User:Andre Castro/2/thesis/formula: Difference between revisions
Andre Castro (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Andre Castro (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
Nine functions have been identified, which follow, apart from a few exceptions, the given sequence: | Nine functions have been identified, which follow, apart from a few exceptions, the given sequence: | ||
[[Image:functions-graph.svg | right]] | |||
''Salutation'': The writer begins by saluting the reader. Often it is only a plain "hi", others times the writer might already try to establish a bound with the reader using a more intimate approach "Hello Deares One" writes Ms Alima Kipkalya. | ''Salutation'': The writer begins by saluting the reader. Often it is only a plain "hi", others times the writer might already try to establish a bound with the reader using a more intimate approach "Hello Deares One" writes Ms Alima Kipkalya. | ||
| Line 76: | Line 78: | ||
''Valediction'' concludes the email. It must be in accordance to whom the writer happens to be. The banker simply writer "Yours Faithfully" followed by his bank contact; the soldier with "Yours in Service."; and the devoted christian widow with "May the Grace of our Lord Jesus Christ,the love of God,and the fellowship of the Holy Spirit be with you and your family." | ''Valediction'' concludes the email. It must be in accordance to whom the writer happens to be. The banker simply writer "Yours Faithfully" followed by his bank contact; the soldier with "Yours in Service."; and the devoted christian widow with "May the Grace of our Lord Jesus Christ,the love of God,and the fellowship of the Holy Spirit be with you and your family." | ||
Revision as of 10:14, 11 February 2013
In this section I will use Vladimír Propp formalist analyzes of Russian fairy tales as models that when applied to spam email may provide a more insightful view over spam formal characteristics. I will try to clarify if spam, likewise Russian folk tales posses repetitive and predictable facet is counterbalanced by picturesque a multiform manifestations of the stories told. After a presenting tentative model of 419's email function, I will draw into the discussion Janet Murray reading of Propp's work as possible model for digital story-telling, that takes advantage of the digital medium. I will be employing Murray's criticism of computer game, as narrative where a limited form of variable substitution takes, which does not succeed in inflecting the direction of the narrative.
Propp's Morphology of the Folktale
In 1928 Vladimír Propp (1928) proposed a formal analyses of Russian fairy tales. His effort were intended to establish a morphology of Russian folktales, a sort of list of ingredients and the sequence in which they come in to the confession a Russian tale. In order to draw such morphology Propp studied the tales by focusing on the "the functions of its dramatis personae"(p.7). In other words, the study focuses on the what action is performed, and not on who performs it or how is performed, as "characters of a tale, however varied they may be, often perform the same action. The actual means of the realization of functions can vary, and as such, it is a variable... But the function, as such, is a constant" (p.8).
A function is a slot belonging to an action, that will be filled both by the way its undertaken and the character that undertakes it. The function forms the constant and stable unit, while the latter constitute its variables. "Function is understood as an act of the character, defined from the point of view of its significance for the course of the action"(p 8). Let's take as an example the function 'lack'. Its summary tell us that "a member of the family lacks or desires something". And its subcategories states that several acts can perform that function, according to the object of lacking: the bride, a magical agent, or a wondrous object.
It should be also noted that the acts performed in each function are interdependent, as in the function interdiction violated the violation will derive from the interdiction.
x
"the form o violation corresponds to the type of interdiction(2 and 3 are a pair)" As and example we can have the following functions
{ } absentation
{ } interdiction
{ } interdiction violated
which have as some of the possible actions:
{ older generation absent / death of parents / younger generation absent } absentation
{ normal / inverted } interdiction
{ (dependent on the violation) } interdiction violated
x
Such system of fixed and finite elements, combined with interchangeable and numerous characters give the tale its "multiformity, picturesqueness, and color, and on the other hand, its no less striking uniformity, its repetition... The sequence of elements ... is strictly uniform. Freedom within this sequence if restricted by very narrow limits which can exactly formulated" (Propp 1926, p.8). And even when certain function are excluded from a tale, the sequence remains unaltered.
what would be gained from structural analysis
Adopting Propp's formal analysis I will dissect a number 419s Fraud emails, trying to isolate its constituting plot events or functions. The email and the identification of the functions can be seen at Email Functions .
<Note: I will use the term writer throughout the functions description. In this context writer refers not to the real author of the email, but to the fictional character who is supposedly writing, and around whom the narrative revolves. <
[WHAT WILL A FORMAL ANALYSIS SHOW US ??]
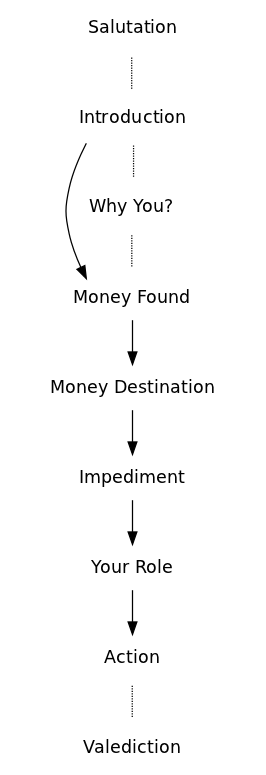
Nine functions have been identified, which follow, apart from a few exceptions, the given sequence:
Salutation: The writer begins by saluting the reader. Often it is only a plain "hi", others times the writer might already try to establish a bound with the reader using a more intimate approach "Hello Deares One" writes Ms Alima Kipkalya.
Why you?: This function, while not central to the plot, tries to justify has the reader received such email. Often the writer refers to her desperate situation, to which the reader can be a way out. This function often appears after the introduction.
Introduction: The writer introduces herself. This is pivotal moment in the narrative, since who the writer happens to be will dictated how the following functions are enacted. Possible characters found so far featuring the role of the writer were a banker, a family member of a state's person, a soldier, a rich but ill widow.
Money Origin: The reader is told about the sum of money that took the writer to contact the reader. The money origin will be dependent to what character is writing the email. The banker comes across money from a deceased client; the relative to the state's person inherits his fortune; the soldier finds money during an armed conflict; the terminally ill woman inherits her deceased husband fortune.
Money Destination: The writer describes the destination she wants to give to the money. This function is also dependent with who is the writer, if it happens to be ill woman she will want to give the money to a charity, the soldier on the other hands wants to keep it for himself.
Impediment: An impediment doesn't allow the money to remain with the writer and she informs the reader as why she isn't able to keep the money. Consequently she needs the reader's cooperation. Like with the Money Destination the impediment is not always clearly stated. Yet, it continues to be dependent on the who the writer is (Introduction). In the particular case of the banker Peter Hayman, it is hard to tell why can't he keep the funds from the deceased client; the daughter cannot checkout the money from the bank until she finds a husband or trustee, the soldier cannot keep the money as it is illegal, the widow is on the verge of death.
Your role: The reader is informed as what her role will be within the portrayed scenario. The reader also learns about her reward for helping out: "It is my intention to compensate you with 30% of the total money for your services", states the daughter (Alima Kipkalya Kones).
Action The receiver is urged to confirm her interest in the proposal by replying to the email and often by proving information on herself. She might be given instruction as what to how to act upon the writer's instruction.
Valediction concludes the email. It must be in accordance to whom the writer happens to be. The banker simply writer "Yours Faithfully" followed by his bank contact; the soldier with "Yours in Service."; and the devoted christian widow with "May the Grace of our Lord Jesus Christ,the love of God,and the fellowship of the Holy Spirit be with you and your family."
Likewise to Propp's morphology
functions tend to follow the same sequence throughout the studied emails.
Is however common for these plots to employ a slightly smaller amount of functions than the entire array of identified ones, as is the case of the first email from Mr. Peter Hayman. Functions also seem to be interrelated, in that the way in which a function is instantiated will have reproductions on to how the following functions are concretized.Yet discrepancy between the thirty one identified by Propp and the meager nine identified in 419 fraud emails gives us a pretty good idea of the discrepancies between these two landscapes.
Janet Murray describes Vladímir Propp's Morphology of the Folktale, as "a recipe for Russian folktale...[which] makes clear that the formulaic underpinning makes folktales more intricate; it allows storytellers to weave together multiple different story sequences without becoming confused" (p.196). In Murray's opinion the formula Propp describes is far more complex than the ones employed in the construction of computer games. "Games that do offer choice-points leading to variant plot events are usually constructed with only shallow detours off the main spine of the plot...Games that do provide narrative variety often do so through a simple substitution system...But games do not allow substitution of thematic plot elements ... the way fairy tales do. Games are limited to very rigid plotlines because they do not have an abstract representation of the story structure that would allow them to distinguish between a particular instantiation and a generic morpheme" (p.198).
If we take a second look at spam, in the light of Murray's criticism of computer game narrative formulas, we might be inclined to see the 419s' structural representation as closer those of games, rather than the ramified and interlaced structure of Russian fairy tales. Although the email writer character changes, and with it so does the mood of the email (the mode of address, the argumentation, etc), there is not much of a change in plot, it remains essentially the same. One very obvious reason for it the fact that the narrative funnels into convincing the reader to give away personal data and money, just like most computer games are channel the player into getting towards the end or outrunning the opponent.
Yet there is a richness to spam, that deserves not to be overlooked. At the onset the scenarios and characters portrayed are very rich. Could it be that spam messages could server as an initial scenario, prone to be appropriated and given an unexpected development, similarly to the appropriation of computer games by artists?
[PROJECT IDEA: Copy the first part of spam mail and write them into a postcard, living the remaining plot to be filled by the recipient. Once complete send the mail back to me. ]
<
the plot remains the same, and reducible to the following points: I have money, you need to help me to keep it, if you help you will be rewarded. These fixed structure fails to surprise us. Simple variations on the same formula could be something like: I have been scammed, as I and poor i cannot afford to prosecute the scammer, therefore I need your monetary help, if I win you'll get a reward. I want to invest in a profitable business, I lack the funds for it, if you become a co-investor you will receive part of the profit [ISN'T SPAMMER ALREADY USING THIS TYPE OF PLOTS ??] "By generating multiple stories that look very different on the surface but that derive from the same underlying moral physics, an author-directed cyberdrama could offer and encyclopedic fictional world whose possibilities would only be exhausted at the point of the interactor's saturation with the core conflict" (p.209). <
I will follow analysis with a discussing what forms of agencies does such a two-fold (repetitive and multiform) quality equip spam's 419s with.
[WHAT 2-FOLD NATURE DO TO SPAM]
repetition and predictability
WHAT DOES THE REPETITION PROVIDE THE TALE OR READERS? Its uniform and repetitive nature allows the audience to know what will be the next action, what will happen to he hero at a give moment, how will he react, etc. [ Why is the uniformity important ??]
- re-iterate what the readers know; they live on clichés of Africa and Africans;
Is repetition and predictability interesting for readers? Do they prefer it to unknown and unpredictable plots
Yet, yes the repetition of the same pattern and the predictability of the plot development playing for or against the spammers? Is it
Repetition and predictability is not something that human audience abject. Popular cultural is filled with examples that thrive on the repetition and foreseeable sequence of events. Clear examples are for instance the James Bond movies, or Italian Commedia dell'arte. Our expectations might be met when Miss Alima Kipkalya Kones asks us to help checkout her deceased father fortune. (The stories ends as we predicted and we fill good about it. Perhaps we don't want to be that challenged by the narrative. We can even speculate on that being the reason that multiform and interactive narrative hasn't yet been accomplished and met with wide audience's interest)
[COULD THE OLIPIO SUBSTITUTION GAMES BE A WAY OUT??]
the substitution of a word for another, could change quite substantially the narrative.
http://web.archive.org/web/20060508084853/http://www.oulipocompendium.com/html/excerpt_frame.html
ideas to develop
- email as space of attention
- email as form of communication, not a medium commonly used to narrate stories.
- Murray - suspension of disbelief
writing character - the central variable. It will dictacte the rest of the narrative:
- how she came across the money
- the impediment to get hold of money
- writing character decorates the storie with the punctuation that will correspond to the expectation towards character.
- exagerated, forming almost a caricature of that character
- commedia dell'arte
bibliography
- Murray, Jannet. 1998. 'Hamlet on the Holodeck: The Future of Narrative in Cyberspace'. MIT Press. Cambridge / London.
- Propp, Vladímir. 1929. 'Morphology of the Folk Tale' The American Folklore Society and Indiana University.