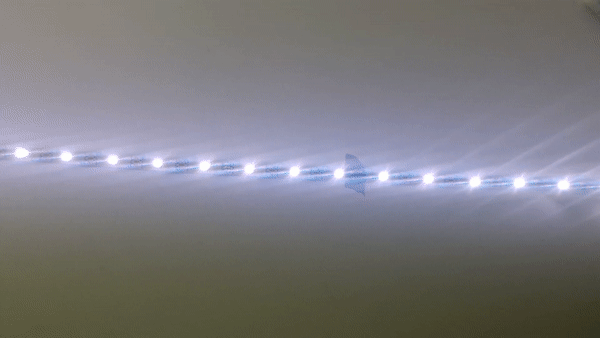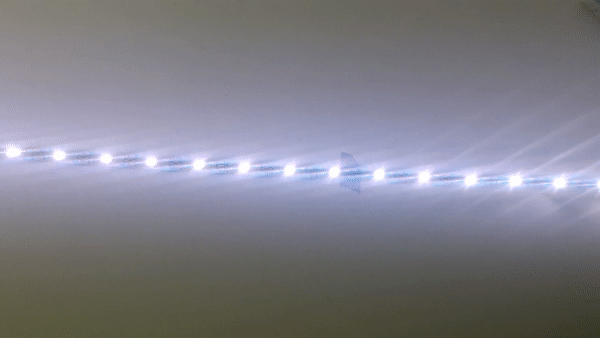
KITT script with a plexiglass
For this experiment I placed an plexisheet on the LED strip to be able to create a stronger light beam
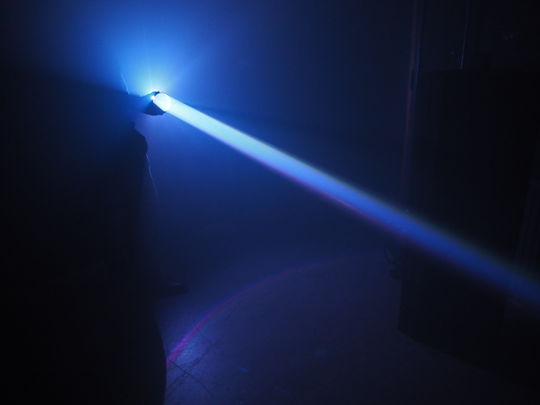
Experiments with Collimators & LEDs
09 | 11 | 18
Plano Convex Lens
Facts:
- 2x small Plano Convex Lenses
- 2x big Plano Convex Lenses
- ADAFRUIT NEOPIXEL 1m (30 LEDs) - 4 used
I was interested, how the different plano convex lenses would create different light beams.
Conclusion
The distance between the LED and the lens is very important. By varying the distance you can control the light beam and measure it to be able to calculate in the formula.
Experiments with the distance between the collimators & LEDs
10 | 11 | 18
Plano Convex Lens
Facts:
- 1x small Plano Convex Lenses
- 1x big Plano Convex Lenses
- ADAFRUIT NEOPIXEL 1m (30 LEDs) - 1 used
- custom build black cardboard box
I was interested, how the different plano convex lenses would create different light beams in different distances to LEDs. Therefor I needed to build a custom box (1mx10cmx10cm) to be able to catch the light beam. The plano convex lenses were attached to a cardboard surface (10cm x 10 cm) and they were free to move in different distance inside of the box.
Conclusion
Having only around 1 cm distance between the plano convex lens and the LED – the light beam is strongest.
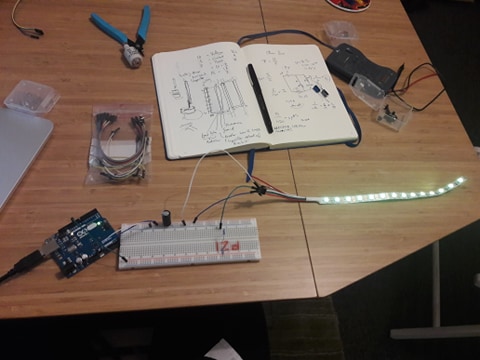
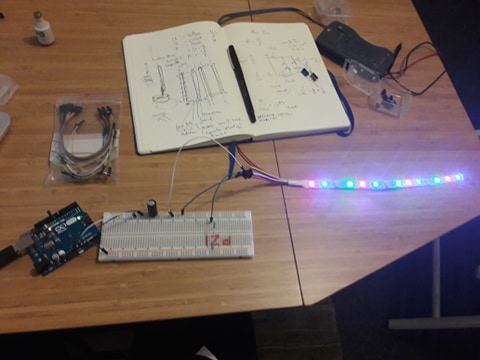
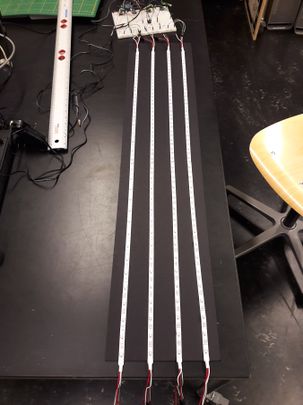
Building a circuit for 4 Adafruit Neopixel LED strips with Joca
13 | 11 | 18
4 Adafruit Neopixel LED strips
To be able to build an infrastructure of controlling 4 Adafruit Neopixel LED strips we needed to extend the breadboards and do some new wiring.
// NeoPixel Ring simple sketch (c) 2013 Shae Erisson
// released under the GPLv3 license to match the rest of the AdaFruit NeoPixel library
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#ifdef __AVR__
#include <avr/power.h>
#endif
// Which pin on the Arduino is connected to the NeoPixels?
// On a Trinket or Gemma we suggest changing this to 1
#define PIN_A 5
#define NUMPIXELS_A 30
#define PIN_B 6
#define NUMPIXELS_B 30
#define PIN_C 9
#define NUMPIXELS_C 30
#define PIN_D 10
#define NUMPIXELS_D 30
// When we setup the NeoPixel library, we tell it how many pixels, and which pin to use to send signals.
// Note that for older NeoPixel strips you might need to change the third parameter--see the strandtest
// example for more information on possible values.
Adafruit_NeoPixel A = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS_A, PIN_A, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
Adafruit_NeoPixel B = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS_B, PIN_B, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
Adafruit_NeoPixel C = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS_C, PIN_C, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
Adafruit_NeoPixel D = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS_D, PIN_D, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
int delayval = 500; // delay for half a second
void setup() {
// This is for Trinket 5V 16MHz, you can remove these three lines if you are not using a Trinket
#if defined (__AVR_ATtiny85__)
if (F_CPU == 16000000) clock_prescale_set(clock_div_1);
#endif
// End of trinket special code
A.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library.
B.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library.
C.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library.
D.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library.
}
void loop() {
// For a set of NeoPixels the first NeoPixel is 0, second is 1, all the way up to the count of pixels minus one.
for(int i=0;i<NUMPIXELS_A;i++){
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
A.setPixelColor(i, A.Color(0,255,255)); // Moderately bright green color.
A.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
B.setPixelColor(i, B.Color(0,255,255)); // Moderately bright green color.
B.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
C.setPixelColor(i, C.Color(0,255,255)); // Moderately bright green color.
C.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
D.setPixelColor(i, D.Color(0,255,255)); // Moderately bright green color.
D.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
delay(delayval); // Delay for a period of time (in milliseconds).
}
}
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 8
#define NUM_LEDS 30
#define PIN_A 5
#define NUM_LEDS_A 30
#define PIN_B 6
#define NUM_LEDS_B 30
#define PIN_C 9
#define NUM_LEDS_C 30
#define PIN_D 10
#define NUM_LEDS_D 30
// Parameter 1 = number of pixels in strip
// Parameter 2 = pin number (most are valid)
// Parameter 3 = pixel type flags, add together as needed:
// NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs)
// NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers)
// NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products)
// NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2)
Adafruit_NeoPixel A = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS_A, PIN_A, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
Adafruit_NeoPixel B = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS_B, PIN_B, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
Adafruit_NeoPixel C = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS_C, PIN_C, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
Adafruit_NeoPixel D = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS_D, PIN_D, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
A.begin();
A.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
//B.begin();
//B.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
//C.begin();
//C.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
D.begin();
D.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off
}
void loop() {
CylonBounce(0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 4, 150, 50);
}
void CylonBounce(byte red, byte green, byte blue, int EyeSize, int SpeedDelay, int ReturnDelay){
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS-EyeSize-2; i++) {
setAll(0,0,0);
setPixel(i, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
for(int j = 1; j <= EyeSize; j++) {
setPixel(i+j, red, green, blue);
}
setPixel(i+EyeSize+1, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
showStrip();
delay(SpeedDelay);
}
delay(ReturnDelay);
for(int i = NUM_LEDS-EyeSize-2; i > 0; i--) {
setAll(0,0,0);
setPixel(i, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
for(int j = 1; j <= EyeSize; j++) {
setPixel(i+j, red, green, blue);
}
setPixel(i+EyeSize+1, red/10, green/10, blue/10);
showStrip();
delay(SpeedDelay);
}
delay(ReturnDelay);
}
void showStrip() {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
A.show();
B.show();
C.show();
D.show();
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
FastLED.show();
#endif
}
void setPixel(int Pixel, byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
A.setPixelColor(Pixel, A.Color(red, green, blue));
B.setPixelColor(Pixel, A.Color(red, green, blue));
C.setPixelColor(Pixel, A.Color(red, green, blue));
D.setPixelColor(Pixel, A.Color(red, green, blue));
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
leds[Pixel].r = red;
leds[Pixel].g = green;
leds[Pixel].b = blue;
#endif
}
void setAll(byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
setPixel(i, red, green, blue);
}
showStrip();
}
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 8
#define NUM_LEDS 30
#define PIN_A 5
#define NUM_LEDS_A 30
#define PIN_B 6
#define NUM_LEDS_B 30
#define PIN_C 9
#define NUM_LEDS_C 30
#define PIN_D 10
#define NUM_LEDS_D 30
// Parameter 1 = number of pixels in strip
// Parameter 2 = pin number (most are valid)
// Parameter 3 = pixel type flags, add together as needed:
// NEO_KHZ800 800 KHz bitstream (most NeoPixel products w/WS2812 LEDs)
// NEO_KHZ400 400 KHz (classic 'v1' (not v2) FLORA pixels, WS2811 drivers)
// NEO_GRB Pixels are wired for GRB bitstream (most NeoPixel products)
// NEO_RGB Pixels are wired for RGB bitstream (v1 FLORA pixels, not v2)
Adafruit_NeoPixel A = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS_A, PIN_A, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
Adafruit_NeoPixel B = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS_B, PIN_B, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
Adafruit_NeoPixel C = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS_C, PIN_C, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
Adafruit_NeoPixel D = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUM_LEDS_D, PIN_D, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
A.begin();
A.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
B.begin();
B.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
C.begin();
C.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
D.begin();
D.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
}
void loop() {
// Slower:
// Strobe(0xff, 0x77, 0x00, 10, 100, 1000);
// Fast:
Strobe(0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 10, 1000, 1);
}
void Strobe(byte red, byte green, byte blue, int StrobeCount, int FlashDelay, int EndPause){
for(int j = 0; j < StrobeCount; j++) {
setAll(red,green,blue);
showStrip();
delay(FlashDelay);
setAll(0,0,0);
showStrip();
delay(FlashDelay);
}
delay(EndPause);
}
void showStrip() {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
A.show();
B.show();
C.show();
D.show();
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
FastLED.show();
#endif
}
void setPixel(int Pixel, byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
#ifdef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// NeoPixel
A.setPixelColor(Pixel, A.Color(red, green, blue));
B.setPixelColor(Pixel, A.Color(red, green, blue));
C.setPixelColor(Pixel, A.Color(red, green, blue));
D.setPixelColor(Pixel, A.Color(red, green, blue));
#endif
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_NEOPIXEL_H
// FastLED
leds[Pixel].r = red;
leds[Pixel].g = green;
leds[Pixel].b = blue;
#endif
}
void setAll(byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++ ) {
setPixel(i, red, green, blue);
}
showStrip();
}
Building a software setup to connect live MadMapper input to 4 Adafruit Neopixel LED strips with Javier
19 | 11 | 18
Live MadMapper Input to Arduino
controlling each pixel individually
the length of them through a slider inside of Madmapper
setup
osc signal from mad mapper through processing and the processing is connected to arduino
Processing
MadmapperToProcessingLEDs
//WdKA - Interaction Station//
//2017////////////////////////
import processing.serial.*;
//Specify the number of Wekinator outputs
final int number_wekinator_outputs = 4;
//Current values in a [0.0 - 1.0] range
float current_values[];
//boolean current_values[];
//Class that parses the data received from Wekinator
WekinatorParser parser;
//OSC port used by Wekinator
final int oscPort = 7001;
//Printing some info in the console if true
final boolean verbose = false;
//Set to false to disable easing (smoothing) effect in the animations
final boolean usingEasing = false;
//Amount of easing
final float easing = 0.05;
//Serial port for communicating with Arduino
Serial myPort;
void setup() {
size(500, 500);
frameRate(60);
//Receiving data
parser = new WekinatorParser(number_wekinator_outputs,oscPort,usingEasing,easing,verbose);
//Serial connection
printArray(Serial.list());
// Change the index (0 in the example) to match your
String portName = Serial.list()[2];
myPort = new Serial(this, portName, 9600);
println(portName+" selected");
}
void draw() {
background(235);
current_values = parser.calculateValues();
//Sending values to Arduno
sendValuesToArduino();
}
void sendValuesToArduino(){
// int servoAngleRange = 180;
String strSent = "";
for(int i = 0; i < number_wekinator_outputs; i++){
strSent += str(int(current_values[i]*100));
if(i != (number_wekinator_outputs-1) ){
strSent += ",";
}
}
strSent += "\r";
myPort.write(strSent);
if(verbose){
println(strSent);
}
}
/*
//Arduino code
//WdKA - Interaction Station//
//2017////////////////////////
#include <Servo.h>
//we define the number of servo motors that we will used
const int numServos = 3;
//The first servo motor is connected to this pin.
//Connect the rest of the servo motors to the next pins (Digital Pins 6 & 7)
const int initialServoPin = 5;
Servo myServos[numServos];
int servoValues[numServos];
void setup()
{
//Initialize Serial comunication
Serial.begin(9600);
//For each one of the servo motros
for(int i = 0;i < numServos;++i){
//attaches the pin to the servo object
myServos[i].attach(i+initialServoPin);
//Initialize the servo motors to the position 0
myServos[i].write(0);
servoValues[i] = 0;
}
}
void loop() {
// if there's any serial available, read it:
while (Serial.available() > 0) {
for(int i = 0;i < numServos;++i){
//attaches the pin to the servo object
servoValues[i] = Serial.parseInt();
//contrain the values between 0 and 180 for the servo motors
servoValues[i] = constrain(servoValues[i], 0, 180);
}
// end of the line
if (Serial.read() == '\r') {
//we move the servos
for(int i = 0;i < numServos;++i){
myServos[i].write(servoValues[i]);
}
}else{
return;
}
}
}
*/
WekinatorParser
import oscP5.*;
//It receives the Wekinator outputs through OSC
class WekinatorParser {
OscP5 oscP5;
// float target_outputs[];
// float current_outputs[];
boolean target_outputs[];
float current_outputs[];
boolean usingEasing = true;
boolean verbose = false;
float easing = 0.0;
int number_wekinator_outputs = 4;
int oscPort = 0;
WekinatorParser(int number_wekinator_outputs,int oscPort,boolean usingEasing,float easing,boolean verbose){
this.number_wekinator_outputs = number_wekinator_outputs;
this.oscPort = oscPort;
this.usingEasing = usingEasing;
this.easing = easing;
this.verbose = verbose;
// target_outputs = new float[number_wekinator_outputs];
// current_outputs = new float[number_wekinator_outputs];
target_outputs = new boolean[number_wekinator_outputs];
current_outputs = new float[number_wekinator_outputs];
for(int i = 0; i < number_wekinator_outputs;i++){
// target_outputs[i] = 0.0;
target_outputs[i] = false;
}
oscP5 = new OscP5(this,oscPort);
}
//It returns the values received from Wekinator. If usingEasing is true, there is some smoothing effect
float[] calculateValues() {
// boolean[] calculateValues() {
/*for (int i = 0; i < number_wekinator_outputs; i++) {
if(usingEasing){
current_outputs[i] += (target_outputs[i] - current_outputs[i]) * easing;
}else{
current_outputs[i] = target_outputs[i];
}
} */
return current_outputs;
}
void oscEvent(OscMessage theOscMessage) {
if(verbose){
theOscMessage.print();
println(" typetag: "+theOscMessage.typetag());
println(" addrPattern: "+theOscMessage.addrPattern());
println(" address: "+theOscMessage.address());
}
if (theOscMessage.addrPattern().equals("/red")) {
Object[] objects = theOscMessage.arguments();
if(verbose){
//println(objects.length);
}
println(theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue());
current_outputs[0] = theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue();
}else if (theOscMessage.addrPattern().equals("/green")) {
Object[] objects = theOscMessage.arguments();
if(verbose){
//println(objects.length);
}
println(theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue());
current_outputs[1] = theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue();
}else if (theOscMessage.addrPattern().equals("/blue")) {
Object[] objects = theOscMessage.arguments();
if(verbose){
//println(objects.length);
}
println(theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue());
current_outputs[2] = theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue();
}else if (theOscMessage.addrPattern().equals("/opacity")) {
Object[] objects = theOscMessage.arguments();
if(verbose){
//println(objects.length);
}
println(theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue());
current_outputs[3] = theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue();
}
}
}
ProcessingtoArduino
import oscP5.*;
//It receives the Wekinator outputs through OSC
class WekinatorParser {
OscP5 oscP5;
// float target_outputs[];
// float current_outputs[];
boolean target_outputs[];
float current_outputs[];
boolean usingEasing = true;
boolean verbose = false;
float easing = 0.0;
int number_wekinator_outputs = 4;
int oscPort = 0;
WekinatorParser(int number_wekinator_outputs,int oscPort,boolean usingEasing,float easing,boolean verbose){
this.number_wekinator_outputs = number_wekinator_outputs;
this.oscPort = oscPort;
this.usingEasing = usingEasing;
this.easing = easing;
this.verbose = verbose;
// target_outputs = new float[number_wekinator_outputs];
// current_outputs = new float[number_wekinator_outputs];
target_outputs = new boolean[number_wekinator_outputs];
current_outputs = new float[number_wekinator_outputs];
for(int i = 0; i < number_wekinator_outputs;i++){
// target_outputs[i] = 0.0;
target_outputs[i] = false;
}
oscP5 = new OscP5(this,oscPort);
}
//It returns the values received from Wekinator. If usingEasing is true, there is some smoothing effect
float[] calculateValues() {
// boolean[] calculateValues() {
/*for (int i = 0; i < number_wekinator_outputs; i++) {
if(usingEasing){
current_outputs[i] += (target_outputs[i] - current_outputs[i]) * easing;
}else{
current_outputs[i] = target_outputs[i];
}
} */
return current_outputs;
}
void oscEvent(OscMessage theOscMessage) {
if(verbose){
theOscMessage.print();
println(" typetag: "+theOscMessage.typetag());
println(" addrPattern: "+theOscMessage.addrPattern());
println(" address: "+theOscMessage.address());
}
if (theOscMessage.addrPattern().equals("/red")) {
Object[] objects = theOscMessage.arguments();
if(verbose){
//println(objects.length);
}
println(theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue());
current_outputs[0] = theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue();
}else if (theOscMessage.addrPattern().equals("/green")) {
Object[] objects = theOscMessage.arguments();
if(verbose){
//println(objects.length);
}
println(theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue());
current_outputs[1] = theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue();
}else if (theOscMessage.addrPattern().equals("/blue")) {
Object[] objects = theOscMessage.arguments();
if(verbose){
//println(objects.length);
}
println(theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue());
current_outputs[2] = theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue();
}else if (theOscMessage.addrPattern().equals("/opacity")) {
Object[] objects = theOscMessage.arguments();
if(verbose){
//println(objects.length);
}
println(theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue());
current_outputs[3] = theOscMessage.get(0).floatValue();
}
}
}
Building a spatial setup for 4 Adafruit Neopixel LED strips
20 | 11 | 18
Lab setup 1
conclusion
no light beam effect
Experimenting with Jem Compact Hazer Pro (haze machine) + plano convex lenses + 4 Adafruit Neopixel LED strips
21 | 11 | 18
conclusion
light beam became visible through the haze
Experimenting with Jem Compact Hazer Pro (haze machine) + opaque acrylic sheets + 4 Adafruit Neopixel LED strips
27 | 11 | 18
conclusion
the brightness of the LED is not strong enough to be able to create a linear light beam with acrylic sheet in space
Diving into PureData 1
20 | 12 | 18
Goal is to create sound generated animations for the LED strip with 144 px on 1m
Conclusion
GEM library needs to be better installed on my computer
Experimenting of creating a strong light beam in combination with movable 3D printed lens holder for adjusting the distance between the light source and lens
11 | 01 | 19
LED Collimator 15 degree for 3W Star type Power LED
Conclusion
The light source was not strong enough
Diving into PureData 2
14 | 01 | 19
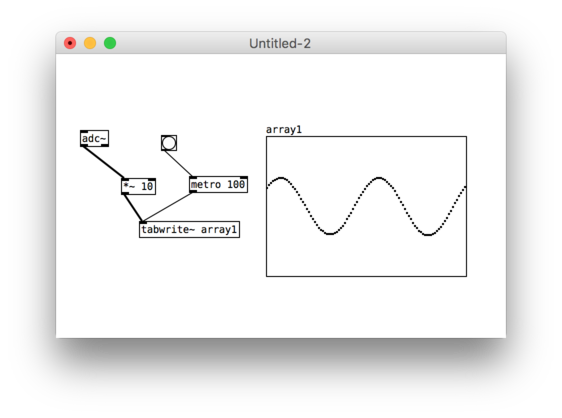
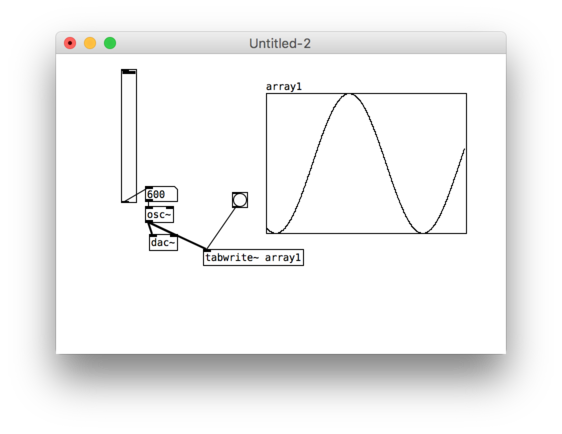
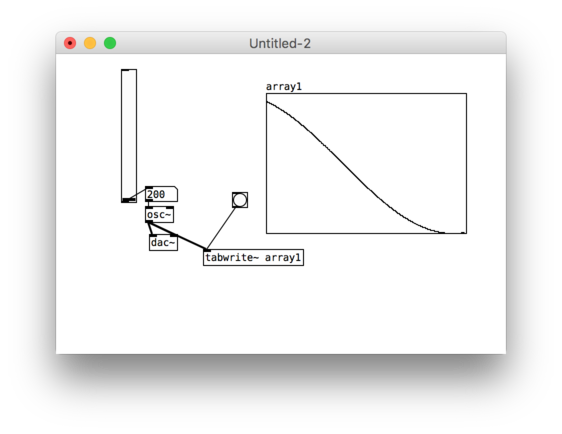
Goal is to create sound generated animations for the LED strip with 144 px on 1m
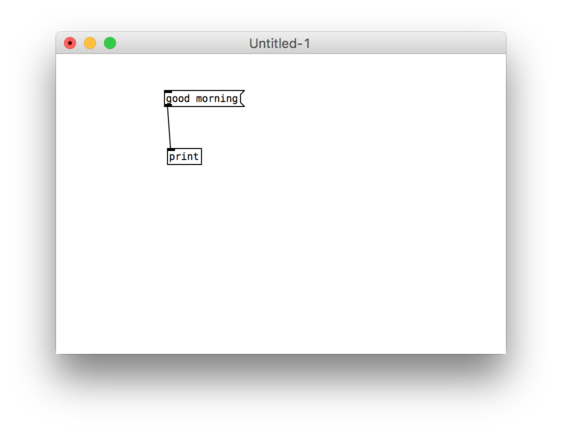
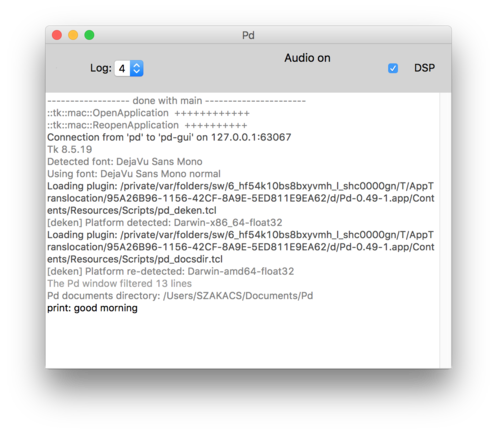
Diving into PureData 3
20 | 01 | 19
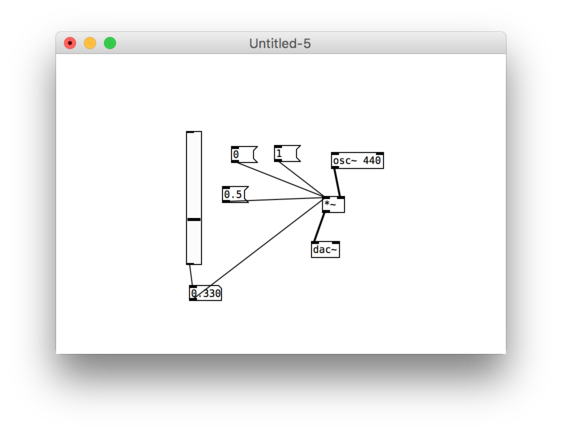
Analysing partials – Fourier Analysis
Fourier transformation
It divides the entire frequency spectrum into parts of equal size and determines the amplitude and phase for each part. One could in turn reconstruct the original signal from these values. The derivation of the component parts is called analysis; the reconstruction is called resynthesis. You can realize this using the objects "rfft~" and "irfft~".
Output = Shows the power of different frequency components that make up that sound. Each of the number represents an amplitude of a particular band of frequencies.