User:Andre Castro/2.1/semniar-2012-10-10-summary: Difference between revisions
Andre Castro (talk | contribs) |
Andre Castro (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 177: | Line 177: | ||
[http://pzwart3.wdka.hro.nl/wiki/Andre_Castro/research/1.3/review_1 The essay The Work of Audiences] departed from Dallas Smythe's work On the Audience Commodity and its Work. In Smythe's view, the audience job consists in creating demand for advertised goods. What advertisers buy when placing an advert on a magazine, TV-show of website is the audiences' attention and their capacity to buy what is being advertised. It happens that the labor of this immaterial work-force changed under the Web 2.0, as noted by Andrejevic. Audiences are no longer simply asked to generate demand for advertised goods, but also to put their creativity to work in producing many of the contents that surround those adverts, and also make the Web. By doing so audiences also develop a community around their creations, and produce information about their behavior, which will be used in targeting advertisement directed at them. In exchange audiences receive a small amount of control over their creations, which are ultimately property of the company hosting them. Following this line of thought I asked whether there was a difference from the work of audiences on platform like Youtube to one like Wikipedia. The situation seems to be that although Wikipedia also lives on audiences' free creative labor, they are given more control over their creations, and engage in discussions over the functioning of Wikipedia. Is this difference enough for the work of audiences to be classified as less exploitative than on Youtube? | [http://pzwart3.wdka.hro.nl/wiki/Andre_Castro/research/1.3/review_1 The essay The Work of Audiences] departed from Dallas Smythe's work On the Audience Commodity and its Work. In Smythe's view, the audience job consists in creating demand for advertised goods. What advertisers buy when placing an advert on a magazine, TV-show of website is the audiences' attention and their capacity to buy what is being advertised. It happens that the labor of this immaterial work-force changed under the Web 2.0, as noted by Andrejevic. Audiences are no longer simply asked to generate demand for advertised goods, but also to put their creativity to work in producing many of the contents that surround those adverts, and also make the Web. By doing so audiences also develop a community around their creations, and produce information about their behavior, which will be used in targeting advertisement directed at them. In exchange audiences receive a small amount of control over their creations, which are ultimately property of the company hosting them. Following this line of thought I asked whether there was a difference from the work of audiences on platform like Youtube to one like Wikipedia. The situation seems to be that although Wikipedia also lives on audiences' free creative labor, they are given more control over their creations, and engage in discussions over the functioning of Wikipedia. Is this difference enough for the work of audiences to be classified as less exploitative than on Youtube? | ||
Revision as of 23:58, 5 December 2012
Project Proposal Draft
Tentative title: PING!!! Me Baby
Short Description
For many of us our relation with spam emails consists in moving them from the inbox to the junk-mail folder, or even better, let them be detected and moved by spam-filters. However, if we take a look some of the unsolicited emails we receive we might find them curious, and might even amuse ourselves with what we find. We might consider them as not too removed from a literary creation, where considerable amount of inventiveness, and awareness to the current global situation and society soft-spots are added to produce persuasive messages.Besides curious glitches are also abound, such as the heavy employment of stereotypes, the unconventional uses of the English language, Google-translate misinterpretations, typos, word obfuscation, recurrence of text fragments, to name some. Being it such an idiosyncratic and rich area of text production I believe it should be embraced as a literary genre.
Consequently I want to experiment with the possibility of using it as a literary device, a template for writing and communication.
<strick>investigating its writing techniques, structure and categories. Based on that knowledge I intend to develop a system where spam methods will be applied to construct a text, over email messages, in collaboration with its receivers - anyone who has received the 1st invitation email and replied to it.</strick> <strick>If we take a close look at some of the spam emails that keep arriving at out email accounts </strick>
However, for various and legitimate reasons, we don't pay much attention, to spam email messages. Would we start to read, and even to respond to unsolicited emails, if rather than trying to persuades us to join some money winning (or loosing) scheme, they would seduce us into collaborative creation, into shared writing processes, or even simply to communicating with someone distant, unknown and different from ourselves? I would like to attempt to answer this question positively.
Methodology
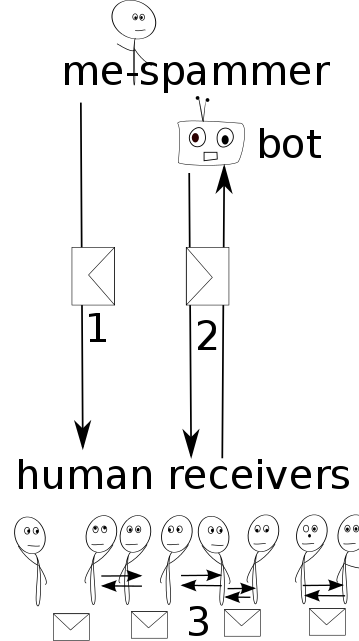
My strategy for attempt giving a positive answer formulated above will consist in appropriating spam as a literary and communication device. In order to do it, I will device a system summed up in the following diagram.
1) To initiate the process I will take on the role of a spammer, by sending one unsolicited email message to a large number of addresses from unknown individuals.
2) If a receiver answers, her message will be replied from my side by employing a bot, who will analyze the received message at different levels, e.g. letter occurrence, word occurrence, keywords, and phrases, and produce a reply that will both relate and "respond" to the receiver's message, but also push into other directions. I try to tell short stories through these text fragments.
This circulation of messages between bot and the human receiver will go on a few times, after which it will be interrupted.
3) At this point the bot will step back function as a proxy forwarding the messages between two human receivers, who happen be in a similar stage of writing process.
The bot will server always as agent connecting humans, either between me to the receivers and back, or between two receivers
This is one possible way of integrating these elements and I want to try it fully in order to see what results it will produce. I however don't see it as the definitive way of doing. Perhaps at later stage I will rearrange them differently, and perhaps bring in new elements and methods.
Outcome
As a first raw outcome I want to store all the communication history and content between myself(and bot) and the receivers; if possible I would also like to keep track of the receiver to receiver exchanges. However at this moment, I cannot decide upon a communication form for the project. Some possible outcomes are a radio play, a book, or a map of these exchanges (taking time as one of its dimensions).
A first test email
As a first test I decide to email some random addresses from address-book and see if any replies would ping back. Here is email sent and the replies:
From: . <.@gmail.com>
It looks like you're writing a letter.
I hope I am not making a mistake, but I think it would be a nice
experience to writing with you.
I must say my writing is all over the place, I can't just stand still.
You know that feeling?
verrrrr veeeerrr verrrr bossss verbose!
and sttutt ttt t eeeringgg stuttering on words??
........................................
........................................
...........................................
....................a....................
............a................a...........
........a.a...........a..............a....
.a................a............a........
OH! Probably I have just now manage to confuse you big time
Confusion can be a natural state /kənˈfjuːʒən/ as well as passivity
/pæsɪv/ and also procrastination /pɹəʊ̆ˌkɹæstɪˈneɪʃə̆n/
Write me some lines, I can only promise it doesn't get any better than this.
And these are the received replies
From: Konsul Gnadenwalze
01101000 01100001 01101000 01100001 00100000 01100111 01110010 01100101
01100001 01110100 00101100 00100000 01101101 01101111 01110010 01100101
00100000 01110000 01101100 01100101 01100001 01110011 01100101 00101110
00100000 00101101 00100000 01100100 01100101 01110010 00100000 01101011
01101111 01101110 01110011 01110101 01101100
--
From: . <.@gmail.com>
295424 294913 295424 294913 32768 294985 299016 294977 294913 299072
33344 32768 295489 295497 299016 294977 32768 299008 295488 294977
294913 299017 294977 33352 32768 33345 32768 294976 294977 299016 32768
295433 295497 295496 299017 299073 295488
--
From: Konsul Gnadenwalze <gnadenwalze@gmail.com>
%68%74%74%70%3a%2f%2f%69%6d%67%75%72%2e%63%6f%6d%2f%34%39%53%67%68
----
From: Danny van der Kleij
I just find it very strange that gmail marked it as "important because
of people in the email converstation" while I have never been emailed
by you before, which means you could use gmails "important" tag to
figure out who is in the bcc
----
From: Catarina Oliveira
??????????????????????????????????
----
From: Alisa Heller
Haha? What s this?
General Work Methodology
The methodology I have employed in the constructions of my works generally begins by encountering a problem or frustration. I come across something in which I see potential, but due to some blockage, it is under-explored. As an example, I found a great wealth of audio material available at Internet Archive, however its interface tended to conceal most of the material. This frustration led me to ask how could the diversity and quantity of material become more apparent and accessible.
A stage of experimentation and research generally follows. At this point I try to broaden my question, find possible angles to approach it, find other approaches to similar problems, engage with my subject and experiment. The Engage with the subject seems crucial. It is a step towards the object of research, trying no to look at it from a distance, but to get close to it, to establish a dialog. This happen more clearly in Data Factory when I tried to engage direct-marking companies' employees into talking with me and clarifying my questions a bout direct-marking and users' privacy.
Loose experimentation seems also important to my work methodology. From it a more precise idea about the materials I am engaging with is formed, and the final approach begins to surface.
The following stage is one of concretization of the elected approach, bringing it from its experimental stage, through various prototypes to its final from. It is at this point when most decisions are made, such as what to include or exclude, in what context should the project exist, how it will function, what will be its appearance. In the example I have been giving, I decided for an online radio, exclusively based on audio material from IA, that would group the sound materials under given programs with specific genres.
The resulting object is rarely, a solution for the problem which initiated the work process. Rather than providing an answer it will be an imaginative solution that ought pose more questions, and show the problem under another, perhaps unexpected, perspective. Hopefully such approach will challenge the value of the object in question, and allow it to reveal itself under another form.
Description of my works in the past year
To begin with I started by writing on the performativity of code. Departing from Katherine Hayle's notion of code performativity I went on looking at how does code perform. How does code, rather than being a descriptive tool, has the capacity to act, to change things in the real world, similarly to a performative speech-act, such as a judge stating: "I pronounce you guilty of the crime", and often with very direct and material effects.
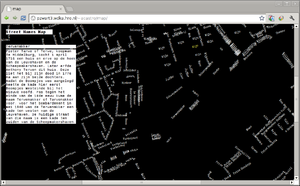
Simultaneously I developed and online map of the streets of Rotterdam. This map - a striped-down version of the original map of Rotterdam - only displayed the city street names against a black background, on the browser. By clicking on each street a request was made to the City of Rotterdam's Archive to provide information on that particular street's name origin. That information was then displayed alongside the map.
What I seemed to be creating here was an interface to access city's archive through a different channel. By having the indexes of the archive - the street names - displayed on the screen I might see and ask for information on streets that I wouldn't be normally interested in. It opened up the possibility for a serendipitous navigation through the city name's history.
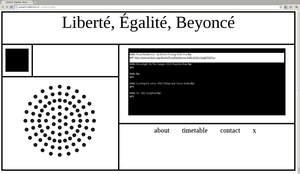
The same serendipitous exploration made its way to the next project, [Radio Liberté Egalité Beyoncé (RLEB)]. RLEB was an online radio-station with a schedule composed of audio content fetched form Internet Archive. One-hour long cycles presented the listener with ten-minutes chunks of various sound materials, picked at chance the archive, from within a specific categories, such as french talk-shows, hiphop, poetry readings, ambient music, etc. The design of website where RLEG was hosted presented a drawing of radio, with which the listener had to interact in order to get the radio playing.
The essay written alongside the RLEB began by tracing the archive's historical ties to power, functioning as a legitimator of power and knowledge. It mentioned the ideology which underlies any archive, even folkloric archive such as Youtube, an which can be best perceived through what is kept from entering the archive. Never-the-less important differences exist between a physical offline archive and a digital online one: the latter has the potential of a wider access, and also to let its item be taken by visitors, without risk of impoverishing it. These differences result in an invitation for appropriation and transformation of the digital archive. When one of its items is taken and transformed, a new version of it appears, and a certain confusion emerges over its origin - which one is the original and which is fictitious? When remixed versions surface, they change the archive into a space of dialogue and emergence of discourses, rather than a site aimed at legitimizing power and knowledge.
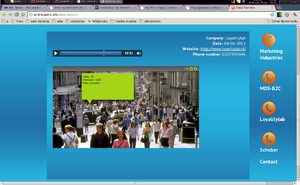
Data Factory looked at direct marking companies' acquisition of consumers data, with the aim to target individual consumers with products which they might be more inclined to buy. It consisted of a small archive of recordings from phone-calls made to such companies. During the calls I tried to sell them their business main ingredient - consumer data - with the catch being the fact that "consumer" here meant only myself. Through the reactions to this simple short-circuit the ideology behind such business model became more apparent. The calls were gathered together in a website, with a certain corporate style, in which they could be listened to, in parallel to images illustrating or ridiculing what was being said.
The essay The Work of Audiences departed from Dallas Smythe's work On the Audience Commodity and its Work. In Smythe's view, the audience job consists in creating demand for advertised goods. What advertisers buy when placing an advert on a magazine, TV-show of website is the audiences' attention and their capacity to buy what is being advertised. It happens that the labor of this immaterial work-force changed under the Web 2.0, as noted by Andrejevic. Audiences are no longer simply asked to generate demand for advertised goods, but also to put their creativity to work in producing many of the contents that surround those adverts, and also make the Web. By doing so audiences also develop a community around their creations, and produce information about their behavior, which will be used in targeting advertisement directed at them. In exchange audiences receive a small amount of control over their creations, which are ultimately property of the company hosting them. Following this line of thought I asked whether there was a difference from the work of audiences on platform like Youtube to one like Wikipedia. The situation seems to be that although Wikipedia also lives on audiences' free creative labor, they are given more control over their creations, and engage in discussions over the functioning of Wikipedia. Is this difference enough for the work of audiences to be classified as less exploitative than on Youtube?