User:Manetta/wordnet/wordnetwords: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="width:800px;"> | |||
==WordNet== | ==WordNet== | ||
WordNet is an English lexical database, created in 1985 in the Cognitive Science Laboratory of the Princeton University. | WordNet is an English lexical database, created in 1985 in the Cognitive Science Laboratory of the Princeton University. | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
===kernal=== | ===kernal=== | ||
* official website: http://wordnet.princeton.edu/wordnet/ | * official website: http://wordnet.princeton.edu/wordnet/ | ||
* official files: http://wordnetcode.princeton.edu/ | * official files: http://wordnetcode.princeton.edu/<br> | ||
* versions: | * versions: | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
:1.2 (1992?) | :1.2 (1992?) | ||
* license: BSD | * license: BSD | ||
* initiated by George Armitage Miller and developed untill currently by Christiane Fellbaum. | |||
<br> | |||
* 3 hypotheses from which WordNet started: | |||
=== | [[File:Wordnet-an-electronic-lexical-database-1998-forword-separability-hypothesis.png]]<br> | ||
<small>separability-hypothesis</small><br><br> | |||
[[File:Wordnet-an-electronic-lexical-database-1998-forword-patterning-hypothesis.png]]<br> | |||
<small>patterning-hypothesis</small><br><br> | |||
[[File:Wordnet-an-electronic-lexical-database-1998-forword-comprihensiveness-hypothesis.png]]<br> | |||
<small>comprihensiveness-hypothesis</small><br><br> | |||
=== WordNet as cultural object (?) === | |||
<span style="color:blue;">[universal language]</span><br> | |||
WordNet is created very much with the presence of machines in mind. And so WordNet could be seen in line of multiple attempts to create an universal language, more specifically: an universal language which would make human-machine communication possible. Therefore it also provides possibilities for human-machine-machine-machine-human communication. | |||
Opposed to John Wilkins' idea for an universal language, in which words would be built from semantic atoms, WordNet is deriving meaning from a network-based structure. *'IS-A-KIND-OF' is a semantic relation*[1]. Though, when initiating WordNet, George Miller came from a 9-year-long research project in which the attempt was close to such atomic idea. <br> | |||
<span style="color:blue;">[leading]</span><br> | |||
As WordNet is a dataset which is prepared to function within various scientific pieces of software, it is the leading source in the range of lexical datasets. From the beginning of the development of WordNet, the makers where very consious of the fact that a relational network structure would enable them to let WordNet avoid scaling problems.<br> | |||
<span style="color:blue;">[applications]</span><br> | |||
One application of WordNet is Pattern, a text mining application in the form of a python library. WordNet is located at ./pattern-2.6/pattern/text/en/wordnet/dict as 12 textfiles. The textfiles contain the data- & index files of adjectives, adverbs, nouns and verbs, accompanied with a definition, id-number, and sometimes supplemented with an example sentence, to show the term in context. The WordNet definitions are used by Pattern within the en-sentiment.xml file, where terms are annotated on their level of positiveness. | |||
Pattern also provides WordNet in the Pattern.en module, for Natural Language Processing (NLP) purposes. The makers write (on clips.ua.ac.ne/pattern): "Because language is ambigious (e.g. I can <--> a can) it uses statistical approaches + regular expressions". The Pattern.en.wordnet module makes it possible to search for related words, descriptions, synonyms and available word senses. | |||
[1]: WordNet - an electronic lexical database (1998) — forword, xvi | |||
=== WordNet in action === | |||
* WordNet is used for '''natural language processing''' purposes. <br> | |||
* difference between MRD / NLP : <br> | |||
:* ''machine readible dictionary (MRD)'' → dictionary which was printed before, but now electronic<br> | |||
:* ''natural language processing (NLP)'' → dictionary made from scratch, with an NLP purpose | |||
* "'''Search engines''' may use either a vocabulary, a taxonomy or an ontology to optimise the search results." [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Machine-readable_dictionary (from)]<br> | |||
==== included as dictionary package (not a complete list) ==== | |||
* Pattern → a web mining module for the Python programming language. | |||
* GoldenDict → a computer open-source dictionary program | |||
* Lingoes → a single-click multi-lingual translation software program | |||
===WordNet elements — *highlights* === | |||
===='entity'==== | ===='entity'==== | ||
the highest level of abstraction in WordNet: 'entity'<br> | the highest level of abstraction in WordNet: 'entity'<br> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 106: | ||
==== WordNet alive | ==== WordNet alive ==== | ||
[[File:Mb-WordNet-alive-tweets-01.png]]<br> | [[File:Mb-WordNet-alive-tweets-01.png]]<br> | ||
| Line 73: | Line 117: | ||
[[File:Mb-WordNet-alive-tweets-05.png]]<br> | [[File:Mb-WordNet-alive-tweets-05.png]]<br> | ||
</div> | |||
Latest revision as of 23:06, 18 May 2015
WordNet
WordNet is an English lexical database, created in 1985 in the Cognitive Science Laboratory of the Princeton University.
kernal
- official website: http://wordnet.princeton.edu/wordnet/
- official files: http://wordnetcode.princeton.edu/
- versions:
- 3.1 (?)
- 3.0 (2006)
- 2.1 (2005)
- 1.7.1 (?)
- 1.7 (?)
- 1.6 (?)
- 1.5 (?)
- 1.4 (?)
- 1.3 (?)
- 1.2 (1992?)
- license: BSD
- initiated by George Armitage Miller and developed untill currently by Christiane Fellbaum.
- 3 hypotheses from which WordNet started:

separability-hypothesis

patterning-hypothesis

comprihensiveness-hypothesis
WordNet as cultural object (?)
[universal language]
WordNet is created very much with the presence of machines in mind. And so WordNet could be seen in line of multiple attempts to create an universal language, more specifically: an universal language which would make human-machine communication possible. Therefore it also provides possibilities for human-machine-machine-machine-human communication.
Opposed to John Wilkins' idea for an universal language, in which words would be built from semantic atoms, WordNet is deriving meaning from a network-based structure. *'IS-A-KIND-OF' is a semantic relation*[1]. Though, when initiating WordNet, George Miller came from a 9-year-long research project in which the attempt was close to such atomic idea.
[leading]
As WordNet is a dataset which is prepared to function within various scientific pieces of software, it is the leading source in the range of lexical datasets. From the beginning of the development of WordNet, the makers where very consious of the fact that a relational network structure would enable them to let WordNet avoid scaling problems.
[applications]
One application of WordNet is Pattern, a text mining application in the form of a python library. WordNet is located at ./pattern-2.6/pattern/text/en/wordnet/dict as 12 textfiles. The textfiles contain the data- & index files of adjectives, adverbs, nouns and verbs, accompanied with a definition, id-number, and sometimes supplemented with an example sentence, to show the term in context. The WordNet definitions are used by Pattern within the en-sentiment.xml file, where terms are annotated on their level of positiveness.
Pattern also provides WordNet in the Pattern.en module, for Natural Language Processing (NLP) purposes. The makers write (on clips.ua.ac.ne/pattern): "Because language is ambigious (e.g. I can <--> a can) it uses statistical approaches + regular expressions". The Pattern.en.wordnet module makes it possible to search for related words, descriptions, synonyms and available word senses.
[1]: WordNet - an electronic lexical database (1998) — forword, xvi
WordNet in action
- WordNet is used for natural language processing purposes.
- difference between MRD / NLP :
- machine readible dictionary (MRD) → dictionary which was printed before, but now electronic
- natural language processing (NLP) → dictionary made from scratch, with an NLP purpose
- machine readible dictionary (MRD) → dictionary which was printed before, but now electronic
- "Search engines may use either a vocabulary, a taxonomy or an ontology to optimise the search results." (from)
included as dictionary package (not a complete list)
- Pattern → a web mining module for the Python programming language.
- GoldenDict → a computer open-source dictionary program
- Lingoes → a single-click multi-lingual translation software program
WordNet elements — *highlights*
'entity'
the highest level of abstraction in WordNet: 'entity'
→ entity -- (that which is perceived or known or inferred to have its own distinct existence (living or nonliving))
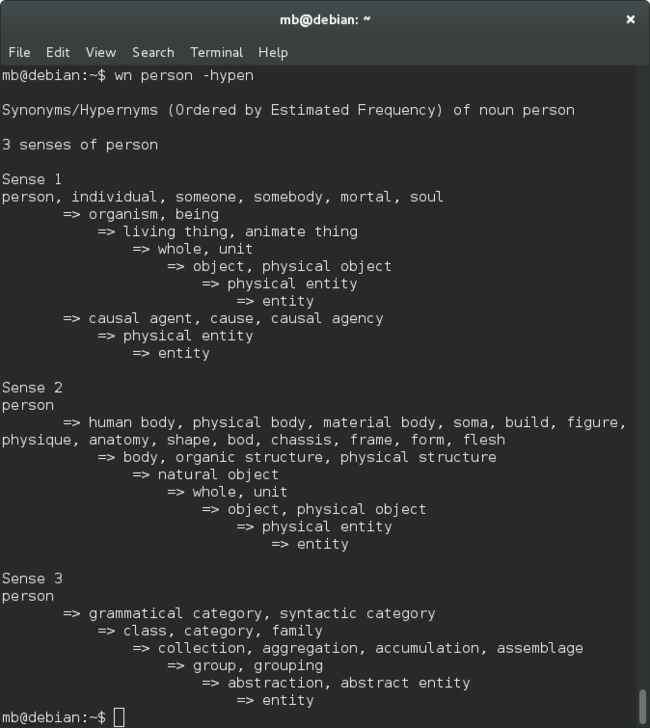
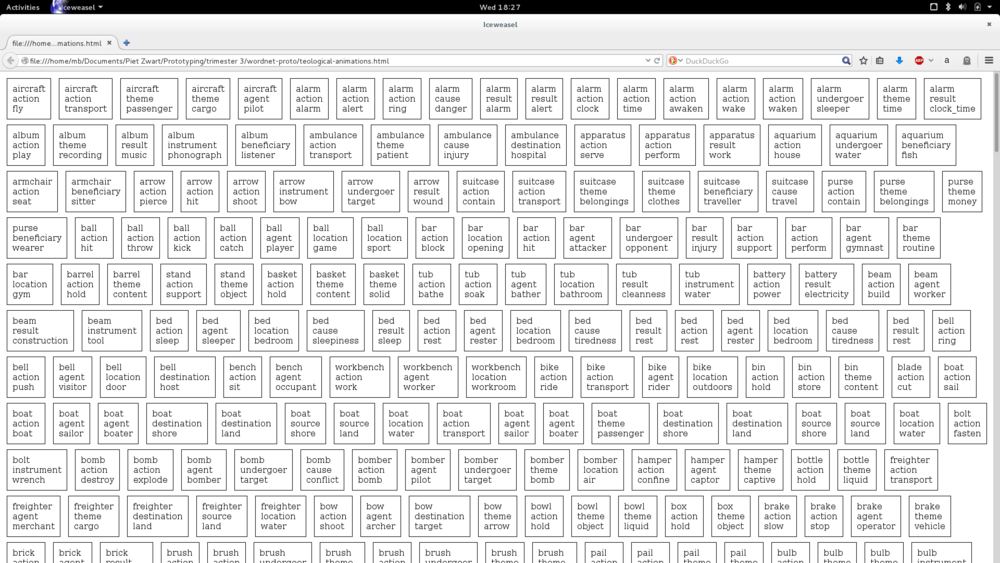
teleological links
→ http://wordnetcode.princeton.edu/standoff-files/teleological-links-README.txt
RELATION: DESCRIPTION:
action Describes the typical intended activity (purpose) which
the artifact was designed for.
e.g., a bed is intended for (ACTION) sleeping
For this typical intended activity, there are 11 roles used to describe it.
Note these relations are between the artifact's activity (not the artifact)
and the object mentioned.
RELATION: DESCRIPTION:
agent a rester is a (typical) AGENT of sleeping on a bed
beneficiary an audience is a (typical) BENEFICIARY of showing a movie
cause tiredness is a (typical) CAUSE of sleeping on a bed
destination a shore is a (typical) DESTINATION of sailing a boat
experiencer a child is a (typical) EXPERIENCER of swinging on a swing
instrument a gun is a (typical) INSTRUMENT of shooting a bullet
location a bedroom is a (typical) LOCATION of sleeping on a bed
result rest is a (typical) RESULT of sleeping on a bed
source a shore is a (typical) SOURCE of sailing a boat
theme a passenger is a (typical) THEME of transporting by boat
undergoer a target is a (typical) UNDERGOER of shooting an arrow
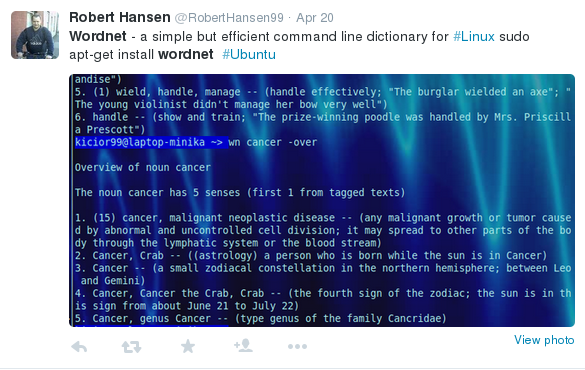
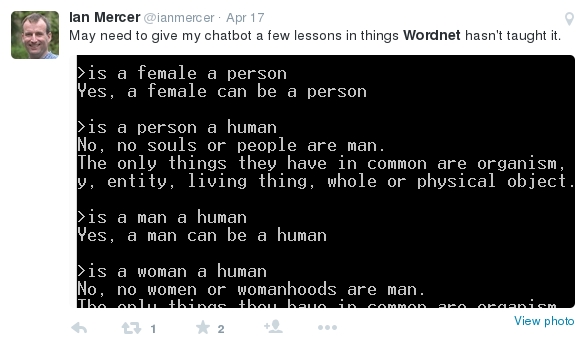
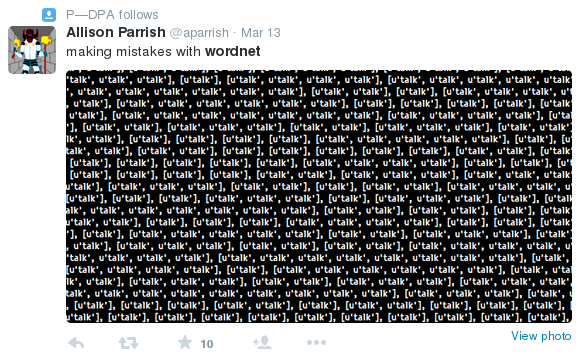
WordNet alive