Null/HTML: Difference between revisions
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==The Internet== | ||
: | ==ARPANET: the first computer network== | ||
== Context for the creation of the ARPANET == | |||
* USA, 1960s | |||
* Cold War | |||
* Soviet Union launched in 1957 Sputnik - the first satellite | |||
* Sputnik trigger a space race between US and the Soviet Union; the US only only change to win was to invest in scientific development | |||
* ARPANET was created by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) | |||
==Aims for the ARPANET== | |||
* create access to remote computers | |||
* allow a variety of computers to join the network and be accessed | |||
* foster collaborative scientific research | |||
* withstanding communications if faced with a nuclear attack | |||
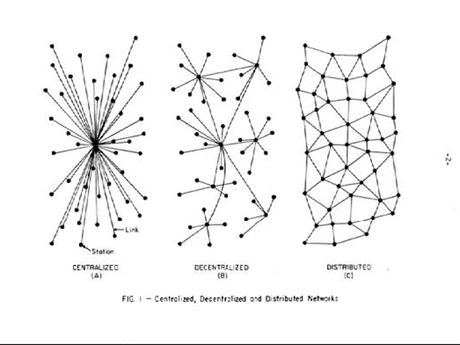
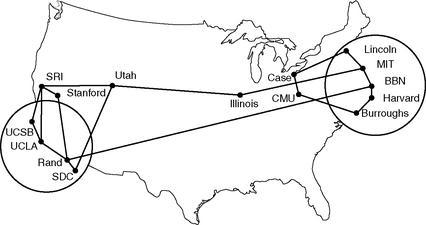
==Characteristics of the ARPANET== | |||
* Distributed network: each node connects to more than 1 other node | |||
** destruction of a node would not interrupt communication | |||
http:// | [[File:Brand-networks-topologies.jpg|3 network topologies|460px]] | ||
[[File:ARPANET-nodes-1971.jpg|ARPANET nodes 1971]] | |||
==Killer App: Email== | |||
* At first the network was not heavily used | |||
* It was difficult to access and use the different computers on the network | |||
* the creation of electronic mail, brought many more users to network, which were simply using it to communicate | |||
* the network changed from a resource sharing system to '''a communication system'''. | |||
==Internet: the network that connected networks== | |||
* by 1980 several digital networks, were functioning, besides ARPANET both in US and Europe: | |||
** USENET, BITNET, FidoNet (Bulletin Board Network), etc | |||
* these were isolated networks, not connected interconnected. | |||
* the task was to connect this networks | |||
* to the wide and integrated network was given the name Internet | |||
Listen to a radio program on Bulletin Board Networks: [http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=120649723|The 'Wild And Woolly' World Of Bulletin Boards] | |||
Documentary "World Brain" <ref>Degoutin, Stéphane, and Gwenola Wagon. World Brain Stéphane Degoutin & Gwenola Wagon, 2012. http://worldbrain.arte.tv.</ref> | |||
----- | |||
==The World Wide Web== | |||
A world wide documentation system, sometimes known as the Web, same times as WWW | |||
==Context of Web's creation== | |||
* conceptualized by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN | |||
* Berners-Lee was frustrated with the difficulty circulation of information inside CERN | |||
** diversity of computers with different systems | |||
** large number of projects and individuals | |||
** large amounts of information with no common system to organize and communicate this information | |||
[[File:tim-berners-lee.jpg|Tim-Berners Lee]] | [[File:tim-berners-lee.jpg|Tim-Berners Lee]] | ||
http://cache.boston.com/universal/site_graphics/blogs/bigpicture/lhc_08_01/lhc11.jpg | |||
Inside one of CERN's experiments. [http://www.boston.com/bigpicture/2008/08/the_large_hadron_collider.html Source] | |||
==Aim: find information== | |||
Tim Berners-Lee wanted to create a system that would: | |||
* give access to files in different computers around the world. | |||
* link the files among themselves | |||
* facilitate the location and retrieval of information | |||
"''Suppose all the information stored in computers everywhere were linked … Suppose I could program my computer to create '''a space in which anything could be linked to anything'''.'' All the bits of information in every computer at CERN, and on the planet, would be available to me and anyone else. These would be a single information space". <ref>Berners-Lee, Tim. Weaving the Web. London: TEXERE, 2000.</ref> | |||
==How== | |||
Tim Berners-Lee | |||
* devised a system that connected information through '''links''' (hypertext) | |||
* created a '''hyper text language''': '''HTML''' (Hyper Text Markup Language) | |||
* wrote an '''interpreter for HTML''' (that transforms HTML code into visual form): a '''web browser''' <ref>[http://line-mode.cern.ch/www/hypertext/WWW/TheProject.html Simulation of the first Web Browser]</ref> | |||
* implemented a systems of addresses - URL - that allowed files in remote computers to be called and reply by sending back a (usually) HTML file. | |||
==Result== | |||
* The Web became a system where information was easier to find | |||
* users of host computers (servers) could easily decide what they said to the world, and also change it | |||
* users became publishers of content on the Web (not even needing access to a server in order to do it) | |||
* that publishing possibility and will triggered the creation of web publishing services and formats (Geocities, blogs, Tumblrs, Facebook walls ,etc) | |||
* in this context the user is not only a consumer, but also a producer of content (or publisher) | |||
---- | |||
== | == Editor, Browser, Go == | ||
* Editor - your HTML writing tool | |||
* Browser - the interpreter of HTML, but also a debug and prototyping space. (Read about what goes on behind the scenes in a Web browser <ref>“Introduction to HTML” https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Guide/HTML/Introduction.</ref>) | |||
* | ==HTML== | ||
* | * HTML is a markup language | ||
* meaning: content is marked with different "values"; e.g: paragraph, bold, italic, heading title, etc | |||
* marking is done through tags that wrap the content | |||
http://publicationstation.wdka.hro.nl/go/kickoff/imgs/html.gif | |||
* In order to '''format content with tags''' you need to enter the content between an opening and closing element. As in the following case: | |||
<nowiki><h1>My Title</h1></nowiki> | |||
** <nowiki><h1></nowiki> is the opening tag | |||
** <nowiki></h1></nowiki> is the closing tag | |||
* at times you'll find '''self-closing tags''' which have no content inside them, like horizontal rulers <nowiki><hr /></nowiki> | |||
or line breaks <nowiki><br/></nowiki> | |||
== | == essential HTML tags == | ||
<pre> | |||
Title Headers: <h1>,<h2>,<h3>,<h4> | |||
Paragraph: <p> | |||
Line break: <br /> | |||
italics: <i> | |||
bold: <b> | |||
Comments: <!-- comments --> | |||
</pre> | |||
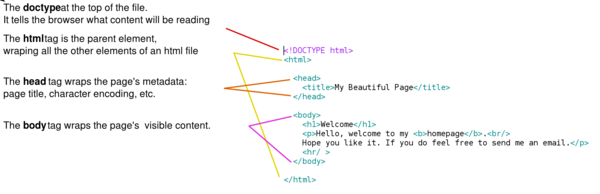
== | == HTML skeleton == | ||
The previous tags only provided content formatting, yet '''to create any working web-page we need to always place the content inside a ''HTML page skeleton'''''. | |||
[[File:skeleton.svg|600px]] | |||
== HTML == | === HTML page boilerplate === | ||
<source lang="html4strict"> | <source lang="html4strict"> | ||
<!DOCTYPE html> | <!DOCTYPE html> | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<head> | <head> | ||
</head> | </head> | ||
<body> | <body> | ||
</body> | </body> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
==HTML element reference== | |||
HTML element reference provides information and examples on every HTML element | |||
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element | |||
==<nowiki><a></nowiki> anchor tag - hyperlinks== | |||
<source lang="html4strict"> | |||
<a href="http://www.worm.org/">Worm website</a> | |||
<br/> | |||
<a href="http://tentrotterdam.nl/">tentrotterdam.nl</a> | |||
</source> | |||
* the href (address) of a link has to be a complete URL: beginning with http or https | |||
== | ==remote links== | ||
Normally, like in the example above, you use links to point users to other sites. | |||
Those are '''remote links''' | |||
==local links== | |||
Also usually you use '''local links'''. | |||
Those are links to other files/pages you have create. | |||
They allow to move within your website. | |||
<source lang="html4strict"> | |||
Go to next <a href="next.html">Next</a> page. | |||
</source> | |||
==<code><img></code> image tag== | |||
<source lang="html4strict"> | |||
<img src="http://data.whicdn.com/images/106829085/large.gif" /> | |||
<br/> | |||
<img src="my-img.jpg" /> | |||
</source> | |||
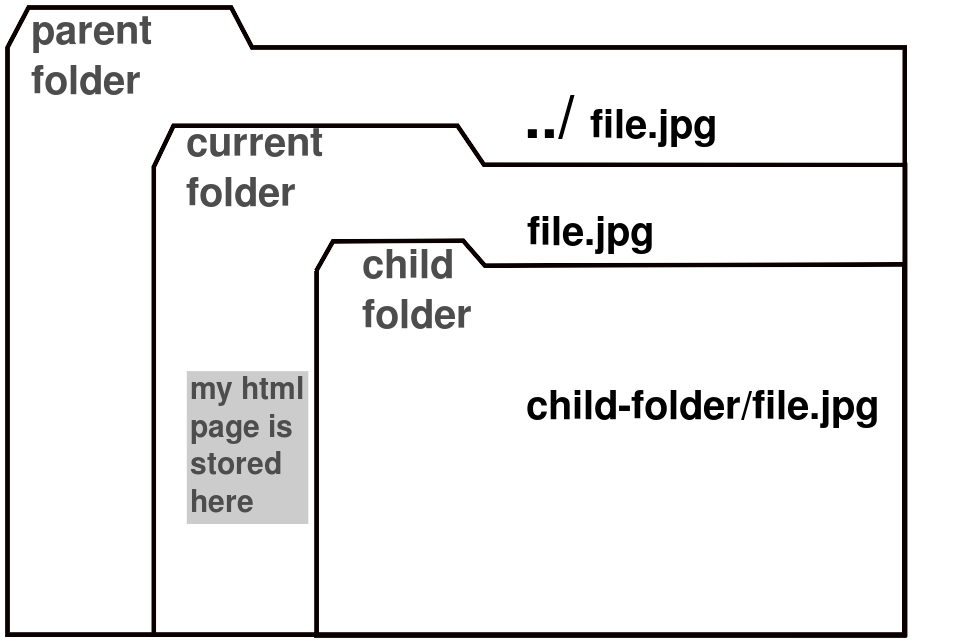
==Local file paths== | |||
Local links and image are some times in parent or child folders, different from the folder of your webpage. | |||
To get an image to load or link to land on the right file, you have to '''indicate the correct path to them'''. | |||
[[File:folder_structure.svg]] | |||
* an | ==Local file paths exercise== | ||
* Create an HTML file, that uses other local images and links to other local html files. | |||
* Move the HTML file to a different folder. | |||
* Keep images and linked pages in the fold they were it. | |||
* Try to make all the local files are '''not broken''' in HTML file | |||
== <nowiki><div></nowiki> div tag == | |||
< | The div tag is essentially a container of other content. | ||
< | <source lang="html4strict"> | ||
</ | <div style="background:black; color:red; width:400px"> | ||
<h1>Beautiful page</h1> | |||
<p>writing stuff | |||
<i>inside</i> | |||
</p> | |||
</div> | |||
</source> | |||
== <nowiki><span></nowiki> span tag== | |||
The span tag is like a color marker on text | |||
<source lang="html4strict"> | |||
<p>A magazine that offers a platform for | |||
<span style="background:red; color:blue; font-size:40px">challenging and engaging</span> | |||
design and art practices</p> | |||
</source> | |||
style it is an attribute | |||
== | ==tags' attributes== | ||
< | attributes are parameters that modify the HTML tags behavior | ||
==<nowiki><a></nowiki> attributes:== | |||
<source lang="html4strict"> | |||
<a href="http://wdka.hro.nl/" target="_self">link</a> <!-- target="_self": Loads the response into the SAME tab--> | |||
<br/> | |||
<a href="http://wdka.hro.nl/" target="_blank">link</a> <!-- target="_blank": Loads the response into a NEW tab--> | |||
</source> | |||
* href: url or file of the link | |||
* target: where (in what window) to display the linked file. | |||
==<code><img></code> attributes:== | |||
<source lang="html4strict"> | |||
<img src="http://www.wdka.nl/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2015/01/Project-Show_I1.jpeg" title="my pic" height="100px" width="200px"/> | |||
</source> | |||
* src: location of the image | |||
* title: title of the image | |||
* width | |||
* height | |||
==inspector== | |||
== Optional Reading == | |||
Stephenson, Neal. “Mother Earth Mother Board.” Wired, http://archive.wired.com/wired/archive/4.12/ffglass_pr.html. | |||
Abbate, Janet. Inventing the Internet. MIT Press, 2000. | |||
==References, Notes and Optional Reading == | |||
<references /> | |||
“The Birth of the Web,” http://home.web.cern.ch/topics/birth-web . | |||
http://home.web.cern.ch/topics/birth-web | |||
Technical | ==Technical Resources == | ||
* https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML - HTML (HyperText Markup Language) | * https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML - HTML (HyperText Markup Language) | ||
* https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element - HTML element reference | * https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element - HTML element reference | ||
Latest revision as of 12:55, 5 October 2015
The Internet
ARPANET: the first computer network
Context for the creation of the ARPANET
- USA, 1960s
- Cold War
- Soviet Union launched in 1957 Sputnik - the first satellite
- Sputnik trigger a space race between US and the Soviet Union; the US only only change to win was to invest in scientific development
- ARPANET was created by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA)
Aims for the ARPANET
- create access to remote computers
- allow a variety of computers to join the network and be accessed
- foster collaborative scientific research
- withstanding communications if faced with a nuclear attack
Characteristics of the ARPANET
- Distributed network: each node connects to more than 1 other node
- destruction of a node would not interrupt communication
Killer App: Email
- At first the network was not heavily used
- It was difficult to access and use the different computers on the network
- the creation of electronic mail, brought many more users to network, which were simply using it to communicate
- the network changed from a resource sharing system to a communication system.
Internet: the network that connected networks
- by 1980 several digital networks, were functioning, besides ARPANET both in US and Europe:
- USENET, BITNET, FidoNet (Bulletin Board Network), etc
- these were isolated networks, not connected interconnected.
- the task was to connect this networks
- to the wide and integrated network was given the name Internet
Listen to a radio program on Bulletin Board Networks: 'Wild And Woolly' World Of Bulletin Boards
Documentary "World Brain" [1]
The World Wide Web
A world wide documentation system, sometimes known as the Web, same times as WWW
Context of Web's creation
- conceptualized by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN
- Berners-Lee was frustrated with the difficulty circulation of information inside CERN
- diversity of computers with different systems
- large number of projects and individuals
- large amounts of information with no common system to organize and communicate this information

Inside one of CERN's experiments. Source
Aim: find information
Tim Berners-Lee wanted to create a system that would:
- give access to files in different computers around the world.
- link the files among themselves
- facilitate the location and retrieval of information
"Suppose all the information stored in computers everywhere were linked … Suppose I could program my computer to create a space in which anything could be linked to anything. All the bits of information in every computer at CERN, and on the planet, would be available to me and anyone else. These would be a single information space". [2]
How
Tim Berners-Lee
- devised a system that connected information through links (hypertext)
- created a hyper text language: HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language)
- wrote an interpreter for HTML (that transforms HTML code into visual form): a web browser [3]
- implemented a systems of addresses - URL - that allowed files in remote computers to be called and reply by sending back a (usually) HTML file.
Result
- The Web became a system where information was easier to find
- users of host computers (servers) could easily decide what they said to the world, and also change it
- users became publishers of content on the Web (not even needing access to a server in order to do it)
- that publishing possibility and will triggered the creation of web publishing services and formats (Geocities, blogs, Tumblrs, Facebook walls ,etc)
- in this context the user is not only a consumer, but also a producer of content (or publisher)
Editor, Browser, Go
- Editor - your HTML writing tool
- Browser - the interpreter of HTML, but also a debug and prototyping space. (Read about what goes on behind the scenes in a Web browser [4])
HTML
- HTML is a markup language
- meaning: content is marked with different "values"; e.g: paragraph, bold, italic, heading title, etc
- marking is done through tags that wrap the content

- In order to format content with tags you need to enter the content between an opening and closing element. As in the following case:
<h1>My Title</h1>
- <h1> is the opening tag
- </h1> is the closing tag
- at times you'll find self-closing tags which have no content inside them, like horizontal rulers <hr />
or line breaks <br/>
essential HTML tags
Title Headers: <h1>,<h2>,<h3>,<h4> Paragraph: <p> Line break: <br /> italics: <i> bold: <b> Comments: <!-- comments -->
HTML skeleton
The previous tags only provided content formatting, yet to create any working web-page we need to always place the content inside a HTML page skeleton.
HTML page boilerplate
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
HTML element reference
HTML element reference provides information and examples on every HTML element
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element
<a> anchor tag - hyperlinks
<a href="http://www.worm.org/">Worm website</a>
<br/>
<a href="http://tentrotterdam.nl/">tentrotterdam.nl</a>
- the href (address) of a link has to be a complete URL: beginning with http or https
remote links
Normally, like in the example above, you use links to point users to other sites.
Those are remote links
local links
Also usually you use local links.
Those are links to other files/pages you have create.
They allow to move within your website.
Go to next <a href="next.html">Next</a> page.
![]()
<img src="http://data.whicdn.com/images/106829085/large.gif" />
<br/>
<img src="my-img.jpg" />
Local file paths
Local links and image are some times in parent or child folders, different from the folder of your webpage.
To get an image to load or link to land on the right file, you have to indicate the correct path to them.
Local file paths exercise
- Create an HTML file, that uses other local images and links to other local html files.
- Move the HTML file to a different folder.
- Keep images and linked pages in the fold they were it.
- Try to make all the local files are not broken in HTML file
<div> div tag
The div tag is essentially a container of other content.
<div style="background:black; color:red; width:400px">
<h1>Beautiful page</h1>
<p>writing stuff
<i>inside</i>
</p>
</div>
<span> span tag
The span tag is like a color marker on text
<p>A magazine that offers a platform for
<span style="background:red; color:blue; font-size:40px">challenging and engaging</span>
design and art practices</p>
style it is an attribute
tags' attributes
attributes are parameters that modify the HTML tags behavior
<a> attributes:
<a href="http://wdka.hro.nl/" target="_self">link</a> <!-- target="_self": Loads the response into the SAME tab-->
<br/>
<a href="http://wdka.hro.nl/" target="_blank">link</a> <!-- target="_blank": Loads the response into a NEW tab-->
- href: url or file of the link
- target: where (in what window) to display the linked file.
![]()
<img src="http://www.wdka.nl/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2015/01/Project-Show_I1.jpeg" title="my pic" height="100px" width="200px"/>
- src: location of the image
- title: title of the image
- width
- height
inspector
Optional Reading
Stephenson, Neal. “Mother Earth Mother Board.” Wired, http://archive.wired.com/wired/archive/4.12/ffglass_pr.html.
Abbate, Janet. Inventing the Internet. MIT Press, 2000.
References, Notes and Optional Reading
- ↑ Degoutin, Stéphane, and Gwenola Wagon. World Brain Stéphane Degoutin & Gwenola Wagon, 2012. http://worldbrain.arte.tv.
- ↑ Berners-Lee, Tim. Weaving the Web. London: TEXERE, 2000.
- ↑ Simulation of the first Web Browser
- ↑ “Introduction to HTML” https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Guide/HTML/Introduction.
“The Birth of the Web,” http://home.web.cern.ch/topics/birth-web .
Technical Resources
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML - HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element - HTML element reference