Prototyping 2013-11-05 (Lens Based Media): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[file:interframe.gif|600px|right|thumb|intra- vs. interframe compression]] | [[file:interframe.gif|600px|right|thumb|intra- vs. interframe compression]] | ||
== | == Encoding/Compressing == | ||
Why do we compress? | Why do we compress? | ||
* Image- and videofile sizes reduced | * Image- and videofile sizes reduced | ||
| Line 39: | Line 38: | ||
** MPEG-2 (DVD's, hardware players), DivX (downloads), H264 (currently has best quality vs. file ratio) | ** MPEG-2 (DVD's, hardware players), DivX (downloads), H264 (currently has best quality vs. file ratio) | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
=== encoding techniques === | |||
* Run length encoding > Looks for identical segments (often lossless) | |||
* Transform coding > Most used (jpeg, DCT, wavelet) (selectively removes ‘non-relevant’ detail from the image). | |||
* [http://www.knotless.com/1/post/2012/07/the-mysteries-of-chroma-sub-sampling.html| Chroma subsampling] >Selective loss of resolution (4:4:4 vs 4:2:0) | |||
* Reducing bit-depth (reducing colour accuracy) | |||
* Fractal compression (replacing pixels with mathematic approximations) | |||
FYI: Uncompressed HD video = 400GB per hour | FYI: Uncompressed HD video = 400GB per hour | ||
[http://www.axis.com/products/video/about_networkvideo/compression.htm| More Info] | [http://www.axis.com/products/video/about_networkvideo/compression.htm| More Info] | ||
Revision as of 22:02, 4 November 2013
Compression & Codecs in video
(File)Format or Container is the shipping box, codec is the goods inside the box.
Format
- determines the way audio and video streams (and other metadata) are stored inside the file
- Examples are :
- .avi (Microsoft -> OLD)
- .wmf (Microsoft -> Unflexible)
- .mov (Apple -> supports a lot of codecs)
- .ogg (Open Source -> but not very well supported by editing software)
- .mkv (Open Source -> but not very well supported by editing software)
- .mp4 (works on virtually all platforms)
Encoding/Compressing
Why do we compress?
- Image- and videofile sizes reduced
- More files to store, or longer videos
- Faster to download
- Downside: someone has to decode!
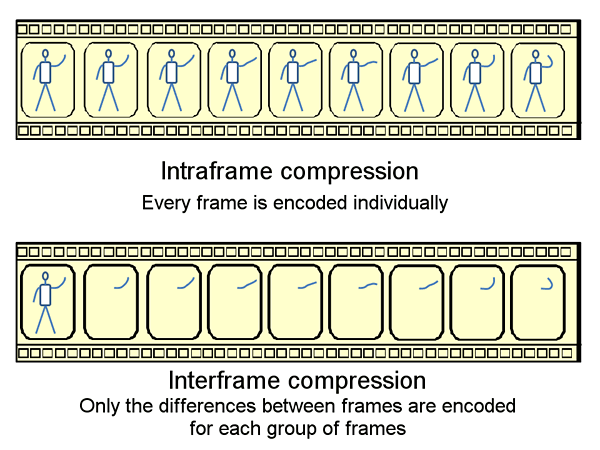
Types of compression
- Intraframe compression
- Compresses each frame (so similar to image compression, with for instance JPG)
- No effective size compression
- High Quality
- Easily readable by edit software
- Apple ProRes, DNxHD (Avid)
- Interframe Compression Looking at delta Frames
- Compress BETWEEN frames
- effective size compression
- Not easy for edit software
- Use for sharing -> final output
- MPEG-2 (DVD's, hardware players), DivX (downloads), H264 (currently has best quality vs. file ratio)
encoding techniques
- Run length encoding > Looks for identical segments (often lossless)
- Transform coding > Most used (jpeg, DCT, wavelet) (selectively removes ‘non-relevant’ detail from the image).
- Chroma subsampling >Selective loss of resolution (4:4:4 vs 4:2:0)
- Reducing bit-depth (reducing colour accuracy)
- Fractal compression (replacing pixels with mathematic approximations)
FYI: Uncompressed HD video = 400GB per hour
More Info
[1]
Encoding Tools
- ffmpeg (ffmpegX for a Mac gui version)
- Mencoder
- Handbrake
- Mpegstreamclip
- Adobe Media Encoder
Bitrate + Framesize
Workflow, Archiving & Delivery
There's no solution to the question 'What is the best setting for my video?". All depends on the platform you will deliver to!
- How do you record?
- How do you edit?
- What do you deliver?
Glitch Art & Data moshing
{{#ev:youtube|mvqakws0CeU?version=3&autohide=1&showinfo=0}}