Research Log: Difference between revisions
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
Cornelia Fales has written most recently of the ‘paradox of timbre’ ...; <br> | Cornelia Fales has written most recently of the ‘paradox of timbre’ ...; <br> | ||
we hear it – of all sonic phenomena timbre carries the most information about a sound source and its location – but we have no complete language to describe it ... When we get to timbre, then, it is only by getting beyond it. But mostly we never get there at all. | we hear it – of all sonic phenomena timbre carries the most information about a sound source and its location – but we have no complete language to describe it ... When we get to timbre, then, it is only by getting beyond it. But mostly we never get there at all. | ||
<br> | |||
How to approach through sound processing, '''a full embodied sound quality''' like timbre? | |||
=Timbre Visualisation= | =Timbre Visualisation= | ||
Try to talk on the microphone and see different types of visualisation through pure data. This can also work with vocal samples | Try to talk on the microphone and see different types of visualisation through pure data. This can also work with vocal samples | ||
Revision as of 14:39, 20 March 2023
Pitch Classification
Voices are classified as:
Female norm: mean F0 of 196-224 Hz
Male norm: mean F0 107-132 Hz
Gender is a spectrum,-not just binary (male vs female)and also not purely categorical
How to reeceive voice as a data and then reproduce it in ways that deconstruct the gender classification?
Open up new auditory perceptions?
Pitch definition
From britanica
pitch, in music, position of a single sound in the complete range of sound. Sounds are higher or lower in pitch according to the frequency of vibration of the sound waves producing them. A high frequency (e.g., 880 hertz [Hz; cycles per second]) is perceived as a high pitch and a low frequency (e.g., 55 Hz) as a low pitch.
https://www.britannica.com/art/pitch-music
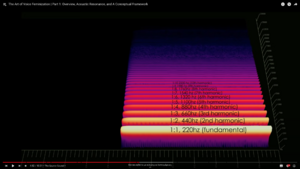
On fundamental frequency f0
The fundamental frequency of a speech signal, often denoted by F0, refers to the approximate frequency of the (quasi-)periodic structure of voiced speech signals.
https://wiki.aalto.fi/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=149890776
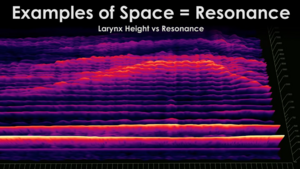
Spectogram and Voice
interface with live spectogram
https://musiclab.chromeexperiments.com/spectrogram/
On Queer Timbre
The Grove Dictionary of Music describes timbre as:
A term describing the tonal quality of a sound; a clarinet and an oboe sounding the same note at the same loudness are said to produce different timbres. Timbre is a more complex attribute than pitch or loudness, which can each be represented by a one-dimensional scale (high–low for pitch, loud–soft for loudness); the perception of timbre is a synthesis of several factors, and in computer- generated music considerable effort has been devoted to the creation and exploration of multi- dimensional timbral spaces. The frequency spectrum of a sound, and in particular the ways in which different partials grow in amplitude during the starting transient, are of great importance in determining the timbre.
With less of an attempt at scientific detachment, Olwage underscores the difficulty of accounting for this parameter of sound:
Cornelia Fales has written most recently of the ‘paradox of timbre’ ...;
we hear it – of all sonic phenomena timbre carries the most information about a sound source and its location – but we have no complete language to describe it ... When we get to timbre, then, it is only by getting beyond it. But mostly we never get there at all.
How to approach through sound processing, a full embodied sound quality like timbre?
Timbre Visualisation
Try to talk on the microphone and see different types of visualisation through pure data. This can also work with vocal samples