|
|
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 4: |
Line 4: |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
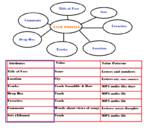
| '''notes after steve tutorial (ideology of choice, explain technolibertarian utopias and the self, explain how it works with a database in a database in database, explain the user as producer and producer of ecology and site Olga G , define restricted lists as templates, john tagg book. photos related to topologies and taxonomies, criminals and photo collection , fv profile pic and mugshot, elaborate on manovich position database narrative etc)''' N= corporate definition-front end abstraction, fb pattern classification-connectivity, on Olga G also “Το υποκείμενο παράγεται από τη σχέση και την αμείλικτη διαμάχη μεταξύ έμβιων όντων και μηχανισμών.”
| |
| from Giorgio Agamben, What is an apparatus,Η ταυτοποίηση όμως δεν εξυπακούεται πως είναι και αναγώγιμη στην ταυτότητα. (becomimg from identification)
| |
|
| |
|
|
| |
| ---
| |
| User profile is supposed to digitaly represent one s identity 1, but it is forming and constructing the individual, particularly in the online world. As a media object it talks about identity curation and construction, power and control, and social hierarchies.As a collection of settings and structured metadata it documents the users identity while forming it through the selection from a limited range of choices and an algorythmic approach to the person. Moreover it provides a template for exercise of control between corporation and their user and among users themselves. User profiles are very common new media objects and can be found in operating systems and in online services and websites, chatrooms and forums . Their existence and growth has been in parallel with the transition from earlier web to the cloud. Social networking, Web2.0 and personalisation of information and services are based upon user profiles.
| |
|
| |
| -
| |
|
| |
| According to Microsoft, "your user profile is a collection of settings that make the computer look and work the way you want it to. It contains your settings for desktop backgrounds, screen savers, pointer preferences, sound settings, and other features. User profiles ensure that your personal preferences are used whenever you log on to Windows. A user profile is different from a user account, which you use to log on to Windows. Each user account has at least one user profile associated with it.2
| |
|
| |
| According to Facebook, "Your profile, is your collection of the photos, stories and experiences that tell your story. Your profile also includes your Timeline". This definition can be found in their Glossary of Terms, where other interesting approaches can be found (what is a friend?Friends are people you connect and share with on Facebook and what is a list?Lists are an optional way to organize your friends on Facebook. )3
| |
|
| |
| Outside the corporate definition framework and ignoring for now that both definitions from Microsoft and Facebook focus clearly on the "front end" and avoid to explain how all this is constructed, one can see that user profiles are attached to the concepts of customisation, authentication, identification and engage the individual in a process of terms and rules accepting. They are collections of settings and metadata associated with a specific user. And they differ from user accounts as a more public expression of them. However, to create a profile one must create an account, either in operating systems or in social networking services. Both accounts and profiles are subject to archiving from the providers and offer a great documentation of the individual which happens silmutaneously with the profile construction. As Facebooks puts its, the user profile is the collection that tells our story.
| |
|
| |
| This process of building ones user profile beginns indeed with an account creation(registration ),accepting terms of services, and verification (via personal email),and later on moves to public profile construction, adjusting personalised settings and filling personal information in existing categories.
| |
|
| |
| The design model of the user profile is the one of the database. Moreover this database driven formation of the online profile is happening within online structures that are themselves databases. For example, when I create an online profile in Facebook, what I do is filling in a database(my profile), my action is happening in a database (Facebook) which happens to exist in "another databse", the Internet. This documents simply the multiplicity of layers of databases that construct online space and its interfaces. Even the layers from user accounts to user profiles consist from different databases.
| |
|
| |
| It seems that identity and database have a structural relationship in the world of user profiles. According to Mark Poster, because of its structure constitutes individuals by manipulating bits of information4 . This illustrates how an identity is formed within a user profile: through language , data entries and the relationships formed among data within the database. Manovich, who talks about the antinarative nature of the web, refers to the database as a new way to structure our experience of ourselves and the world . He talks also about the projection of the ontology of computers to culture; the world is reduced to data structures and algorithms. Applying this idea to the self, we see the current state of production of the self dominated by data structures and algorithms. Sociologist Giddens has written about the reflexive project of the self, where the subject, within information overload and fragmentation has to be able create a coherent personal narrative, in order to reflect and understand itself. If we apply Manovich's thinking as a response to Giddens, we would encounter the antinarrative web and the databases as enemies of any self-reflection. Morevoer we could easily see that the story facebook claims that tells about us is problematic by definition.
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| -
| |
|
| |
| Profile is a linguistic construction that mediates a social construction: one;s identity/ies. But what identity is it mediating?By providing a very controled space and using controled vocabulary puts the individual in the position to enter data in the database that will regenerate the persons identity in the context of that system. This linguistic construction mediates at the same time the choices of the individual alltough they are template choices. The use of these choices, from food preferences to the choices that affect what kind of data we contribute, show that our user profiles mediate a controled curation of identity. It is this controlled curation that illustrates the technolibertarian utopias related to identity exploration and alternative identities. The internet as a tool for personal freedom, the multiple identities, the personal webpage as emancipatory media(Cheung), the early work of Turkle, all these ideas collapsed particularly within the social networking era.
| |
|
| |
| User profile assigns also that identity with specific regulations , duties and rights predetermined, therefore mediates power relations and control. These relationships are formed not only between the institution/corporation and the user but even among users themself. A feature of facebook, the report of a user, is examplary of that. Again this relationships can be traced as well within one's self: one of one;s identities controling another. Furthermore, power and control are based on the practise of one documenting him/herself while creating all this accounts and profiles. From a preselected range of choices, understandable from computers, one is documenting in a written record him self by self-classification and data entering.This process affects not only self-presentation but self-understanding as well.
| |
|
| |
| It also mediates certain hierarchies, within society and within one 's self. In order to create a profile in a social network for example one has to be present through ones account in an operating system, lets say Windows. And reversed, ones online profiles lead back to ones profile in the operating system. Maintaining profiles in operating systems involves again hierachies, by distinguishing administrators by user and assigining specific regulations or rights to them. In the online context, the administrator of our profiles becomes the webservice providor, the corporation.
| |
|
| |
| During her lectures What was the user, Olg G has spoken about the user as producer of himself. While this user is producing himself, the ecology of the medium is also produced she claims. Applying this thinking on user profiles online we find users constructing themselves by filling databases, while contributing to the never ending economy of online media, which is based on user's online performance.
| |
|
| |
| -
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| from nickname to name: The history of chatrooms, forums and social networking sites proves that the "real" name of a user was and is not always needed in the formation of ones profile. Chatrooms for example have been requiring users to create profiles under nicknames asking for their email of course for "verification" reasons. There are plenty websites that are web2.0 products that require one to create a profile in order to construct his/her collections. A good example would be Pinterest. In their majority these webservices allow user to use a fictional name in their profile. Lately, Facebook and Google+ have been doing important movements related to user "real" names. Facebook and its strict policy which is under ongoing acceleration, with the latest to exclude drag-queens using stage names. Their alternative for all these users is to create a Fun page. Google+ is another POLICY SOS WHAT HTEY ESAY???interesting example. Tim Carmody calls it " Social media as a means to establishing identity"6. He continues that Google wants your real name because simply it has much more value in advertising, to cross relate your account to your buying behaviour. its interesting to observe the differencies in policies from lets say fb to google+, and the importance of users feedback in this decisions_+article google+ and identity. In come cases usernames and names given in the account creation are the same but not always.+fb names, alternative name etc.
| |
|
| |
| portraits and profile pictures: is a very visual but also psychological concept that can be found in any kind of art and includes normally a face and its charakteristics. In modern society , portrait relates with photography as a means to understand , monitor and document the world and the individual. Gallison and Daston in their book Objectivity comment on the relation of the lense(from microscopes to cameras) with scientific objectivity, which they see a the suppression of some aspect of the self 7. Moreover, Evi Sambanikoy source 8writes about the photographer as the reporter of the objectified subject.8 John Tagg.........Here i m interested in the majority of users that make use of photographic portraits and not drawing/paintings.
| |
|
| |
| Our portraits in our user profiles are our profile pics. The selfie corresponds to the "democratisation" of the use of the camera by individuals and appears succesfull in motivating people document themselves online.Ludovico and Cirio, in their "facetofacebook:smiling in the eternal party" refer to the face as the viewpoint as a major point of reference in the world, stronger even than names .They argue that facebook profiles are so effecting in representing real people through a a specifi element:the profile picture.9 They also connect profiles pictures with the technology of facial recognition and its possible use by authorities.
| |
|
| |
| email= identification or identity: E mail is used here in order to offer the company a "verification" that we are humans and that we consiously create our profile. It is also used in order to extract data about our emailing list and to force connectivity from the beginning of our profile life. +++++ User authentication , mozilla persona.
| |
|
| |
| password:a PASSword makes it perfektly clear that the access to the online self is through language codes. Is serves as the greatest application of personalisation with regards to privacy and security. Still, creating passwords online can always be surveilled by corporations which offer the whole environment of password creation. Passwords are also subject to computer viruses. So the self can be hacked, Terence mc Keena ? source 10 STALLMAN STORY source11
| |
|
| |
| -
| |
|
| |
| '''social networking and user profiles'''
| |
|
| |
| process of becoming (screenshots interpretation()
| |
| categories and protokols elaboration,
| |
| facebook API lists etc
| |
|
| |
|
| SCREENSHOTS FB | | SCREENSHOTS FB |
| Line 66: |
Line 15: |
| [[File:Fbaaaaaaa.png|150px|]] | | [[File:Fbaaaaaaa.png|150px|]] |
| [[File:Fbaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.jpg|150px|]] | | [[File:Fbaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.jpg|150px|]] |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| '''end'''
| |
|
| |
| User profiles are linguistic constructions, which occur in very linguistic structures, starting from the source code of websites we use to computers as linguistic devices and our linguistic-textual participation) and are the constructions that produce the self of the online user.
| |
|
| |
| creates algormithmically individuals by suggesting friends , likes, trying to create a COHERENT identity (g+ utube example), restricted from protocols, archived, connected strategically , unified.
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| '''sources'''
| |
|
| |
| 1. User Profile, wikipedia
| |
| 2. What is your user profile, Microsoft,
| |
| 3. User Profile, Facebook glossary of terms
| |
| 4. Poster, Mark . The mode of information
| |
| 5. Manovich, Lev. Database as symbolic form
| |
| 6. Carmody, Tim.Google+ Identity Crisis: What’s at Stake With Real Names and Privacy
| |
| 7. Gallison and Daston. Objectivity.
| |
| 8. Sambanikou.
| |
| 9. Cirio and Ludowico, Face to facebook.
| |
| 10. Terence mc Keena, lecture; the world is made of language
| |
| 11. Stallman password story
| |
|
| |
| olga g.
| |
| olia l
| |
| john tagg
| |
| net delusion
| |
| dragona-frown-the endless game of the self with the mechanism
| |
| Giorgio Agamben, What is an apparatus
| |