Pi GPIO PWD LED: Difference between revisions
Andre Castro (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
How to change the brightness of an LED using the Pi's GPIO pins? | How to change the brightness of an LED using the Pi's GPIO pins? | ||
Based on: https://www.admfactory.com/breathing-light-led-on-raspberry-pi-using-python/ | |||
==setup and testing== | ==setup and testing== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 13: | ||
[[File:pwm.png]] | [[File:pwm.png]] | ||
==Circuit== | |||
Connect the LED to pin 12, as in the following schematic. Taking care with the LED polarity | |||
[[File:breathingLed01.png|300px]] | |||
==Code== | |||
=== increasing / decreasing LED intensity === | |||
<source lang="python"> | |||
#!/usr/bin/env python3 | |||
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO | |||
import time | |||
LedPin = 12 | |||
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Numbers pins by physical location ## or GPIO.BCM | |||
GPIO.setup(LedPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set pin mode as output | |||
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # Set pin initial value to low(0V) | |||
p = GPIO.PWM(LedPin, 1000) # set Frequece to 1KHz | |||
p.start(0) # Start PWM output, Duty Cycle = 0 | |||
pwd_change_time = 0.1 # time it waits at every step of DutyCycle | |||
try: | |||
# loop indefinitly through 2 sub loops (increasing and decreasing duty cyle-brightness): | |||
while True: | |||
for dc in range(0, 101, 5): # Increase duty cycle: from 0 to 100, in steps of 5 | |||
p.ChangeDutyCycle(dc) # Change duty cycle | |||
time.sleep( pwd_change_time ) # wait to get to next value | |||
time.sleep(1) | |||
for dc in range(100, -1, -5): # Decrease duty cycle: from 100 to 0, in steps of 5 | |||
p.ChangeDutyCycle(dc) | |||
time.sleep( pwd_change_time ) | |||
time.sleep(1) | |||
except KeyboardInterrupt: #Ctl-c will interrup | |||
p.stop() | |||
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # turn off led | |||
GPIO.cleanup() # clean up resources | |||
</source> | |||
=== random LED intensity === | |||
<source lang="python"> | |||
#!/usr/bin/env python3 | |||
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO | |||
import time | |||
from random import randint | |||
LedPin = 12 | |||
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Numbers pins by physical location ## or GPIO.BCM | |||
GPIO.setup(LedPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set pin mode as output | |||
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # Set pin initial value to low(0V) | |||
p = GPIO.PWM(LedPin, 1000) # set Frequece to 1KHz | |||
p.start(0) # Start PWM output, Duty Cycle = 0 | |||
pwd_change_time = 0.1 # time it waits at every step of DutyCycle | |||
dc_end=0 | |||
try: | |||
# loop indefinitly: | |||
while True: | |||
dc_start = dc_end # start at value led was left of | |||
dc_end = randint(0,100) # select random number between 0 and 100 | |||
if dc_start > dc_end: # if start value > end value: range step has to be negative | |||
step = - 5 | |||
else: | |||
step = 5 | |||
for dc in range(dc_start, dc_end, step): | |||
p.ChangeDutyCycle(dc) # Change duty cycle | |||
time.sleep(pwd_change_time ) | |||
time.sleep(1) | |||
except KeyboardInterrupt: #Ctl-c will interrup | |||
p.stop() | |||
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # turn off led | |||
GPIO.cleanup() # clean up resources | |||
</source> | |||
[[Category:Cookbook]] | |||
[[Category:RaspberryPi]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:12, 21 November 2018
How to change the brightness of an LED using the Pi's GPIO pins?
Based on: https://www.admfactory.com/breathing-light-led-on-raspberry-pi-using-python/
setup and testing
Start by following the basic setup and testing of the Pi's GPIO in RaspberryPi_GPIO
PWD
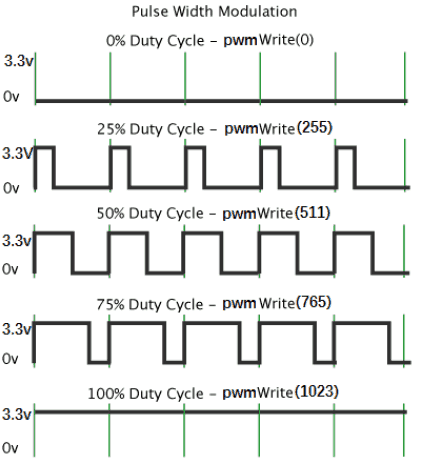
The way to change the brightness of an LED in digital electronics (only binary values are used 0v-5V or 0V-3.3V and no values in between), consists in creating a square waves that changes rapidly between 0V and 3.3V. By changing the portion of the time when the signal is on (3.3V) versus the time that the signal is off(0V) we can change the intensity of the LED. This technique is called Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), as we are modulating the "on" width of the wave.
Circuit
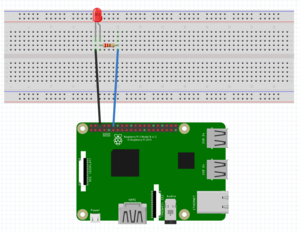
Connect the LED to pin 12, as in the following schematic. Taking care with the LED polarity
Code
increasing / decreasing LED intensity
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
LedPin = 12
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Numbers pins by physical location ## or GPIO.BCM
GPIO.setup(LedPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set pin mode as output
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # Set pin initial value to low(0V)
p = GPIO.PWM(LedPin, 1000) # set Frequece to 1KHz
p.start(0) # Start PWM output, Duty Cycle = 0
pwd_change_time = 0.1 # time it waits at every step of DutyCycle
try:
# loop indefinitly through 2 sub loops (increasing and decreasing duty cyle-brightness):
while True:
for dc in range(0, 101, 5): # Increase duty cycle: from 0 to 100, in steps of 5
p.ChangeDutyCycle(dc) # Change duty cycle
time.sleep( pwd_change_time ) # wait to get to next value
time.sleep(1)
for dc in range(100, -1, -5): # Decrease duty cycle: from 100 to 0, in steps of 5
p.ChangeDutyCycle(dc)
time.sleep( pwd_change_time )
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt: #Ctl-c will interrup
p.stop()
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # turn off led
GPIO.cleanup() # clean up resources
random LED intensity
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
from random import randint
LedPin = 12
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Numbers pins by physical location ## or GPIO.BCM
GPIO.setup(LedPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set pin mode as output
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # Set pin initial value to low(0V)
p = GPIO.PWM(LedPin, 1000) # set Frequece to 1KHz
p.start(0) # Start PWM output, Duty Cycle = 0
pwd_change_time = 0.1 # time it waits at every step of DutyCycle
dc_end=0
try:
# loop indefinitly:
while True:
dc_start = dc_end # start at value led was left of
dc_end = randint(0,100) # select random number between 0 and 100
if dc_start > dc_end: # if start value > end value: range step has to be negative
step = - 5
else:
step = 5
for dc in range(dc_start, dc_end, step):
p.ChangeDutyCycle(dc) # Change duty cycle
time.sleep(pwd_change_time )
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt: #Ctl-c will interrup
p.stop()
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # turn off led
GPIO.cleanup() # clean up resources