TGC3 Beginners Guide: Difference between revisions
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==== Python & OSC ==== | ==== Python & OSC ==== | ||
<pre> | |||
#!/usr/bin/env python | |||
import os, random, time | |||
while True: | |||
freq = str(random.randint(0,10)*110) | |||
print(freq) | |||
os.system('echo "'+freq+';" | pdsend 3000') | |||
time.sleep(0.25) | |||
</pre> | |||
== Floppy == | == Floppy == | ||
Revision as of 11:10, 13 October 2017
Intro
The Tetra Gamma Circulaire 3 (TGC3), AKA XPUB Special Issue 2, is an unknown concrete floppy music publication. It is an experimental platform designed to investigate experimental ways of publishing sonic, visual and textual works and instruments.
This work is a collaboration between the polymorph production platform DE PLAYER and the Experimental Publishing (XPUB) study path of the Media Design Master at the Piet Zwart Institute, Willem de Kooning Academie. Current contributions include works on dance, democracy, drones, surveillance, body movement, silence, improvisation, and the fine line between everything and nothing. We encourage anyone to contribute new pieces so as to develop an ever growing library of works to be experienced on the TGC3.
Hardware
The TCG3 is an accumulation of various computer peripherals that can be accessed in many different ways (WiFi, speakers, microphone, camera, Bluetooth, electro-conductive touch pads). It was designed as an open platform to allow for many kinds of applications, and contributions.
The core of the TGC3 is a single board computer (SBC) called a RaspberryPi and running the GNU/Linux distribution Raspbian. Works are contained on floppy disks and launched on insertion. To be more precise, each floppy contains the programmatic instructions so as to make the tiny computer behave in a certain way, and make use of some of all of its peripherals. This system therefore allows for a rather large range of possibilities, where the TGC can become anything from an audiovisual noise instrument to a poetry broadcasting device or spying and tracking camera. Last but not least, there is no default Internet connectivity on the TGC3, but local websites, stored on each floppy, can be accessed by connecting to the TGC3 local WiFi hotspot. This feature can be used to provide contextual documentation for the work, or publish browser-based art off the Internet.
Software
Contributions can be made in the form of Python scripts and applications, Pure Data (Pd) patches, JavaScript and static HTML and CSS written websites. Access to the various hardware peripherals can be made using standard Python modules and Pure Data externals, but also via the UNIX filesystem. The main inputs available to read from are the microphone, the camera, the electro-conductive touch pads, and the web interface. The main outputs to send data to are the audio speakers and the web interface. For instance one program, written with Python or Pd, could listen to the incoming sound amplitude captured from the microphone and generates graphics files to be loaded on a simple static website. The website could be visible on mobile devices connected to the TGC3 WiFi network, and a dedicated machine could video-project the website as well to create an interactive installation.
Examples
To give you an example of the ability of the TGC3, we have provided some examples of possible submissions. Provided are some examples of basic setups to get you started and the inner workings of some current submissions to demonstrate the breadth of the possible complexity.
Pure Data
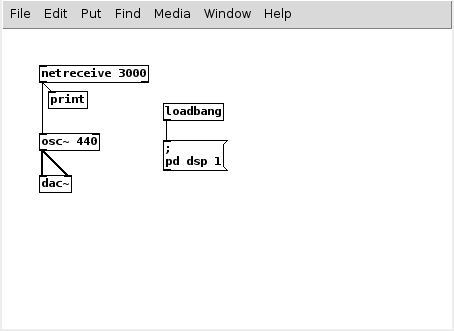
When working with Pure Data, depending on your desired output, there are some minimum requirements in your patch. Below is an example of some of the basic modules that you might want to use when starting your patch.
In this example you will notice a few modules that you might want to use. First of all to enable sound the sound engine you will need to place loadbang connected to pd dsp 1. This will initiate the sound engine on load which will allow for sound synthesis, and analysis. Also there is an example for interfacing with external code via network data like the Open Sound Control protocol using the netreceive object. Lastly you can see some basic sound output being generated via the osc~ (oscillator) object generating a tone at 440Hz, which is being made audible by going to the dac~ (digital to analogue converter) object.
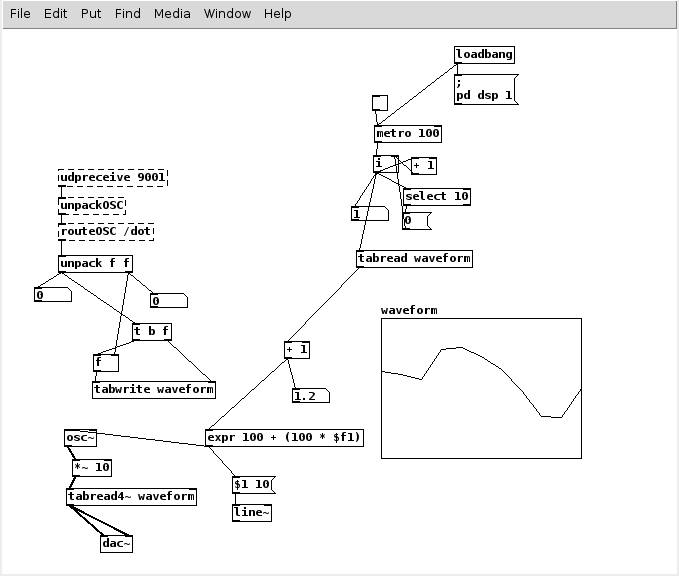
The TGC3 can handle very complex patches. The following example is the inner workings of an interactive sound instrument that interfaces over OSC. In this case the netreceive object is replaced by the udpreceive object.
You can see even in this patch the building blocks that remain from the basic example. Notice too the loadbang going to the metro (metronome) objects. This makes sure that the patch's functionality, launches along with the sound engine. Outside of the few modifications to the basic example, the patch's complexity only lies in between the input and output stages.
Python & OSC
#!/usr/bin/env python
import os, random, time
while True:
freq = str(random.randint(0,10)*110)
print(freq)
os.system('echo "'+freq+';" | pdsend 3000')
time.sleep(0.25)
Floppy
The setup of the Floppy is key in the functionality of the system. Below we have provided a map of the file and folder structure of your future floppy submission.
FLOPPY ├── LICENSE ├── main.pd ├── main.py ├── noweb │ └── index.html └── README
In the root of the Floppy disk there needs to contain a LICENSE and README text file, your initial code file(s) named either main.py or main.pd format, and a noweb folder containing local website files you wish to have accessible over the local hotspot. Any other files you may need can be arranged in any style you choose so long as you correctly reference them in your code.